Isolation and Culture of Mouse Primary Cerebellar Granule Neurons
Abstract
Source: Laaper, M., et al. Modeling Neuronal Death and Degeneration in Mouse Primary Cerebellar Granule Neurons. J. Vis. Exp. (2017)
This video demonstrates the technique for isolating and culturing primary mouse cerebellar granule neurons. Cells are treated with an antimetabolite to eliminate proliferating glial cells and produce a pure culture of cerebellar granule neurons.
Protocol
All procedures involving sample collection have been performed in accordance with the institute's IRB guidelines.
1. Experimental Preparation
NOTE: The following stock solutions can be prepared and maintained until use.
- Dissection Solution
- Dissolve 3.62 g of sodium chloride (NaCl), 0.2 g of potassium chloride (KCl), 0.069 g of sodium phosphate (NaH2PO4∙ H2O), and 1.306 g of D-(+)-Glucose in 500 mL of distilled H2O. Then add 12.5 mL of HEPES Buffer, 450 µL of Phenol red solution, and 20 mL of BSA fraction V to the solution. Adjust to pH 7.4 using 1 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Sterilize with a 0.22 µm filter and store at 4 °C. This solution will remain stable for up to one week to 10 days.
- Trypsin
- Prepare a stock solution at a concentration of 25 g/L of trypsin in 0.9% sodium chloride. Store the solution at -20 °C.
- Trypsin Inhibitor
- Prepare a stock with a concentration of 10 mg/mL by dissolving 1 g of chicken egg white trypsin inhibitor in 100 mL of 1 mM HCl. Store this solution at -20 °C.
- DNase
- Dissolve 100 mg of DNase 1 in 10 mL of sterile water to generate a 10 mg/mL stock. Store the solution at -20 °C.
- MgSO4
- Add 6.02 g of magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) to 50 mL of distilled water (H2O) to generate a 1 M stock. Store the solution at 4 °C.
- CaCl2
- Dissolve 0.735 g of calcium chloride (CaCl2∙ 2H2O) in 50 mL of distilled H2O to a stock concentration of 100 mM. Store solution at 4 °C.
- KCl
- Dissolve 3.7275 g of KCl in 50 mL of distilled H2O to a stock concentration of 1 M. Store solution at 4 °C.
- D-(+)-Glucose
- Dissolve 1.802 g of D-(+)-glucose in 50 mL of distilled H2O to a stock concentration of 100 mM. Store the solution at 4 °C.
- Cell Culture Media
- Prepare cell culture media as follows: 5 mL of heat-inactivated dialyzed Fetal Bovine Serum, 500 µL of 200 mM L-Glutamine, 100 µL of 50 mg/mL Gentamycin and 1 mL of 1.0 M KCl should be added to 45 mL of filter sterilized Eagle's minimal essential media (E-MEM) that is supplemented with 1.125 g/L D-Glucose to generate 50 mL of cerebellar granule neuron culture media. Store media at 4 °C.
- Cytosine Beta-D- Arabino Furanoside
- Dissolve 48 mg of cytosine beta-D-arabinofuranoside in 10 mL of growth media to a stock concentration of 20 mM. Store solution at -20 °C.
- Poly-D-Lysine
- To generate a 2 mg/mL poly D-lysine stock, add 10 mL of sterile H2O to 20 mg of poly D-lysine. Stock poly D-lysine should be stored at -80 °C in 100 µL aliquots.
NOTE: The following solutions should be prepared prior to dissection and maintained at 4 °C until use.
- To generate a 2 mg/mL poly D-lysine stock, add 10 mL of sterile H2O to 20 mg of poly D-lysine. Stock poly D-lysine should be stored at -80 °C in 100 µL aliquots.
- MgSO4 Supplemented Dissection Solution
- Add 300 µL of stock MgSO4 to 250 mL of dissection solution.
- Trypsin Dissection Solution
- Add 100 µL of stock trypsin and 12 µL of stock MgSO4 to 10 mL of dissection solution.
