Abstract
Source: Bourgognon, M., et al. Kupffer Cell Isolation for Nanoparticle Toxicity Testing. J. Vis. Exp. (2015)
In this video, we demonstrate the isolation of Kupffer cells or liver macrophages from the mouse liver. The liver is perfused with a digestion solution followed by density gradient separation. The isolated adherent Kupffer cells can be used for further analysis.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Perfusion and Cell Collection (Figure 1)
- Prepare freshly all reagents described in the material table.
- Warm the EGTA (Ethylene Glycol Tetra-acetic Acid)/HBSS (Hank's Balanced Salt Solution) Solution (50 ml per mouse) and the Collagenase Solution (100 ml per mouse) for 30 min at 40 °C.
- Rinse the pump flexible tubing first with 70% ethanol. Pour 40 ml of EGTA/HBSS Solution into a centrifuge tube immersed in the water bath and rinse the pump flexible tubing with pre-warmed EGTA/HBSS Solution.
- Perform terminal anesthesia using a barbiturate to reliably produce unconsciousness before respiratory depression and death. Inject phenobarbitone at 1 mg/kg, i.p. into a female or male CD1 mouse (35-45 g). Confirm the anesthesia by toe pinching.
- Shave abdominal hairs and sterilize the abdominal surface using a 70% ethanol solution.
- Cut through the abdominal cavity and expose the portal vein and inferior vena cava by moving the intestine laterally to the left of the abdomen.
- Start the pump at a speed of 1-3 ml/min with EGTA/HBSS Solution and cannulate the portal vein using a 23 g butterfly needle (wings cut). Clamp the section of the portal vein cannulated with the 23 G needle and then flip the serrefine forceps at the surface of the opened mouse abdomen. The liver should quickly pale within the first 30 sec of EGTA/HBSS Solution perfusion.
- Rapidly incise the lower part of the inferior vena cava to avoid excess pressure building in the liver, and then increase the flow rate gradually to 7 ml/min, over the first minute of perfusion. The animal dies due to bleeding secondary to vena caval venipuncture.
- When less than 5 ml of EGTA/HBSS Solution is remaining in the centrifuge tube, fill it up with Collagenase Solution (40-50 ml). Increase the flow rate gradually to 10 ml/min, over 30 sec.
- Make the liver swell by applying pressure to the inferior vena cava, using tweezers, for 5-10 sec intervals. This can be done periodically (5-10 times during digestion). This step will improve the liver cell dissociation and reduce the perfusion time with collagenase.
- When less than 10 ml of Collagenase solution remains within the centrifuge tube, pour 40-50 ml of pre-warmed Collagenase solution into the centrifuge tube.
- After 10-15 min of perfusion and about 70-80 ml of Collagenase Solution perfused, apply a small pressure on the surface of the liver with a forceps. A print of the pressure indicates that liver cells are dissociated.
- Remove the liver from the abdominal cavity in one piece and place it in a centrifuge tube containing 20-30 ml of Kupffer Cells Isolation Medium. Keep liver cells on ice or at 4 °C for a maximum period of 3 hr to avoid affecting liver cell viability.
- Repeat the perfusion procedure on several animals if needed, while keeping the perfused liver on ice. Pool one to three livers for purification and proceed with stage 3.
2. Preparation of the Density Gradient for Centrifugation (Figure 2)
- Proceed with the following steps (sections 2, 3 & 5) under sterile conditions and keep cells on ice or at 4 °C. Prepare the SIP (Solution of Isotonic coated silica Particles) by mixing 15.3 ml of coated silica particle solution with 1.7 ml of 10 x PBS.
- To make 20 ml of 25% SIP solution, mix 5 ml of SIP with 15 ml of PBS. To make 20 ml of 50% SIP solution, mix 10 ml of SIP with 10 ml of PBS.
- Fill one centrifuge tube with 20 ml of the 50% SIP solution. Tilt the centrifuge tube at an angle close to 90° and slowly add the 25% SIP solution (20 ml) on the side wall of the tube using a 25 ml serological pipette, without touching the surface of the 50% SIP layer. When adding the 25% SIP solution, progressively reduce the angle of the tube. Keep the density gradient on ice until use.
3. Kupffer Cell Purification (Figure 3)
- Put one perfused liver in a Petri dish with 15 ml of Kupffer Cell Isolation Medium. Rupture the Glisson's capsule (membrane of the liver) using scissors and release all liver cells into the Kupffer cell isolation medium. Filter the solution through a 100 µm cell strainer to be collected in a centrifuge tube. Repeat the perfusion procedure on additional perfused livers and pool the cells in the same centrifuge tube (15 ml from one mouse, and up to 45 ml from three mice).
