Antimicrobial Peptides Produced by Selective Pressure Incorporation of Non-canonical Amino Acids
Summary
The protocol presents the Escherichia coli-based selective pressure incorporation of non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) into the lactococcal antimicrobial peptide nisin. Its properties can be changed during recombinant expression via substitution with desired ncAAs in defined growth media. Resulting changes in bioactivity are mapped by growth inhibition assays and fluorescence microscopy.
Abstract
Nature has a variety of possibilities to create new protein functions by modifying the sequence of the individual amino acid building blocks. However, all variations are based on the 20 canonical amino acids (cAAs). As a way to introduce additional physicochemical properties into polypeptides, the incorporation of non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) is increasingly used in protein engineering. Due to their relatively short length, the modification of ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides by ncAAs is particularly attractive. New functionalities and chemical handles can be generated by specific modifications of individual residues. The selective pressure incorporation (SPI) method utilizes auxotrophic host strains that are deprived of an essential amino acid in chemically defined growth media. Several structurally and chemically similar amino acid analogs can then be activated by the corresponding aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and provide residue-specific cAA(s) → ncAA(s) substitutions in the target peptide or protein sequence. Although, in the context of the SPI method, ncAAs are also incorporated into the host proteome during the phase of recombinant gene expression, the majority of the cell's resources are assigned to the expression of the target gene. This enables efficient residue-specific incorporation of ncAAs often accompanied with high amounts of modified target. The presented work describes the in vivo incorporation of six proline analogs into the antimicrobial peptide nisin, a lantibiotic naturally produced by Lactococcus lactis. Antimicrobial properties of nisin can be changed and further expanded during its fermentation and expression in auxotrophic Escherichia coli strains in defined growth media. Thereby, the effects of residue-specific replacement of cAAs with ncAAs can deliver changes in antimicrobial activity and specificity. Antimicrobial activity assays and fluorescence microscopy are used to test the new nisin variants for growth inhibition of a Gram-positive Lactococcus lactis indicator strain. Mass spectroscopy is used to confirm ncAA incorporation in bioactive nisin variants.
Introduction
The discovery of antibiotics in the twentieth century and the parallel development of new antimicrobial compounds against pathogenic microorganisms enabled targeted treatments of bacterial infections. However, due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcusaureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), MDR (multidrug-resistant) Salmonella typhimurium phage type 10 (DT10), and Klebsiella pneumoniae, it is urgently necessary to generate new antimicrobial agents1. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are versatile, often highly specific compounds that are promising candidates for the development of new drugs thanks to their physicochemical properties, flexibility, size, hydrophobicity, and mode of action2. AMPs are small peptides usually consisting of 7 – 100 amino acids. Often, they have a cationic structure rich in positively charged arginine and lysine residues, which interact with the targeted microbial cell membrane, which is oppositely charged3. A particular subgroup of AMPs are ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptides (RiPPs)4. These are produced by many organisms from the kingdom of fungi and the domain of bacteria. One of the best known and widely used RiPPs is nisin, naturally produced by the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis). Active against a panel of Gram-positive bacteria, nisin has been used as a biopreservative in the food industry for more than 50 years due to its antimicrobial properties and the absence of evolved resistance in the targeted microbial strains5. Studies have shown that nisin destabilizes and generates pores in bacterial cell membranes, leading to antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens6. By binding to lipid II, bacterial cell wall synthesis is inhibited7. Nisin is encoded by nisA as a linear precursor peptide, which is composed of a leader and a core peptide region (Figure 1). After ribosomal synthesis, prenisin is first modified by the dehydratase NisB. Here, serine and threonine residues in the prepeptide core region are dehydrated to dehydroalanine (Dha) and dehydrobutyrine (Dhb)8. Subsequently, the dehydrated residues are coupled with cysteine to form lanthionine rings (hence the name "lantibiotic" for lanthionine ring-containing antibiotics) by an enzyme-catalyzed Michael addition. This posttranslational modification (PTM) is catalyzed by the cyclase NisC. In L. lactis, the modified prenisin is then transported out of the cell by transporter NisT, and the leader peptide is cleaved by the proteinase NisP to release the mature and active nisin form9. The responsible leader peptidase NisP has a high substrate specificity, since it only processes modified nisin efficiently10.
In general, active RiPPs result from the action of PTM enzymes (for instance NisBC), which drastically increase the chemical space of short peptides, e.g., via acetylation, glycosylation, methylation or phosphorylation. This level of complexity can further be expanded by the direct incorporation of ncAAs. While often feasible, chemical synthesis of AMPs is a challenge for large-scale production due to their structural complexity. For example, the total chemical synthesis of the lantibiotic lactosin S in 71 reaction steps was achieved with a final yield of 10% and that of nisin with a crude yield of only 0.003%11,12. Therefore, biological production offers a viable alternative, due to the generation of correct stereocenters and high product concentration.
Up to today, more than 150 ncAAs, e.g., having functional groups containing fluorine or azides, have been incorporated into recombinant proteins, and several examples of ncAA-modified AMPs have been reported13,14,15,16. With the introduction of ncAAs, novel physicochemical properties can be generated compared to conventional mutagenesis. The diversity of existing peptides can be increased, possibly leading to novel antibiotics.
One method for the incorporation of ncAAs into recombinant peptides is selective pressure incorporation (SPI) based on the use of auxotrophic bacterial strains17. These strains are not capable of synthesizing the corresponding cAA analog of the ncAA. The methodology uses the frequently observed relaxed substrate specificity, a feature of many natural aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs)18. Apart from their natural cAA substrates, these enzymes are often capable to recognize and activate the desired ncAA and to charge it onto their cognate tRNA(s). This leads to ribosomal incorporation of the ncAA into the target gene product in a residue-specific manner (i.e., cAA → ncAA substitution). This is of course only possible when the desired ncAA is structurally and chemically similar to the canonical amino acid and tolerated by the cell physiology, the translation machinery and the target peptide or protein sequence. In a particular experimental setup, the auxotrophic host cells are cultured in defined medium supplied with a limiting concentration of the native amino acid to be substituted. The cellular growth or exchange by cAA-free medium leads to intracellular depletion of the cAA. In the next step, the ncAA is added and the target gene expression is induced. Inevitably, ncAAs are now also incorporated in many other proteins in the host cell during this phase of target gene expression. Nonetheless, the toxicity of the SPI setup is kept at a low level since the Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain is transformed with a plasmid carrying the target gene under control of a strong promoter (commonly the highly competitive T7 promoter/ RNA polymerase system)19. Immediately after induction (usually when the cAA is exhausted), the host cells cease to grow and their cytoplasmic enzymatic machineries are used mainly for expression of the plasmid-based target gene. Site-directed mutagenesis can be used to define the site(s) of residue-specific ncAA installation in the target gene20.
As a model peptide for the incorporation of ncAAs, the pentacyclic AMP nisin A was chosen. It is 34 amino acids long and has only a single proline residue in the core peptide sequence (Figure 1). As in subtilisin, ericin A and S, and epidermin as well as in nisin Z and nisin Q, the conserved proline seems to be essential for activity9,21. The cAA proline plays a particularly important role in peptidyl-prolyl amide rotation and secondary structure stabilization. Its side chain ring conformations (exo / endo puckers) are responsible for a thermodynamic stabilization of the amide bond. Targeted chemical modifications (such as hydroxylations, fluorinations, methylations) of prolyl puckers often critically influence the folding stability, scaffold rigidity and functions of many biological structures22. Thus, it is plausible to expect that the Pro→ proline analog substitutions will endow ring B, the second ring of nisin, with novel and unusual properties.
