Isolating and Culturing Chick Embryonic Neurons on a Multi-Electrode Array
Abstract
Source: Sanchez, K. R., et al., Assessment of the Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds on the Development of Vertebrate Neural Network Function Using Multi-electrode Arrays. J. Vis. Exp.(2018)
This video demonstrates a method to isolate neurons from the forebrain of an early-stage chick embryo and culture them on a microelectrode array to form a neuronal network.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Material Setup
- Incubate chick eggs in a commercially available tabletop egg incubator at 37 °C. Incubate eggs for 7 days for E7 embryos.
- Prepare multi-electrode arrays (MEAs). Sterilize the required number of MEAs by soaking them in 70% ethanol for 3 to 4 h and then rinsing them three times in approximately 10 mL of sterile distilled water in the biosafety level-II (BSLII) hood.
NOTE: The MEAs contain 64 nanoporous platinum electrodes arranged in an 8 x 8 grid. The electrode diameter is 30 µm, and the spacing between the electrodes is 200 µm. Do not use denatured ethanol to sterilize the MEAs, as this will lead to corrosion. - Place the MEAs inside a sterile container with a lid (to maintain sterile conditions) and move to a tabletop incubator. Bake for at least 6 hours at 55 °C. This step is critical for proper sterilization, and the temperature should not exceed 60 °C. To maintain sterility, move the dish containing MEAs to the BSLII hood for storage until further use.
NOTE: We use an oven-safe glass baking dish with a plastic lid and surface sterilize it with 70% ethanol and place it in the BSLII hood for drying. - Aliquot the extracellular matrix (ECM) solution. Thaw the vial at 4 °C overnight and freeze 100 µL aliquots at -20 °C.
NOTE: ECM is shipped frozen. It should not be brought to room temperature until ready to coat as it polymerizes at room temperature and is impossible to coat once polymerized. ECM without growth factors is preferred to prevent additional effects due to unknown factors. - Sterilize all dissection instruments (Dumont #5 forceps, curved forceps, small scissors, and spring scissors) and self-sealing material-coated dissection dishes with 70% ethanol and let them dry in the dissection hood.
2. Chick Embryonic Neuron Culture and Network Activity
- On the day of plating, remove a vial of ECM from the -20 °C freezer, spray with 70% ethanol, and place it on ice. Dilute to 25% by adding 300 µL cold neurobasal medium inside the BSLII hood.
- Using a P200 pipetteman add 100 µL of 25% ECM to the center of the MEA taking care not to touch the electrodes and remove immediately leaving a thin film on the surface. Cover the MEA and place in the CO2 incubator (37° C and 5% CO2) until ready to plate the neurons.
- Sterilize the outer shell of an E7 egg (embryonic day 7, incubated at 37 °C for 7 days) with 70% ethanol. Decapitate the embryo into a Sylgard bottom dissection dish containing cold sterile Hank's Balanced Salts Solution (HBSS) without calcium. Cut around the eyes and remove the eyeballs. Using DuMont #5 fine forceps and spring scissors make an incision on the ventral side and remove the outer layers of skin to expose the forebrain and optic tectum. Peel and remove the pial membrane carefully. Transfer the forebrain into another petri dish and cut it into small pieces of about 2 mm with spring scissors.
NOTE: There should not be any blood vessels attached to the forebrain after removal of the pial membrane. If available, it is preferable to perform the dissection in a sterile dissection hood, although we have obtained fairly good results when dissection is performed outside a hood as long as the instruments and dissection area are thoroughly sterilized with 70% ethanol. - Using a sterile transfer pipette, collect the pieces of forebrain into a 15 mL centrifuge tube and remove as much of the HBSS as possible after letting them sink to the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
- Add 1 mL of 0.05% trypsin/ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (Trypsin/EDTA) (pre-warmed to 37 °C) and incubate at 37 °C for 15 minutes.
- Using a Pasteur pipette, carefully remove trypsin without disturbing the pieces of tissue and add 1 mL of neurobasal medium. Let the pieces of tissue sink to the bottom and remove the medium. Repeat this wash once more. This step is to wash off the trypsin/EDTA.
- Add 2 mL of neurobasal medium and start triturating. Trituration involves taking a sterile fire-polished Pasteur pipette and gently passing the tissue through it several times until no more pieces are seen. If any pieces remain after repeated passes, just leave them to settle to the bottom.
NOTE: Avoid frothing while triturating – if froth does form, stop and remove by aspiration. - Dilute the re-suspended cells 1:10 with neurobasal medium and count viable cells using Trypan Blue dye and a hemocytometer. Mix 50 µL of the diluted cells with 50 µL of Trypan Blue solution in a 0.5 mL centrifuge tube. Add 10 µL to the hemacytometer after placing on the coverslip and count the bright clear cells (blue cells are dead and should not be counted).
NOTE: Typical cell numbers from a single E7 optic tectum range between 1 and 5 x 107 cells/mL. - Plate the dissociated cells on ECM-coated MEAs at a density of 2,200 cells/square mm. For our MEA system, this translates to approximately 130,000 cells per MEA. Add the neurobasal medium to bring the volume in the MEA to 1 mL and place MEAs in the CO2 incubator overnight for cell attachment and neurite extension (Figure 1).
NOTE: For MEAs of different areas and electrode numbers, different cell densities could be tried – in general, higher cell density results in greater network activity, but also leads to shorter-lived cultures.
Representative Results
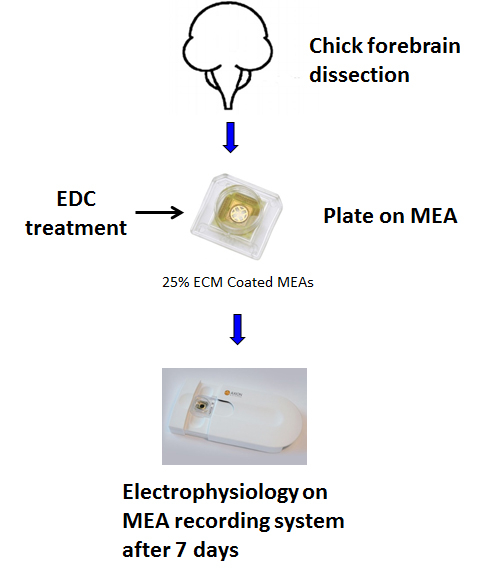
Figure 1: Schematic of the protocol depicting the steps from dissection of chick forebrain to dissociation, plating, and recording of network activity.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| #5 foreceps | Fine Science Tools | 11251-10 | |
| Axion Muse MEA | Axion Biosystems | M64-GL1-30Pt200 | |
| Curved forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11272-50 | |
| Ethanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 64-17-5 | |
| HBSS | Fisher | 14170112 | |
| Hemacytometer | Fisher | 02-671-6 | |
| Matrigel Growth Factor Reduced, Phenol Red-Free | BD Biosciences | 356231 | |
| Neurobasal medium | BrainBits | Nb4-500 | |
| Pasteur pipettes | Fisher | 13-678-20A | |
| Spring scissors | Fine Science Tools | 15514-12 | |
| Sylgard bottom dissection dishes | Living Systems Instrumentaion | DD-90-S-BLK-3PK | |
| Trypan Blue dye | Fisher | 15-250-061 | |
| Trypsin-EDTA | Fisher | 15400054 |

