Cytotoxicity Assay of Staphylococcus aureus Strains on Neutrophils following Phagocytosis
Abstract
Source: Dankoff, J. G. et al., Quantifying the Cytotoxicity of Staphylococcus aureus Against Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes. J. Vis. Exp. (2020)
In this video, we demonstrate an assay to detect the cytotoxicity of virulent and less virulent Staphylococcus aureus strains against human neutrophils following phagocytosis using flow cytometry.
Protocol
1. S. aureus cytotoxicity assay against human polymorphonuclear leukocytes following phagocytosis
NOTE: Growth curves defined by the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) and concentration of bacteria must be determined empirically for the S. aureus strains to be tested before beginning this assay. The success of these experiments requires the consistent harvest of equal concentrations of each S. aureus strain tested at the mid-exponential growth phase using the OD600 of sub-cultured bacteria.
- Start overnight cultures of S. aureus strains and subculture bacteria as described below.
- Culture S. aureus overnight in tryptic soy broth (TSB) using a shaking incubator set at 37 °C. For these studies, 20 mL of TSB in separate 150 mL Erlenmeyer flasks were inoculated with frozen cultures of S. aureus strains USA300 or USA300ΔsaeR/S and grown for approximately 14 h with shaking at 250 rpm.
- Subculture S. aureus by performing a 1:100 dilution of overnight bacterial culture with fresh media. Incubate at 37 °C with shaking.
- Harvest subcultured S. aureus when it has reached mid-exponential growth by transferring 1 mL of cultured bacteria to a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube and centrifuging at 5,000 × g for 5 min at room temperature.
NOTE: Under our growth conditions, USA300 and USA300ΔsaeR/S reached the mid-exponential growth phase after approximately 135 min incubation. - Wash S. aureus following centrifugation by aspirating the supernatant, resuspending the pelleted bacteria in 1 mL of DPBS, vortexing the sample for 30 s, and centrifuging at 5,000 × g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Opsonize S. aureus by resuspending the bacterial pellet in 1 mL of 20% human serum diluted with DPBS and incubating at 37 °C with agitation for 15 min.
- Centrifuge opsonized bacteria at 5,000 x g for 5 minutes at room temperature. Wash S. aureus following centrifugation by aspirating the supernatant, resuspending the pelleted bacteria in 1 mL DPBS, and then vortexing the sample until the bacterial pellet is completely broken apart plus an additional 30 seconds. Centrifuge bacteria at 5,000 × g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Resuspend opsonized S. aureus strains in 1 mL RPMI, vortex the sample until the bacterial pellet is completely broken apart, and then for an additional 30 s. Place bacteria on ice.
- Dilute opsonized S. aureus strains to the desired concentration with ice-cold RPMI. Vortex for 30 s and place on ice.
- Confirm the concentration of opsonized S. aureus by plating 1:10 serial dilutions of bacteria on tryptic soy agar.
NOTE: Because differences in the concentration of bacteria used in this assay can have a major impact on subsequent PMN plasma membrane permeability (Figure 1A), it is essential that the concentration of each strain tested is determined for every experiment and is equivalent between strains. - Gently add 100 µL/well of each S. aureus strain or RPMI (for positive and negative controls) to PMNs in the 96-well plate on ice. Gently rock plate to distribute S. aureus in wells.
- Synchronize phagocytosis by centrifuging the plate at 500 × g for 8 min at 4 °C. Incubate the plate at 37 °C immediately following centrifugation (T = 0).
- At desired times, remove the plate from the incubator and place it on ice. Add 40 µL of 0.5% Triton X-100 to the positive control well.
- Gently pipette the samples up and down in each well to pull off all PMNs adhered to the plate completely, then transfer the samples to flow cytometry tubes on ice containing 200 µL of ice-cold DPBS with 1 µL of propidium iodide.
- Analyze samples for propidium iodide staining using flow cytometry.
- Measure the proportion of propidium iodide-positive PMNs using flow cytometry. When bound to DNA, propidium iodide has excitation/emission at 535/617 nm.
Representative Results
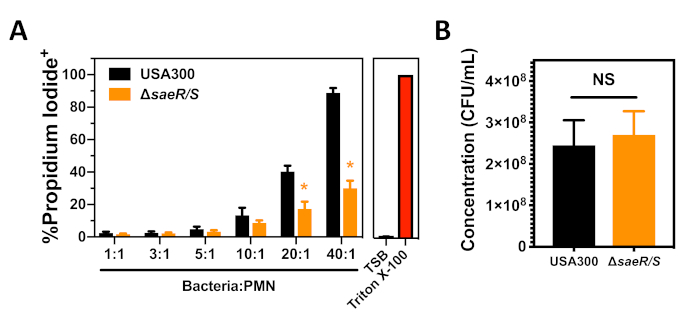
Figure 1: Flow cytometry analysis of PMNs following phagocytosis of S. aureus. (A) The proportion of propidium iodide positive PMNs 90 min after the phagocytosis of different concentrations of USA300 or USA300∆saeR/S. (B) The concentration of opsonized S. aureus strains used for the experiments is shown in panel A. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 4 separate experiments with * p ≤ 0.01 as determined by the two-tailed t-test.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 1.5 mL micro-centrifuge tubes with Snap Caps | VWR | 89000-044 | Used in washing cells |
| 12x75mm Culture tubes | VWR | 60818-430 | Used as flow cytometry tubes |
| 50 mL conical centrifuge tubes | VWR | 89039-656 | For dispensing media |
| Bacto Tryptic Soy Broth, Soybean-Casein Digest Medium | FischerScientific | 211823 | For growing cell cultures |
| Bright-Line Hemocytometer | Sigma-Aldrich | Z359629 | Cell counting apparatus |
| DPBS, 1x (Dulbecco's Phosphate Buffered Saline) with calcium and magnesium | Corning | 21-030-CV | Used in washing cells |
| Ficoll-Paque PLUS | GE Healthcare | 17-1440-02 | PMN purification |
| Fisherbrand Sterile Polystyrene Disposable Serological Pipets | FischerScientific | 13-678-11E | For aspirating liquid |
| Greiner CELLSTAR 96 well plates | Millipore Sigma | M0687 | Plate for holding experimental samples |
| OMICRON Syringe Filters | Omicron Scientific | SFPV13R | For filtering supernatants |
| Propidium iodide | ThermoFisher Scientific | P3566 | Membrane impermeable DNA stain |
| PYREX Brand 4980 Erlenmeyer Flasks | Cole-Parmer | EW-34503-24 | For growing cell cultures |
| RPMI 1640, 1X without L-glutamine, phenol red | Corning | 17-105-CV | Used in resuspending cells |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma-Aldrich | X100 | Membrane integrity positive control |