Here, a proline-auxotrophic E. coli strain was used for recombinant nisin production. This requires the expression of the prepeptide gene nisA as well as the modification enzyme genes nisBC. The genetically encoded peptide product carries an N-terminally His-tagged leader for purification via affinity chromatography. For activity determination, L. lactis expressing and secreting NisPT is used to activate the recombinant nisin variants from E. coli cell lysates or purified peptide samples (Figure 1). The mature AMP is released after cleavage of the leader by NisP. In this agar diffusion method, the AMP sample diffuses into the solid growth medium and can inhibit the growth of the Gram-positive microorganism. After incubation, this can be observed visually by growth inhibition halos. In addition to L. lactis as an indicator, modified nisin variants showed antimicrobial activity against Enterococcus faecalis, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Lactobacillus johnsonii21,23.
An alternative and experimentally different method to incorporate ncAAs in RiPPs is stop codon suppression (SCS)24. For this, an orthogonal tRNA / aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS) pair is required for the corresponding ncAA. Ideally, all these three components are bioorthogonal, i.e., they do not interact with the endogenous tRNAs and aaRSs. An ncAA-specific aaRS can be generated by modification of the enzyme active site and screening of genetic libraries of mutant synthetases25. Furthermore, the introduction of an ncAA requires a codon which is reassigned and which does not encode for the cAA. Commonly, the amber stop codon is used24,26.
Recently, SPI was established for the incorporation of α-chloroacetamide-containing and click-chemistry-compatible ncAAs into NisA27. For example, Nε-alloc-lysine was incorporated into the lasso peptide captistruin with site-specific (SCS) and residue-specific (SPI) incorporation methods and subsequently modified in vitro by ruthenium-catalyzed metathesis28. In comparison to SPI, the SCS method is more complicated since an orthogonal tRNA / aaRS pair has to be co-expressed. To date, o-pairs for proline incorporation have been developed29, but to the best of our knowledge, no example of proline analog incorporation has been reported.
It should be noted that not all ncAAs can be incorporated using the SPI methodology. First, the uptake of ncAAs into the cytoplasm is regulated by a multitude of transport proteins that are embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane, which is the inner membrane for Gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. Normally, E. coli is capable of transporting a wide range of amino acid analogs into the cell with side chains structurally and chemically similar to canonical amino acids. Second, many chemically reactive or unstable ncAAs might act as an inhibitor towards cellular growth, as they are toxic for the metabolism and physiology of the host cell30. Thus, the uptake and toxicity of the ncAA for the production host should be tested beforehand. To avoid inactivation of the PTM machinery as a side effect, a strictly controlled expression setup of the responsible genes can be used to incorporate the natural amino acid into the modification enzymes (e.g., nisBC) and the ncAA into the target gene (e.g., nisA). This can be accomplished using two different promoters and induction of target gene expression, as demonstrated in specially designed SPI protocols31. As outlined above, the SPI method relies on the relaxed substrate specificity of the aaRS, which allows for ncAA activation and cognate tRNA charging. Subsequently, the tRNA is delivered to the ribosome followed by amide bond formation and folding of the target (poly)peptide. In this processes, proofreading and editing mechanisms may become relevant32. For these reasons, it is of great importance to have a target ncAA that is structurally and chemically similar to the cAA. Other crucial points are sufficient stability (both in the growth media and exposed to the cellular metabolism) and solubility of the ncAA. Additionally, it should be either commercially available or easy to be synthesized chemically.
Here, we describe a protocol for SPI, allowing residue-specific incorporation of ncAAs into recombinant RiPPs. Particularly, different proline analogs are incorporated into the antimicrobial peptide nisin A using E. coli as host organism. Mass spectrometry is used to verify amino acid replacement and peptide products are analyzed for bioactivity using growth inhibition assays and fluorescence microscopy using microbial indicator strains.
The basic requirement for successful recombinant nisin expression with defined ncAAs requires a suitable proline auxotrophic E. coli strain. For this auxotrophy, proA has to be dysfunctional, for instance achieved by genomic knockout. Cells fully deprived of intracellular Pro biosynthesis (i.e., deletion of proABC) without possibility for reversion are stable auxotrophs. Widely used gene knockout methods are phage transduction or single-gene knockout according to Datsenko & Wanner33. Furthermore, proA knockout strains can be obtained from public repositories such as Addgene, CGSC or the Keio collection. Since the recombinant nisABC expression shown here relies on the use of T7 promoters, the expression host strain has to carry an inducible gene for T7 RNA polymerase. This can be accomplished by introduction of the λDE3 prophage into the host genome, for example using the commercial kit. Alternatively, strains such as BL21(DE3) can be made auxotrophic as described above.
Protocol
1. Cloning of expression vectors and transformation of an auxotrophic production strain
Herein, the genes for nisin biosynthesis, namely nisABC, have been taken from L. lactis and transferred into T7-based plasmid expression vectors. Full DNA sequences of nisABC can be found in GenBank entry X6830734. The gene for the precursor peptide (nisA) has been placed on a pET-3a vector that confers ampicillin resistance. Genes for the dehydratase (nisB) and cyclase (nisC) have been placed on vector pRSFDuet-1, as reported earlier35, which confers kanamycin resistance.
NOTE: For nisA, the codons of the last four amino acids (ASPR) of the leader sequence were mutated to encode VSLR36 to render the proline residue in the core peptide unique and to ensure proper prepeptide processing by NisP. At the N-terminus, a hexa-histidine tag flanked by linker residues was added for purification purposes (see Figure 1).
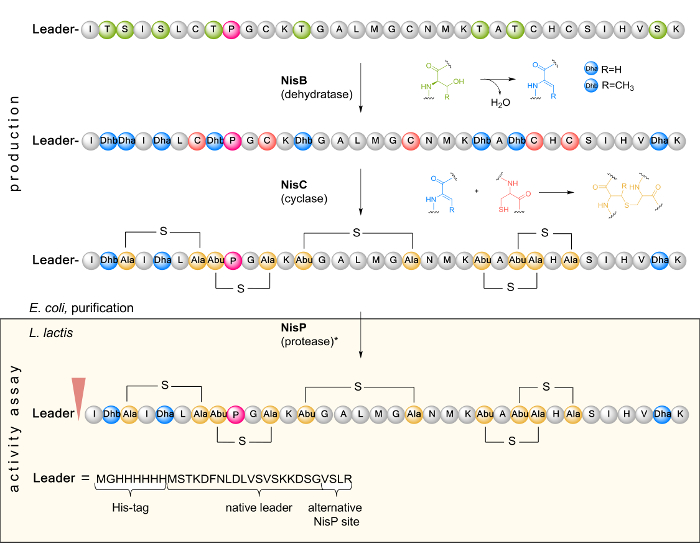
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the biosynthesis and PTM of NisA in E. coli as well as leader cleavage by the L. lactis indicator strain in a subsequent activity assay. In the first step, the inactive linear prenisin (composed of a leader and a core peptide region containing a unique proline (pink) at position 9) encoded by nisA is ribosomally synthesized. Next, prenisin is posttranslationally modified by dehydration of serine and threonine residues to dehydroalanine (Dha) and dehydrobutyrine (Dhb) as catalyzed by NisB. The cyclase NisC forms the thioether bridges via Michael addition of cysteine sulfhydryl groups with Dha or Dhb. The inactive modified prenisin is purified from E. coli and tested for antimicrobial activity. Here, it is transported into the cell of the Gram-positive L. lactis indicator strain. The leader is cleaved by protease NisP (as indicated by an arrowhead) to release fully active nisin. It can also be removed in vitro by treatment with trypsin (*). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Use standard heat-shock protocol37 or electroporation38 to transform the proline auxotrophic E. coli strain (see above) with the plasmids pET-3a nisA(VSLR) and pRSFDuet-1 nisBC.
- Pipette 25-100 µL of transformed cell suspension onto agar plates containing ampicillin, kanamycin and 1% (w/v) glucose. Use a plate spreader or glass beads to spread the solution evenly on the plates.