- Centrifuge the cell suspension at 50 x g for 2 min at 4 °C. Parenchymal cells (hepatocytes) will be in the pellet and non-parenchymal cells (including Kupffer cells) will be in the supernatant.
- Collect the supernatant in a clean centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 50 x g for 2 min each. Repeat this step three more times.
- Centrifuge at 1,350 x g for 15 min to pellet non-parenchymal cells. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 10 ml of Kupffer Cell Isolation Medium.
- Add the non-parenchymal cell solution on the discontinuous isotonic gradient 25/50% as described in 2.3. Centrifuge at 850 x g for 15 min without acceleration or break.
- Localize the enriched Kupffer cell fraction appearing turbid within the 25% SIP fraction close to the 25/50% SIP interface (Figure 3). Using a 10 ml serological pipette, aspirate about 12 ml of the enriched Kupffer cell fraction. Transfer cells into a centrifuge tube containing 35-40 ml of Kupffer Cell Isolation Medium. Mix gently and centrifuge at 1,350 x g for 15 min at 4 °C to pellet cells.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend cells in 5-10 ml of pre-warmed Kupffer Cell Culture Medium. Count cells (hemocytometer) and measure the viability using trypan blue staining.
- Plate the purified non-parenchymal cells in 24-well plates at a density of 5 x 105 cells/well. Incubate the cells at 37 °C and 5% CO2 (Figure 3). After 30 min, gently remove the medium, wash with pre-warmed Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) once then replace it with 500 µl of fresh and pre-warmed Kupffer Cell Culture Medium (per well).
Representative Results
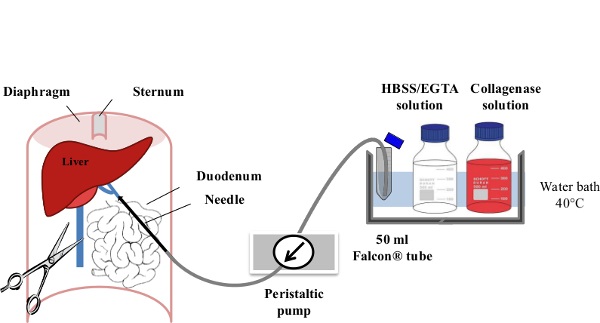
Figure 1: Liver Perfusion. After anesthesia of the mouse, the digestive tract is laterally moved to the left of the abdomen in order to make the portal vein (PV) accessible. The PV is cannulated using a slow flow rate (1-3 ml/min) of EGTA/HBSS Solution and the inferior vena cava (IVC) is immediately ruptured to avoid any excess pressure within the liver. Within the first minute of perfusion, the flow rate is gradually increased to 7 ml/min. The Collagenase Solution is then perfused at 10 ml/min until its full digestion is achieved.

Figure 2: Preparation of the density gradient. All procedures are carried out under sterile conditions. The SIP is prepared by mixing 15.3 ml of coated silica particle solution with 1.7 ml of 10 x PBS. A 5 ml of SIP is mixed with 15 ml of PBS to make 20 ml of 25% SIP solution. 10 ml of SIP is mixed with 10 ml of PBS to make 20 ml of 50% SIP solution. A centrifuge tube containing the 50% SIP solution (20 ml) is tilted and the 25% SIP solution (20 ml) is slowly added using a serological 25 ml pipette.