- Trypsin Inhibitor Solution 1
- Add 164 µL of stock trypsin inhibitor, 250 µL of stock DNase 1 and 12 µL of stock MgSO4 to 10 mL of dissection solution.
- Trypsin Inhibitor Solution 2
- Add 1040 µL of stock trypsin inhibitor, 750 µL of stock DNase 1 and 12 µL of stock MgSO4 to 10 mL of dissection solution.
- CaCl2 supplemented dissection solution
- Add 10 µL of stock CaCl2 and 25 µL of stock MgSO4 to 10 mL of dissection solution.
- Poly D-Lysine Coated Culture Dishes
- To coat culture dishes, dilute 100 µL of stock poly D-lysine in 40 mL of sterile H2O. For 35 mm Nunc culture dishes, add 2 mL of diluted poly D-Lysine solution. For 4 well plates, add 300 µL of diluted poly D-Lysine to each well.
- Let the poly D-lysine sit for 1 h before aspirating and washing each well with 4 mL or 600 µL (for 35 mm culture dishes or 4 well plates, respectively) of sterile H2O. Then aspirate the H2O and let the dishes air dry for 1 h.
2. Brain Extraction and Isolation of Cerebellum
- Decapitate a 6-7 day-old mouse pup using decapitation scissors. Perform the dissection of the brain in a sterile tissue culture hood.
- To remove the brain, grasp the head using a pair of forceps and cut through the skin toward the anterior of the head using microdissection scissors, as demonstrated in Figure 1. Then cut through the skull bone using a new pair of scissors to minimize the risk of contamination. Remove the skull covering the brain using forceps and tease out the brain using forceps or a spatula.
- As needed, cut through the optic nerve to facilitate getting the brain out as a whole.
- Place the brain in the dissection solution which is supplemented with MgSO4. Keep the solution and the brain on ice.
- Following brain removal, under a dissection microscope, dissect out the cerebellum from the brain while still in MgSO4 supplemented dissection solution, and remove the meninges using fine forceps. Turn the cerebellum to its ventral side and insure removal of the choroid plexus.
- Pool the cerebella into a 35-mm dish containing ~1 mL of MgSO4-supplemented dissection solution.
- Chop the tissue into small pieces and transfer it into a 50 mL tube containing 30 mL of MgSO4 buffered dissection solution.
3. Mouse Cerebellar Granule Neuron Isolation and Culturing
- Centrifuge the 50 mL tube containing the chopped cerebral tissue for 5 min at 644 x g and 4 °C.
- Remove the supernatant and add 10 mL of trypsin dissection solution. Then shake the tube at high speed for 15 min at 37 °C.
- Add 10 mL of trypsin inhibitor solution 1 to the tube and rock gently for 2 min.
- Centrifuge the tube for 5 min at 644 x g and 4 °C.
- Remove the supernatant and add 2 mL of trypsin inhibitor solution 2, and then transfer to a 15 mL tube.
- Triturate the tissue in the 15 mL tube until the solution becomes murky. Then let settle for 5 min.
- Remove the clear supernatant and transfer the supernatant to a new tube containing 1 mL of CaCl2 supplemented dissection solution.
- Add another mL of trypsin inhibitor solution 2 to the bottom of the tube containing the pellet from step 3.6. Triturate again and let settle for 5 min. Remove the supernatant and add it to the tube containing the supernatant from step 3.7 (That is a repeat of steps 3.6-3.7). Repeat this process until most of the tissue is mechanically dissociated.
- Add 0.3 mL of CaCl2-supplemented dissection solution to the supernatant collection for every mL of supernatant.
- Mix the tube contents and then centrifuge for 5 min at 644 x g.
- Remove the supernatant and add 10 mL of fresh media to the pellet and mix.