- Incubate plates overnight at 37 °C.
- The following afternoon, use a single colony to inoculate 10 mL LB medium containing ampicillin, kanamycin and 1% (w/v) glucose in a 50 mL flask.
- Shake culture overnight (12-16 h) at 37 °C and 200 rpm.
- Take 250 µL sterile 80% glycerol and 550 µL culture, mix well in a 2 mL tube and store as frozen cell stock at 80 °C.
2. New minimal medium (NMM) preparation
NOTE: This protocol uses NMM20 as a chemically defined liquid bacterial growth medium. Also, it is advised to follow the order of preparation strictly. Otherwise, precipitation can occur. For amino acid forms differing from those listed in the Materials table (e.g., hydrochlorides), check solubility. NMM19 contains 19 amino acids except for the cAA to be replaced (here, proline) by the ncAA analog. See Table 1 for the final ingredient concentrations. Depending on the bacterial strain used for production, biotin and thiamine may be optional.
- Preparation of the amino acid mixture
- Dissolve 0.5 g Phe, Trp and Tyr in 100 mL ddH2O with the addition of a few drops of concentrated HCl until dissolution.
- Weigh out 0.5 g of each of the remaining 16 amino acids. Mix with 22 mL of 1 M KH2PO4 and 48 mL of 1 M K2HPO4. Add ddH2O to ~800 mL. Stir until the solution becomes clear.
- Add the dissolved Phe, Trp and Tyr and adjust the volume of the solution to 1 L with ddH2O.
- Sterilize the amino acid mixture by vacuum filtration with a bottle top filter unit.
- Stock solutions for NMM19
- First, prepare 1 M stock solutions of the following components: (NH4)2SO4, KH2PO4, K2HPO4, MgSO4 and a 5 M stock solution of NaCl. Sterilize by autoclaving.
- Prepare 50 mL stocks of D-glucose (1 M), CaCl2 (1 g/L), FeCl2 (1 g/L), thiamine (10 g/L), biotin (10 g/L) and trace elements (CuSO4, ZnCl2, MnCl2, (NH4)2MoO4; 1 mg/L). Sterilize each by filtration with a syringe filter.
- NMM19 preparation
- Mix all stock solutions to obtain a final concentration of 7.5 mM (NH4)2SO4, 1.7 mM NaCl, 22 mM KH2PO4, 50 mM K2HPO4, 1 mM MgSO4 and 20 mM D-glucose, 50 mg/L amino acid mix, 1 µg/L CaCl2, 1 µg/L FeCl2, 10 µg/L thiamine, 10 mg/L biotin and 0.01 µg/mL trace elements.
3. Expression of Recombinant Nisin with Incorporation of Proline Analogs by SPI
In this section, recombinant expression of the prepeptide (here: nisA) and PTM genes (here: nisBC) is performed. First, cells are grown in the presence of all cAAs, since LB complex medium is used. Glucose is added to repress the target gene expression at background level, which could otherwise lead to the production of wild-type peptide (here: nisin) due to leakiness of the promoters. Only after the target cAA (here: proline) is depleted, the ncAA is added and target gene expression is induced in chemically defined medium. Incubation of liquid cultures should be performed in suitable flasks with aeration (e.g., 500 mL in a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask at 200 rpm).
- Using a sterile pipette tip, start a fresh overnight culture from frozen cell stock or fresh colony (see step 1). Use 25 mL LB medium containing ampicillin, kanamycin and 1% (w/v) glucose and incubate overnight (12-16 h) at 37 °C and 200 rpm.
- Inoculate 1 L of sterile fresh medium with 10 mL overnight culture (1% v/v) and incubate at 37 °C and 200 rpm until OD600 = 0.5.
- Centrifuge at 4 °C for 15 min at 4,500 x g.
- Pour off the supernatant and resuspend the pellet with 20 mL NMM19 (prepared in step 2.3) containing antibiotics and 1% (w/v) glucose. Centrifuge at 4 °C for 10 min at 4,500 x g.
- Resuspend cell pellet in 500 mL of the same medium and incubate at 30 °C and 200 rpm for 1 h.
NOTE: At this step, the cAA depletion (here, proline) takes place. - Divide the culture into equal parts (one for each ncAA). Induce each culture with 1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and supply 1 mM proline analogs (4S/R-fluoroproline, 4S/R-hydroxyproline or 4S/R-methanoproline).
NOTE: As control, one culture can be supplied with 1 mM proline, resulting in wild-type peptide production. - Incubate overnight (12-16 h) at 28 °C and 200 rpm.
- Centrifuge the cell cultures in 50 mL tubes at 4 °C for 20 min at 5,000 x g. Pour off the supernatant and store pellets at -80 °C until purification.
4. Isolation and Purification of His-tagged Nisin Analogs
Peptides are purified under denaturing conditions with guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl)39, a strong denaturant.
Caution: GuHCl is harmful if swallowed or inhaled and causes skin and serious eye irritation. Wear eye protection and gloves.
- Prepare 250 mL of binding buffer (5 M GuHCl, 300 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris, pH 7.4), wash buffer (300 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris, 25 mM imidazole, pH 7.4) and elution buffer (300 mM NaCl, 25 mM Tris, 250 mM imidazole, pH 7.4). For these, transfer the solids into a 250 mL bottle and fill up to 200 mL with ddH2O. Mix well and adjust the pH to 7.4 with 1 M NaOH or HCl. Then, fill up to 250 mL with ddH2O. Filter all buffer solutions using a bottle top filter unit.
- Cell lysis
Here, a sonicator (with 200 W maximum high frequency (HF) output) is used; note that power settings needed for cell disruption may differ for other instruments. All steps are performed on ice. Alternatively, chemical cell lysis, a liquid homogenizer or a French press can be used.- Add 12 mL binding buffer to each centrifuge tube (from step 3.8) and resuspend by vortexing.
- Submerge the tip of the sonicator probe into the cell suspension. Set sonicator at 40% amplitude with pulse of 1 s on / 5 s off for 15 min.
NOTE: Clean the sonicator tip between samples to avoid carryover. Wipe the sonicator probe with 70% ethanol. - Centrifuge the lysed cell suspension at 4 °C for 40 min at 15,000 x g to pellet cell debris. Transfer the supernatants to a new reaction tube.
- Affinity chromatography
For immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC)40, a peristaltic pump or an FPLC system can be used with a 1 mL cartridge (here filled with Ni-NTA resin). For preparation of buffers, see step 4.1.
NOTE: IMAC purification is feasible since the produced recombinant peptide carries an N-terminally His-tagged leader, which is removed in step 6 by leader peptidase NisP, releasing mature nisin. Perform purification at room temperature or at 4 °C. Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute if applicable for the IMAC cartridge.- First, wash the cartridge with 5 column volumes (cv) of ddH2O to remove storage buffer.
- Equilibrate with 10 cv of binding buffer.
- Process cell lysate (step 4.2) using a syringe filter to remove particles, then apply to the cartridge.
- Wash with 15 cv of wash buffer in order to remove nonspecific and unbound material.
- Elute with 10 cv of elution buffer and collect 1 mL fractions in 1.5 mL tubes. Store the fractions at 4 °C for short term (up to 3 days) or at -20 °C for longer terms.
- For storage, wash the cartridge with 10 cv of ddH2O followed by 5 cv of 20% ethanol.
5. LC-ESI-TOF Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Nisin Analogs
NOTE: See Materials table for example instrumentation for liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-TOF-MS).
- Perform HPLC separation of 15-20 µL peptide solution (prepared in step 4.3) on a C5 column with a mobile phase of water (A) and acetonitrile (B) both supplemented with 0.1% formic acid and a gradient from 5-80% B over 20 min. For mass spectrometry (MS), use elution after 5 min.