Figure 3: Purification of Kupffer Cells by density gradient centrifugation and cell adhesion. All procedures are carried out under sterile conditions. (A) After the rupture of the Glisson’s capsule, liver cells are filtered through a 100 µm strainer. The suspension is centrifuged at x 50 g to discard hepatocytes (pellets) and collect the non-parenchymal cell fraction (supernatant). This step is repeated 3 times. Non-parenchymal cells are added on top of a discontinuous isotonic gradient and centrifuged at 800 x g for 15 min. Kupffer cells collected from the 25% SIP cushion are purified further by cell adhesion selection. (B) Cells are plated in a 24-well plate and incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 30 min. Non-adherent cells are washed once with 500 µl of HBSS. Kupffer cells display their adherent morphology 4 hr after plating when f-CNTs can be added to the cells. The scale bar represents 25 µm.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Euthatal (pentobarbital sodium) | Merial | ||
| CD1 mice | Charles River | – | Mouse weight should vary from 35 to 45 g. We advise the use of male CD1 mice as their weight increase rapidly (e.g. a male CD1 mouse of 7 weeks old exceeds 35 g in weight). It is also advised to contact the animal supplier in advance to arrange for the delivery of older animals. Alternatively animals can be in-house to reach the desired weight. |
| HBSS (Ca2+ and Mg2+ free, with bicarbonate) | Life Technologies | 14175-053 | HBSS must be Ca2+ free. |
| Ethylene Glycol Tetraacetic Acid (EGTA) tetrasodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | E8145 | EDTA can also be used but EGTA has the advantage of chelating Ca2+ selectively. |
| HEPES (1M) | Life Technologies | 15630-056 | 100 ml |
| Collagenase type-IV | Worthington | CSL-4 | It is advised to test different batches of collagenase or at least mention to the supplier the product has to be suitable for liver cell isolation |
| Low glucose DMEM | Sigma-Aldrich | D5523 | 500 ml |
| RPMI (with sodium pyruvate and Glutamax®) | Life Technologies | 12633-012 | 500 ml |
| Penicillin/Steptomycin | Life Technologies | 15140-122 | 100 ml |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | First-Link | 60-00-850 | 500 ml |
| Trypan blue solution | Sigma-Aldrich | T8154 | 100 ml |
| Coated silica particle solution (Percoll®) | GE Healtcare | 17-0891-02 | Percoll® is very stable and can be kept for several years |
| 1x Phosphate-Buffered Saline | Life Technologies | 10010-023 | 500 ml |
| 10x Phosphate-Buffered Saline | Life Technologies | 70011-036 | 500 ml |
| Butterfly blood collection set (23G/305mm long tubing) | BD | 367288 | |
| Syringe Filters (0.22 μm Blue Rim) | Minisart | 16534-K | |
| Centrifuge Tubes (50 ml Blue Cap) | BD Biosciences, Falcon | 35 2070 | |
| Petri dish (90 x 15 mm) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | BSN 101VR20 | |
| 100 μm cell strainer | BD | 352360 | |
| Peristaltic pump | Watson Marlow | SciQ 300 | Rinse tubing before and after each usage with sterile PBS and 70% ethanol. |
| 24-well plates | Corning | 3526 | |
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5810R | |
| Serrefine forceps | Hammacher GmbH | Art. Nr. HSE 004-35 / Cat. Nr. 221-0051 | The serrefine forceps allow to clamp the vessel cannulated with the 23G needle without the need of holding the forceps during the perfusion procedure. URL: (http://www.hammacher.de/Laboratory-Products/Clamps-forceps/Serrefines/HSE-004-35-Serrefine::25126.html) |
| Cell scraper | BD Biosciences, Falcon | 353086 | Cut blade extremities with a pair of scissors to scrape cells in 24-well plates. |
| EGTA (Ethylene Glycol Tetraacetic Acid)/HBSS (Hank's Balanced Salt Solution) Solution | HBSS containing 0.5 mM EGTA and 25 mM HEPES. Adjust pH to 7.4. Prepare 50 ml for each liver to perfuse. | ||
| Collagenase Solution | DMEM low glucose containing collagenase type IV at 100 UI/ml, 15 mM HEPES and 1% Penicllin/Streptamycin (v/v). Adjust pH to 7.4. Prepare 100 ml for each liver to perfuse. After adding the collagenase, it is advised to warm up the solution for 30 min before use. This allows the collagenase activity to be optimum. | ||
| Kupffer Cell Isolation Medium | RPMI containing, 1% Non-Essential Amino-Acids (v/v),1% glutamax® (v/v) and 1% Penicllin/Streptomycin (v/v). Prepare at least 100 ml for 1-3 livers. | ||
| Kupffer Cell Culture Medium | RPMI containing 10% Fetal Bovine Serum, 1% Non-Essential Amino-Acids (v/v),1% Glutamax® (v/v) and 1% Penicllin/Streptamycin (v/v). Prepare at least 100 ml for 1-3 livers. | ||
| SIP (solution of isotonic coated silica particles) | Mix 1.7 ml of 10x Phosphate Buffered Saline with 15.3 ml of Percoll® to obtain 17mL of SIP. | ||
| 25% SIP solution | Mix 5 ml of SIP with 15 ml of 1x Phosphate Buffered Saline | ||
| 50% SIP solution | Mix 10 ml of SIP with 10 ml of 1x Phosphate Buffered Saline | ||
| Lysis Buffer | DMEM media with 0.9% Triton X-100 | ||
| PBS/BSA Solution | Prepare fresh Phosphate-Buffered Saline pH 7.4 with 1% Bovine Serum Albumin. |