- Cells may then be counted and diluted to a concentration of 1.5 x 106 cells/mL. Please note that in general, 10 million cells are expected from each dissected brain, dependent on trypsinization time and efficiency of dissection. Plate cells on previously made poly D-lysine plates. For 4-well plates, plate 0.5 mL, giving 7.5 x 105 cells per well. For 35-mm dishes, plate 4 mL, giving 6 x 106 cells per plate.
- After 24 h, add cytosine-β-arabino furanoside (AraC) to the plates to reduce glial contamination. For each mL of media 0.5 µL of 20 mM AraC is required. Addition of AraC does not require a media change. If cells are to be maintained for 7-8 days, repeat this treatment on day 3.
- Maintain cultures in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C and feed with 100 µL of 100 mM glucose added to the culture for every 2 mL of media every 2 days past 5 days. A complete media change is not required.
Representative Results
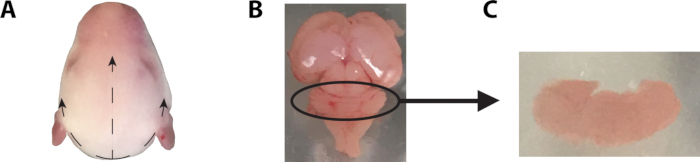
Figure 1: Removal of mouse brain and dissection of cerebellum. (A) To extract the brain of a 6-7 day old mouse, using a pair of forceps, grasp the head and cut the skin anteriorly along the dotted lines using a pair of microdissection scissors. Be careful to cut only the skin and connective tissue, too deep an incision may puncture the skull and damage the brain. These three incisions, straight along the midline, and two curving laterally, allow for the skin to be pushed back, revealing the skull. Once exposed, the skull can be penetrated with the tip of the scissors and cut anteriorly. Great care must be taken not to damage the cerebellum to facilitate identification and removal of meninges. Once cut, forceps may be used to peel back the skull, exposing the brain, which may then be teased out into a cool dissection solution using a pair of forceps or spatula. In order to remove the brain, the optic nerve may need to be severed. (B) Once removed from the skull, the meninges should be removed from the cerebellum using a pair of fine-tipped forceps. (C) Using a pair of fine-tipped forceps, the cerebellum is dissected from the remaining tissue and inspected to ensure complete removal of the meninges.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Distilled water | Gibco | #15230162 | |
| 200 mM L-Glutamine | Gibco | #25030081 | |
| 35 mm Nunc culture dishes | Gibco | #174913 | |
| BSA V Solution | Sigma Aldrich | #A-8412 | |
| CaCl2 • 2H2O | Sigma Aldrich | #C-7902 | |
| Chicken Egg White Trypsin Inhibitor | Sigma Aldrich | #10109878001 | |
| Cytosine beta-D-Arabino Furanoside | Sigma Aldrich | #C-1768 | |
| D-(+)-Glucose | Sigma Aldrich | #G-7528 | |
| DNase1 | Sigma Aldrich | #11284932001 | |
| Eagle-minimal essential medium | Sigma Aldrich | #M-2279 | |
| Glycine | Sigma Aldrich | #G-5417 | |
| Heat inactivated dialyzed Fetal Bovine Serum | Sigma Aldrich | #F-0392 | |
| Hepes Buffer | Sigma Aldrich | #H-0887 | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Sigma Aldrich | #216763 | |
| 50 mg/mL Gentamycin | Sigma Aldrich | #G-1397 | |
| MgSO4 | Sigma Aldrich | #M-2643 | |
| N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid | Sigma Aldrich | #M-3262 | |
| Phenol Red Solution | Sigma Aldrich | #P-0290 | |
| Trypsin | Sigma Aldrich | #T-4549 | |
| Opti-MEM I Reduced Serum Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 31985070 | |
| KCl | VWR | #CABDH9258 | |
| NaCl | VWR | #CABDH9286 | |
| NaH2PO4H2O | VWR | #CABDH9298 | |
| Poly D-lysine | VWR | #89134-858 | |
| DMEM | Wisent | #319-005-CL | |
| FBS | Wisent | #080-450 |