NOTE: Depending on peptide content and affinity to the HPLC column, sample volumes and separation may need optimization. - Use appropriate software to deconvolute the measured mass spectra and calculate the different peptide charge states41. Compare the observed peptide species mass to the calculated wild-type mass altered by the cAA → ncAA substitution. Take into account that the linear prepeptide is posttranslationally modified by eight dehydrations (-8 H2O) and five cyclizations (see Figure 1).
NOTE: Using sodium-containing buffers, MS analysis in positive mode can show sodium adducts. These become visible as additional peaks with higher deconvoluted mass (for each sodium adduct, the observed deconvoluted mass is 22.99 Da higher). To remove these adducts, HPLC purification42 or extensive dialysis43 can be performed.
6. Antimicrobial Activity Test
- Preparation of GM17-agar plates under sterile conditions
- Prepare an overnight culture of the indicator strain L. lactis NZ9000 carrying plasmid pNG nisPT44 at 30 °C in M17 broth45 with 1% (w/v) glucose (=GM17) and 5 µg/mL chloramphenicol.
- Measure OD600, inoculate fresh medium to OD600 = 0.1 and incubate until OD600 = 0.4-0.6. Then place the flask on ice.
Note: Each OD600 measurement will consume culture volume. Keep in mind that for each assay agar plate, 1 mL bacterial culture will be needed. If required, scale up the liquid culture volume accordingly. - For 1.5% agar, weigh out 4.5 g agar in a glass media bottle. Add 300 mL ddH2O, mix, and autoclave.
- Prepare 2x M17 broth (two-times concentrated) in 300 mL ddH2O and autoclave.
- Mix 25 mL 2x M17 broth containing 10 µg/mL chloramphenicol and 2% glucose with 1 mL L. lactis preculture (4% v/v).
- Add 25 mL molten 1.5% agar (freshly autoclaved or heated in a microwave).
NOTE: Prior to this, let the bottle cool to the touch (around 50 °C). This is necessary since L. lactis is a mesophilic organism sensitive to high temperatures. - Pour the solution into a large petri dish. Dry plates for 10-15 min.
- Sterilize the ends of a glass Pasteur pipette by flame. Wait for it to cool down, then use the wide end to create holes in the solidified GM17-agar.
- Sample preparation
- Take 1 mL of the E. coli expression cultures (created in step 3.7) in a labelled 1.5 mL tube and centrifuge for 3 min at 7,000 x g. Aspirate the remaining medium and resuspend the cell pellet in 500 µL Na-P (50 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 made from 0.5 M sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.5 M disodium hydrogen phosphate).
- Sonicate the samples on ice (compare step 4.2.2). Submerge the tip of the sonicator probe into the cell suspension. Set sonicator at 30 % amplitude with pulse of 1 s on and 5 s off for 3 min.
- Centrifuge the cell lysate for 10 min at 13,000 x g to pellet cell debris. Transfer the supernatant to a new reaction tube on ice.
- Dilute and normalize the cell extract supernatants to 1 mL OD600 = 0.6, relative to the harvested cell density, with Na-P.
- Activity test
- Add 40 µL of each normalized sample into a hole of the indicator agar plate (Figure 3). Use chloramphenicol at 400 µg/mL as antibacterial control compound. Use elution buffer as a negative control. Wait until all samples are diffused into the agar. Incubate the plate overnight at 30 °C.
- Take pictures of the agar plates using a flatbed scanner or digital camera. Growth inhibition halo sizes can be measured by hand or using ImageJ46.
7. Fluorescence Microscopy
In order to observe the effect of AMPs on bacterial cells, light and fluorescence microscopy can be used. Note that the nisin mode of action relies on the destabilization and the formation of pores in bacterial membranes6. Here, Nile red is used to stain the bacterial cell membrane, which becomes scattered and aggregated upon cell lysis.
NOTE: See Materials table for example instrumentation. Amounts of added AMP solution can be adjusted depending on peptide concentration and bioactivity.
- Cell preparation
- Prepare 10 mM Nile red stock solution in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Grow L. lactis indicator strain to OD600 = 1.0 as in step 6.1.1-6.1.2.
- Centrifuge 1 mL culture for 3 min at 4 °C and 5,000 x g.
- Discard supernatant, resuspend in 1 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)47.
- Centrifuge and resuspend again.
- Add 1 µL Nile red stock solution, mix gently.
- Microscopic Image Acquisition
- Add 30 µL of cell preparation on a cover slide while exciting at 520 nm.
- Set acquisition time 0.2 s, kinetic series 0.1 Hz, series length 200 images.
- Add 0.3 – 1.5 µL of cell lysate or IMAC sample (from step 6.2.4 or 4.3.5, respectively). For IMAC samples, elution buffer can be used as a negative control.
- Monitor and record fluorescence emission at λ ≥ 560 nm.
- Data analysis
- Microscopy image sequences are stored as movie files (.avi). Single images are analyzed with ImageJ46.
Representative Results
This protocol is designed to enable the production of ncAA-modified nisin variants with residue-specific incorporation of proline analogs by the SPI method. Previously, the feasibility and yields of 24 mg/L were reported for recombinant production of fully modified wild-type nisin39. Using the SPI method, target peptide/protein yields are frequently good and can reach quantities close to wild-type production48. As first experiments, recombinant wild-type RiPP production should be tested in the chosen auxotrophic host. Here, the proline-auxotrophic E. coli MG1655 ΔproBA::frt ΔproC::frt (DE3) was used as host strain. For the incorporation of ncAAs, cultivation and induction timing as well as medium composition and temperature can be optimized towards maximum peptide yield.
Antimicrobial activity assay
Wild-type recombinant nisin production and purification were performed following the protocol above. In this case, proline was used instead of its ncAA derivatives at step 3.6. An antimicrobial activity assay was used to verify RiPP production and to compare the antimicrobial activity before and after purification. For the activity assay, elution fractions and IMAC flow-through were used directly and tested against the Gram-positive L. lactis indicator strain (Figure 2). As this strain expresses NisP, the nisin variants contained in E. coli cell lysates or purified peptide samples, respectively, become activated by proteolytic cleavage of the leader peptide. Evidently, the flow-through showed growth-inhibitory activity. This can be explained by bioactive material not binding to the IMAC column. The tested elution fractions all showed increased activity compared to the unpurified sample, indicating a concentration of the His-tagged peptide by IMAC. Note that the elution buffer (as negative control) did not influence the growth of L. lactis in this assay.
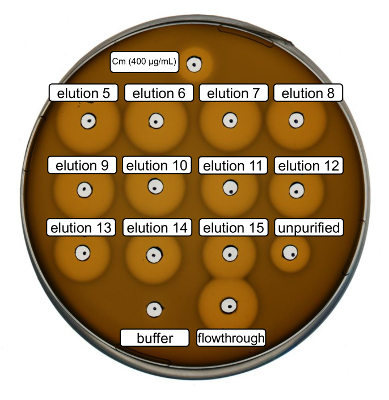
Figure 2. Antimicrobial activity test after IMAC purification of recombinantly produced wild-type nisin. Elution fractions 5 to 15 and the flow through of IMAC purification were tested in comparison with the unpurified cell lysate (diluted for OD600 normalization) against the L. lactis indicator strain. The size of growth inhibition halos indicates antimicrobial activity. Chloramphenicol at a concentration of 400 µg/mL was used as a positive control and the IMAC elution buffer as negative control. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
To prove the antimicrobial activity of recombinantly produced nisin variants containing six different proline analogs, an activity assay was performed to test the inhibition of the L. lactis indicator strain. Figure 3 shows growth inhibition for five of the six samples produced using proline analogs. The best results (as judged from halo sizes) were observed for the incorporation experiments of analog (4R)-fluoroproline, (4R)-hydroxyproline and (4S)-methanoproline. Comparing the growth inhibition halo size to the wild-type nisin produced and tested in parallel, all three nisin variants showed similar inhibition strength. However, the halo size alone cannot be used to asses a specific activity, since the concentration of AMP was not determined. Therefore, the assays serve only to test qualitatively whether the antimicrobial activity of the resulting nisin variants is preserved or lost. To determine the specific activity, the concentration of the nisin variants must be quantified (see Discussion).
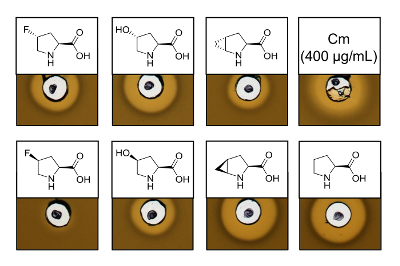
Figure 3. Antimicrobial activity assay of cell lysates containing nisin variants produced via SPI with proline analogs. Comparison of nisin variants with recombinant wild-type samples. All samples were OD600-normalized after cell lysis relative to the harvested cell culture density. Halos indicate bioactivity in form of indicator strain growth inhibition. First row from left to right: (4R)-fluoroproline, (4R)-hydroxyproline, (4R)-methanoproline and chloramphenicol (400 µg/mL; antimicrobial positive control). Second row: (4S)-fluoroproline, (4S)-hydroxyproline, (4S)-methanoproline and proline (wild-type control). Note the chemical nomenclature; e.g., (4R)-fluoroproline is also referred to as trans-4-fluoroproline. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
LC-ESI-TOF mass spectrometry
Subsequent to IMAC purification, the incorporation of the ncAAs into nisin was analyzed by LC-ESI-TOF mass spectrometry. Figure 4 shows the deconvoluted mass spectra of a nisin variant containing (4R)-fluoroproline. This variant was IMAC purified as described above and afterwards analyzed by LC-ESI-TOF mass spectrometry, so it still carried the leader. The main peak in Figure 4A corresponds to the modified nisin containing (4R)-fluoroproline with a deconvoluted mass of 6883.18 Da (calculated mass 6882.05 Da, calculated mass of the corresponding wild-type peptide with proline at position 9 is 6864.06 Da). The two peaks with lower abundance and higher mass correspond to sodium adducts as indicated. Figure 4B shows differently charged species of the main compound as found by the deconvolution algorithm. For example, the peak at 1148.11 m/z corresponds to the six-fold charged species ([M+6H]6+).
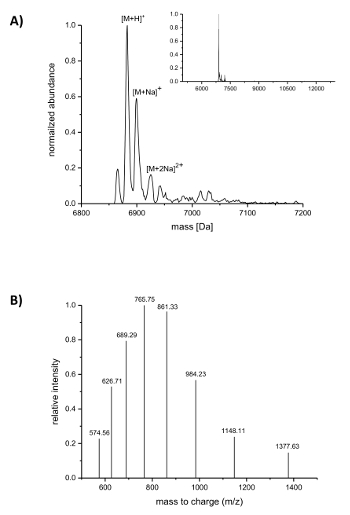
Figure 4. LC-ESI-TOF mass spectrometry of IMAC-purified recombinant nisin variants containing (4R)-fluoroproline. (A) Deconvoluted mass spectrometry chromatogram (zoomed out in the inset) for the nisin variant (still carrying the leader) with (4R)-fluoroproline (expected masses (Da): [M+H]+ = 6882.05, [M+Na]+ = 6904.03, [M+2Na]2+ = 6926.02). (B) Compound spectra for species [M+H]+. Expected masses (Da): [M+5H]5+ = 1377.41, [M+6H]6+ = 1148.01, [M+7H]7+ = 984.15, [M+8H]8+ = 861.26, [M+9H]9+ = 765.67, [M+10H]10+ = 689.21, [M+11H]11+ = 626.64, [M+12H]12+ = 574.50. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Fluorescence microscopy
Antimicrobial activity of recombinant nisin and its ncAA-containing variants can also be shown by direct observation of the L. lactis indicator strain via fluorescence microscopy. Nile red, a highly hydrophobic fluorescent dye, was used to stain the bacterial cell membrane. Figure 5 shows the qualitative change of the aggregation state of the cell culture and single cell morphology. Cells were stained with Nile red and deposited on a microscopy cover slide. The upper row shows the cells directly at the beginning when buffer, recombinant wild-type nisin, or nisin containing (4R)-fluoroproline, or (4R)-hydroxyproline were added. The lower panel shows the corresponding images after 20 minutes of incubation.

Figure 5. Fluorescence microscopy of recombinant nisin effects on Gram-positive cells. Microscopic images of 30 µL L. lactis indicator strain (OD600 = 1) marked with Nile red were taken before (upper panel) and after (lower panel) 20 min incubation with 1 µL buffer (A), 0.3 µL recombinant wild-type nisin (B) and 0.6 µL nisin variants containing (4R)-fluoroproline (C) and (4R)-hydroxyproline (D). Blue circles mark regions with aggregated or deformed cells, blue arrows point to regions where diffusion of fluorescent membrane fragments can be observed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 5A shows that the general appearance of the cells did not change within 20 minutes of observation. Only the number of cells that deposited during the time rose and, therefore, a larger amount of cells is visible within the 80 µm x 80 µm of the observed region. Figure 5B shows that the Gram-positive cells appeared aggregated and blurry (marked with blue circles) after 20 minutes of exposure to wild-type nisin, even when low amounts (here, 0.3 µL IMAC elution) were added. In addition, light material diffused from the cells into the buffer, indicating that membrane fragments marked with Nile red were mobilized during the timeframe (marked by blue arrows). These findings indicate cell lysis as it was shown to occur upon treatment with nisin6,49. Similar effects were observed after incubation with the nisin variant containing (4R)-fluoroproline (Figure 5C) and nisin containing (4R)-hydroxyproline (Figure 5D) both showing large amounts of distorted and aggregated cells after 20 minutes, in marked contrast to the control sample (Figure 5A).
| Component | Concentration |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 7.5 mM |
| NaCl | 8.5 mM |
| KH2PO4 | 22 mM |
| K2HPO4 | 50 mM |
| MgSO4 | 1 mM |
| D-Glucose | 20 mM |
| All canonical amino acids (except for the one to replace) |
50 mg/L |
| Ca2+ | 1 µg/mL |
| Fe2+ | 1 µg/mL |
| Trace elements (Cu2+, Zn2+, Mn2+, MoOH2+) |
0.01 µg/mL |
| Thiamine | 10 µg/mL |
| Biotin | 10 µg/mL |
Table 1. Composition of NMM19 chemically defined bacterial growth medium after preparation according to step 2.
Discussion
By using SPI for insertion of proline analogs, the targeted nisin structures can be substantially modified, creating novel peptide variants with unique sequence combinations and chemical properties. In this way, the basic limit of classical gene technology can be circumvented, which is constrained to the side chain chemistries of the 20 cAAs. In vivo chemical diversification of nisin as exemplified above demonstrates a general approach to complement natural PTMs and to dramatically enhance the chemical space of RiPPs. We believe that expanding the repertoire of the natural amino acids holds great promise especially for AMPs. In proteins, a tremendous range of functionalities can be realized through a defined arrangement of the 20 cAAs in three-dimensional structures. With only 7-100 aa in length3, ways to achieve such structural features only through cAAs would be limited for AMPs. It is thus not surprising that natural AMPs in form of RiPPs are commonly extensively post-translationally modified4. In the same fashion, ncAAs as alternative building blocks hold great promise to improve their pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic parameters (see Baumann et al. 201735 and references therein).
The SPI methodology used in this work benefits from a relatively easy experimental setup, straightforward execution and high reproducibility. Due to global substitution, multisite ncAA incorporation into target peptides is also feasible. On the other hand, the method may not be adequate for replacement of amino acids frequently occurring in the target gene product. In principle, undesired positions can be changed by site-directed mutagenesis, but these additional changes might also affect several AMP properties including structure and bioactivity. Once an auxotrophic strain for production is available, several ncAAs can be tested without requiring extensive changes on the genetic level. Moreover, the method is not limited to auxotrophic E. coli strains, but can also be performed using the natural production host. For example, Zhou et al. showed that SPI for production of novel RiPPs also works in the naturally Trp-auxotroph L. lactis: Using defined media, three tryptophan analogs were incorporated at four positions in nisin50.
Since the SPI method leads to global replacement of the chosen cAA by the ncAA, it is generally applicable to a broad range of target peptides and proteins. A range of auxotrophic E. coli strains is available (see step 1), allowing several cAAs each to be tested for replacement by ncAAs. Met analogs incorporated using metA-deficient strains (e.g., B834(DE3)) are most commonly employed. Examples of isostructural Met analogues are azidohomoalanine (Aha) and homopropargylglycine (Hpg), commercially available ncAAs which can be efficiently incorporated. Both introduce bioorthogonal handles which allow attachment of molecules carrying a compatible alkyne or azide functionality, respectively. For example, fluorescent dyes or polyethylene glycol (PEG) moieties can be attached by copper(I)-catalyzed azide alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC)51.
Although both recombinant ncAA incorporation methods (SPI and SCS) usually achieve sufficient target quantities, yields are often reduced relative to wild-type production of the corresponding peptides and proteins. As the purities often correlate with production efficiency, additional purification steps may be required, especially for low-abundant species. In this particular case of recombinant nisin production, the His-tagged leader sequence greatly simplifies RiPP purification by selective enrichment from the cell lysates. The purification shown in this protocol improves the purity and concentration of nisin, but often does not yield AMP purities sufficient to determine the yield and specific activity. Besides IMAC, commonly used AMP purification methods include HPLC, ion exchange chromatography (IEC) and precipitation (e.g.. using acetone or trichloroacetic acid (TCA)) or combinations thereof – resulting in a multistep purification scheme52. It should be noted that their commonly polycationic nature can facilitate IEC purification. Freeze-drying is frequently used to store purified AMPs.
Ideally, ncAAs for incorporation into AMPs should be commercially available at affordable prices or easily produced by simple and reproducible chemical synthesis protocols. An equally important prerequisite for the SPI method is that the ncAA is recognized, activated and charged onto the cognate tRNA by the endogenous or co-expressed aaRS. This can be tested in vitro by amino acid activation or tRNA aminoacylation assay53. As an easy alternative, SPI test expressions of model proteins such as green fluorescent protein (GFP) conducted both in presence and in absence of ncAA supplementation can be performed. Furthermore, solubility in the growth medium and cell permeability as well as chemical stability constitute important factors.
In this example, antimicrobial activity was screened using a Gram-positive indicator strain. As it expresses the leader peptidase NisP, the final step of nisin maturation is catalyzed. Removal of the leader sequence (His-tagged for purification purposes) can also be performed in vitro by treatment with purified NisP50 or trypsin54. Beyond the scope of this work, pathogenic organisms and multidrug resistant strains can then be tested for bacteriostatic or bactericidal inhibition by AMPs using a similar methodology. Clinically relevant target species include MRSA, MDR Mycobacterium tuberculosis, VRE, Acinetobacter baumannii, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Besides the agar plate diffusion assay presented here, growth inhibition can also be performed using appropriate liquid media inoculated with the bacterial species and supplemented with AMP. Using broth dilution methods, the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) can be determined using pure peptides55. The activity assay presented here can also be used to estimate the bioactivity and potency of AMP-containing solutions relative to reference compounds, for example commercially available nisin.
Recombinant production of RiPPs is often feasible39, which commonly includes co-expression of PTM genes. As soon as the production strain is transferred into a chemically defined or synthetic minimal medium containing a suitable ncAA, residue-specific replacement of the corresponding cAA takes place. Thus, other RiPPs can be produced by the same methodology, provided that their recombinant production is feasible and conditions can be found where ncAA incorporation and PTM yield sufficient amounts of target product. Note that besides the host cell proteome, the peptide PTM machinery can also become ncAA-modified during SPI. Consequently, the timing of target expression induction and length of the following incubation period can require optimization. Since ncAA incorporation into the PTM enzymes can affect their stability and activity, the production of the processed RiPP can in principle be affected. Sufficient PTM enzyme efficacy is indicated by the formation of processed prepeptide, as detected by MS and bioactivity assays. As introduced above, different inducible promoters could be employed in order to produce the PTM genes first (in absence of the ncAA) followed by induction of the precursor peptide gene in presence of the ncAA. In general, the production of cAA-containing target peptide must be suppressed before addition of the ncAA, which is why tight repression of the precursor gene is required. Within this protocol, this is achieved by catabolic repression through the addition of glucose to the growth medium. Especially since the PTM enzymes required for prepeptide processing originate usually from a genetically distant host, expression temperature and codon usage of the corresponding genes can require optimization if recombinant production has not yet been established. In principle, the presence of ncAAs in the prepeptide can interfere with recognition and processing of the PTM enzymes, in the case of nisin NisBC and NisP. For ncAA incorporation into AMPs, it is thus recommended to perform small-scale expression experiments first to identify suitable expression conditions and reliability of the AMP activity assay.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
J.H.N., T.B. and M.B. acknowledge funding by the EU FW7 program (SYNPEPTIDE). F.-J.S. and T.F. acknowledge funding by the Federal Ministry of Education and Science (BMBF Program “HSP 2020”, TU-WIMIplus Project SynTUBio) and the German Research Foundation (Cluster of Excellence “Unifying concepts in Catalysis”).
Materials
| sodium chloride | Carl Roth, Germany | P029 | |
| guanidine hydrochloride | Carl Roth, Germany | 0035.2 | |
| dipotassium hydrogen phosphate | Carl Roth, Germany | P749.3 | |
| potassium dihydrogen phosphate | Carl Roth, Germany | 3904.3 | |
| sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate | Carl Roth, Germany | K300.2 | |
| disodium hydrogen phosphate | Carl Roth, Germany | P030.2 | |
| L-alanine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3076.2 | |
| L-arginine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3144.3 | |
| L-asparagine monohydrate | Carl Roth, Germany | HN23.1 | |
| L-aspartic acid | Carl Roth, Germany | T202.1 | |
| L-cysteine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3467.3 | |
| L-glutamine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3772.1 | |
| L-glutamic acid | Carl Roth, Germany | 3774.1 | |
| L-glycine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3187.3 | |
| L-histidine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3852.3 | |
| L-isoleucine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3922.3 | |
| L-leucine | Carl Roth, Germany | 3984.3 | |
| L-lysine monohydrate | Carl Roth, Germany | 4207.2 | |
| L-methionine | Carl Roth, Germany | 9359.4 | |
| L-phenylalanine | Carl Roth, Germany | 4491.2 | |
| L-proline | Carl Roth, Germany | T205.3 | |
| L-serine | Carl Roth, Germany | 4682.4 | |
| L-threonine | Carl Roth, Germany | T206.2 | |
| L-tryptophan | Carl Roth, Germany | 4858.2 | |
| L-tyrosine | Carl Roth, Germany | T207.2 | |
| L-valine | Carl Roth, Germany | 4879.4 | |
| ammonium sulfate | Carl Roth, Germany | 3746.3 | |
| magnesium sulfate | Carl Roth, Germany | 0261.2 | |
| D-glucose | Carl Roth, Germany | 6780 | prepare a 20% (w/v) solution for addition into molten agar |
| calcium chloride | Carl Roth, Germany | PN93.2 | |
| iron(II) chloride | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | 372870 | |
| thiamine hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | T1270 | |
| biotin | Carl Roth, Germany | 3822.2 | |
| copper(II) sulfate | Merck, Germany | 102792 | |
| manganese(II) chloride | Carl Roth, Germany | KK36.2 | |
| zinc chloride | Merck, Germany | 108816 | |
| immonium orthomolybdate | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | 277908 | |
| glycerol | Carl Roth, Germany | 7533.3 | |
| isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | I6758 | |
| ampicillin sodium salt | Carl Roth, Germany | K029.5 | working concentration 100 µg/mL for E. coli, prepare 100 mg/mL stock in ddH2O |
| kanamycin sulfate | Carl Roth, Germany | T832.2 | working concentration 50 µg/mL for E. coli, prepare 50 mg/mL stock in ddH2O |
| chloramphenicol | Carl Roth, Germany | 3886.1 | working concentration 5 µg/mL for L. lactis, prepare 37 mg/mL stock in ethanol |
| (4S)-fluoroproline | Bachem, Switzerland | F-3970 | |
| (4R)-fluoroproline | Bachem, Switzerland | F-3975 | |
| (4S)-hydroxyproline | Bachem, Switzerland | F-1395 | |
| (4R)-hydroxyproline | Bachem, Switzerland | F-2980 | |
| (4S)-methanoproline | chemically synthesized | ||
| (4R)-methanoproline | chemically synthesized | ||
| hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Carl Roth, Germany | P074.4 | |
| ethanol | VWR, Germany | 20825.324 | |
| M17-broth | Sigmal-Aldrich, Germany | 56156 | commercial product, see Terzaghi BE & Sandine WE, Appl Microbiol., 1975, 29(6):807-13 for contents and preparation |
| agar-agar | Carl Roth, Germany | 5210.5 | |
| Nisin from Lactococcus lactis | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | N5764 | commercial product, can be used as reference for bioactivity |
| dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) | Carl Roth, Germany | A994.1 | |
| imidazole | Carl Roth, Germany | 3899.3 | |
| 1.5 mL autosampler vial for LC-MS | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | Supelco 854165 | |
| acetonitrile | VWR, Germany | HiPerSolv CHROMANORM ULTRA for LC-MS, 83642 | LC-MS grade required |
| formic acid | VWR, Germany | HiPerSolv CHROMANORM for LC-MS, 84865 | LC-MS grade required |
| 1 mL Ni-NTA IMAC column, e.g. HisTrap FF Crude | GE Healthcare, UK | 29-0486-31 | different manufacturers and resins available for IMAC |
| 0.45 µm bottle top filter unit | VWR, Germany | 10040-470 | sterile filtration of solutions using a vacuum pump |
| 0.45 µm syringe filter PVDF membrane | Carl Roth, Germany | CCY1.1 | sterile filtration of solutions using a syringe and to remove particles from cell lysates |
| luer-lock syringe, PP, 50 ml | Carl Roth, Germany | T552.2 | sterile filtration of solutions |
| 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes | Eppendorf, Germany | 30120086 | |
| petri dishes (polystyrene, sterile) | Carl Roth, Germany | TA19 | |
| Nile red | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | 72485 | |
| E. coli ΔproA strain | CGSC, Keio collection | JW0233-2 | proline-auxotrophic E. coli K-12 strain |
| E. coli B834(DE3) | Novagen (Merck), Germany | 69041 | methionine-auxotrophic E. coli B strain |
| λDE3 Lysogenization Kit | Novagen (Merck), Germany | 69734-3 | |
| Lactococcus lactis NZ9000 pNG nisPT | bacterial indicator strain, see Khusainov R & Kuipers OP, PLoS One, 8 (9), e74890 | ||
| benchtop centrifuge for 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes | Eppendorf, Germany | 5427 R | |
| peristaltic pump | GE Healthcare, UK | P1 | |
| FPLC system | GE Healthcare, UK | Äkta Purifier 10 or the like | |
| inverted microscope | Nikon | TI Eclipse wide-field fluorescence microscope with 100x (N.A. 1.4) objective and Mercury Lamp | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| electron multiplying CCD (EMCCD) camera | Andor Technologies, UK | Andor Luca | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| fluorescence excitation filter | Thorlabs, USA | Dichroic cube (TLV-U-MF2-TRITC) | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| fluorescence emission filter | AHF Analysentechnik, Germany | T 560 LPXR | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| cover slip 24 x 60 mm | Carl Roth, Germany | LH26.1 | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| Immersion Oil | Carl Zeiss, Germany | Immersol 518 F | example setup for fluorescence microscopy |
| probe sonicator | Bandelin, Germany | Sonopuls HD3200 with sonotrode MS-72 | 200 W maximum HF output |
| C5 HPLC column (2.1×100 mm, 3 µm particle size) | Sigma-Aldrich, Germany | 567227-U | example setup for mass spectrometry |
| ESI-TOF coupled to HPLC system | Agilent, USA | Agilent 6530 Accurate Mass QTOF with 1260 HPLC | example setup for mass spectrometry |
References
- Ferri, M., Ranucci, E., Romagnoli, P., Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 57 (13), 2857-2876 (2017).
- Bahar, A. A., Ren, D. Antimicrobial peptides. Pharmaceuticals. 6 (12), 1543-1575 (2013).
- Ageitos, J. M., Sánchez-Pérez, A., Calo-Mata, P., Villa, T. G. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): Ancient compounds that represent novel weapons in the fight against bacteria. Biochem Pharmacol. 133, 117-138 (2017).
- Arnison, P. G., et al. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat Prod Rep. 30 (1), 108-160 (2013).
- Lubelski, J., Rink, R., Khusainov, R., Moll, G. N., Kuipers, O. P. Biosynthesis, immunity, regulation, mode of action and engineering of the model lantibiotic nisin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65 (3), 455-476 (2008).
- Shin, J. M., Gwak, J. W., Kamarajan, P., Fenno, J. C., Rickard, A. H., Kapila, Y. L. Biomedical applications of nisin. J Appl Microbiol. 120 (6), 1449-1465 (2016).
- Scherer, K. M., Spille, J. -. H., Sahl, H. -. G., Grein, F., Kubitscheck, U. The lantibiotic nisin induces lipid II aggregation, causing membrane instability and vesicle budding. Biophys J. 108 (5), 1114-1124 (2015).
- Jung, G. Lantibiotica – ribosomal synthetisierte Polypeptidwirkstoffe mit Sulfidbrücken und α,β-Didehydroaminosäuren. Angew Chemie. 103 (9), 1067-1084 (1991).
- Rink, R., et al. Lantibiotic structures as guidelines for the design of peptides that can be modified by lantibiotic enzymes. 生物化学. 44 (24), 8873-8882 (2005).
- Lagedroste, M., Smits, S. H. J., Schmitt, L. Substrate Specificity of the Secreted Nisin Leader Peptidase NisP. 生物化学. 56 (30), 4005-4014 (2017).
- Ross, A. C., Liu, H., Pattabiraman, V. R., Vederas, J. C. Synthesis of the lantibiotic lactocin S using peptide cyclizations on solid phase. J Am Chem Soc. 132 (2), 462-463 (2010).
- Fukase, K., et al. Synthetic Study on Peptide Antibiotic Nisin. V. Total Synthesis of Nisin. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 65 (8), 2227-2240 (1992).
- Dumas, A., Lercher, L., Spicer, C. D., Davis, B. G. Designing logical codon reassignment – Expanding the chemistry in biology. Chem Sci. 6 (1), 50-69 (2015).
- Kuthning, A., Durkin, P., Oehm, S., Hoesl, M. G., Budisa, N., Süssmuth, R. D. Towards Biocontained Cell Factories: An Evolutionarily Adapted Escherichia coli Strain Produces a New-to-nature Bioactive Lantibiotic Containing Thienopyrrole-Alanine. Sci Rep. 6, 33447 (2016).
- Piscotta, F. J., Tharp, J. M., Liu, W. R., Link, A. J. Expanding the chemical diversity of lasso peptide MccJ25 with genetically encoded noncanonical amino acids. Chem Commun (Camb). 51 (2), 409-412 (2015).
- Hartman, M. C. T., Josephson, K., Lin, C. -. W., Szostak, J. W. An expanded set of amino acid analogs for the ribosomal translation of unnatural peptides. PLoS One. 2 (10), 972 (2007).
- Johnson, J. A., Lu, Y. Y., Van Deventer, J. A., Tirrell, D. A. Residue-specific incorporation of non-canonical amino acids into proteins: recent developments and applications. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 14 (6), 774-780 (2010).
- Ibba, M., Söll, D. Aminoacyl-tRNAs: setting the limits of the genetic code. Genes Dev. 18 (7), 731-738 (2004).
- Studier, F. W., Moffatt, B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 189 (1), 113-130 (1986).
- Budisa, N., Steipe, B., Demange, P., Eckerskorn, C., Kellermann, J., Huber, R. High-level biosynthetic substitution of methionine in proteins by its analogs 2-aminohexanoic acid, selenomethionine, telluromethionine and ethionine in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 230 (2), 788-796 (1995).
- Rink, R., et al. Dissection and modulation of the four distinct activities of nisin by mutagenesis of rings A and B and by C-terminal truncation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 73 (18), 5809-5816 (2007).
- Kubyshkin, V., Durkin, P., Budisa, N. Energetic contribution to both acidity and conformational stability in peptide models. New J Chem. 40 (6), 5209-5220 (2016).
- Molloy, E. M., Field, D., O’Connor, P. M., Cotter, P. D., Hill, C., Ross, R. P. Saturation mutagenesis of lysine 12 leads to the identification of derivatives of nisin A with enhanced antimicrobial activity. PLoS One. 8 (3), 58530 (2013).
- Wang, L., Brock, A., Herberich, B., Schultz, P. G. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science. 292 (5516), 498-500 (2001).
- Liu, C. C., Schultz, P. G. Adding new chemistries to the genetic code. Annu Rev Biochem. 79, 413-444 (2010).
- Anderson, J. C., Wu, N., Santoro, S. W., Lakshman, V., King, D. S., Schultz, P. G. An expanded genetic code with a functional quadruplet codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (20), 7566-7571 (2004).
- Zambaldo, C., Luo, X., Mehta, A. P., Schultz, P. G. Recombinant macrocyclic lanthipeptides incorporating non-canonical amino acids. J Am Chem Soc. 139 (34), 11646-11649 (2017).
- Al Toma, R. S., et al. Site-directed and global incorporation of orthogonal and isostructural noncanonical amino acids into the ribosomal lasso peptide capistruin. Chembiochem. 16 (3), 503-509 (2015).
- Chatterjee, A., Xiao, H., Schultz, P. G. Evolution of multiple, mutually orthogonal prolyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pairs for unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109 (37), 14841-14846 (2012).
- Budisa, N., Pal, P. P. Designing novel spectral classes of proteins with a tryptophan-expanded genetic code. Biol Chem. 385 (10), 893-904 (2004).
- Voller, J. -. s., Thi To, T. M., Biava, H., Koksch, B., Budisa, N. Global substitution of hemeproteins with noncanonical amino acids in Escherichia coli with intact cofactor maturation machinery. Enzyme Microb Technol. 106, 55-59 (2017).
- Moghal, A., Hwang, L., Faull, K., Ibba, M. Multiple Quality Control Pathways Limit Non-protein Amino Acid Use by Yeast Cytoplasmic Phenylalanyl-tRNA Synthetase. J Biol Chem. 291 (30), 15796-15805 (2016).
- Datsenko, K. A., Wanner, B. L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 97 (12), 6640-6645 (2000).
- Engelke, G., Gutowski-Eckel, Z., Hammelmann, M., Entian, K. D. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic nisin: genomic organization and membrane localization of the NisB protein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 58 (11), 3730-3743 (1992).
- Baumann, T., Nickling, J. H., Bartholomae, M., Buivydas, A., Kuipers, O. P., Budisa, N. Prospects of In vivo Incorporation of Non-canonical Amino Acids for the Chemical Diversification of Antimicrobial Peptides. Front Microbiol. 8, 124 (2017).
- Plat, A., Kluskens, L. D., Kuipers, A., Rink, R., Moll, G. N. Requirements of the engineered leader peptide of nisin for inducing modification, export, and cleavage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 77 (2), 604-611 (2011).
- JoVE Science Education Database. Basic Methods in Cellular and Molecular Biology. Bacterial Transformation: The Heat Shock Method. J Vis Exp. , (2017).
- JoVE Science Education Database. Basic Methods in Cellular and Molecular Biology. Bacterial Transformation: Electroporation. J Vis Exp. , (2017).
- Shi, Y., Yang, X., Garg, N., van der Donk, W. A. Production of lantipeptides in Escherichia coli. J Am Chem Soc. 133 (8), 2338-2341 (2011).
- Hochuli, E., Bannwarth, W., Döbeli, H., Gentz, R., Stüber, D. Genetic Approach to Facilitate Purification of Recombinant Proteins with a Novel Metal Chelate Adsorbent. Nat Biotechnol. 6 (11), 1321-1325 (1988).
- Zhang, Z., Marshall, A. G. A universal algorithm for fast and automated charge state deconvolution of electrospray mass-to-charge ratio spectra. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 9 (3), 225-233 (1998).
- JoVE Science Education Database. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). J Vis Exp. , (2017).
- JoVE Science Education Database. Dialysis: Diffusion Based Separation. J Vis Exp. , (2017).
- Khusainov, R., Kuipers, O. P. The presence of modifiable residues in the core peptide part of precursor nisin is not crucial for precursor nisin interactions with NisB- and NisC. PLoS One. 8 (9), 74890 (2013).
- Terzaghi, B. E., Sandine, W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 29 (6), 807-813 (1975).
- Schindelin, J., Rueden, C. T., Hiner, M. C., Eliceiri, K. W. The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol Reprod Dev. 82 (7-8), 518-529 (2015).
- . Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2006 (1), (2006).
- van Hest, J. C. M., Tirrell, D. A. Efficient introduction of alkene functionality into proteins in vivo. Febs Lett. 428 (1-2), 68-70 (1998).
- Prince, A., et al. Lipid-II Independent Antimicrobial Mechanism of Nisin Depends On Its Crowding And Degree Of Oligomerization. Sci Rep. 6 (1), 37908 (2016).
- Zhou, L., et al. Incorporation of tryptophan analogues into the lantibiotic nisin. Amino Acids. 48 (5), 1309-1318 (2016).
- Presolski, S. I., Hong, V. P., Finn, M. G. Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry for Bioconjugation. Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 3 (4), 153-162 (2011).
- Abts, A., et al. Easy and rapid purification of highly active nisin. Int J Pept. 2011, 175145 (2011).
- Francklyn, C. S., First, E. A., Perona, J. J., Hou, Y. -. M. Methods for kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Methods. 44 (2), 100-118 (2008).
- van Heel, A. J., et al. Production and Modification of Five Novel Lantibiotics Using the Promiscuous Nisin Modification Machinery. ACS Synth Biol. 5 (10), 1146-1154 (2016).
- Wiegand, I., Hilpert, K., Hancock, R. E. W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc. 3 (2), 163-175 (2008).

