Intra-prostatic Injection of Cancer Cells: A Technique to Deliver Cancer Cells for Establishing Orthotopic Prostate Cancer Mouse Model
Abstract
Source: Anker, J. F. et al. Bioluminescent and Fluorescent Orthotopic Syngeneic Murine Model of Androgen-dependent and Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Vis. Exp. (2018)
In this video, we demonstrate the procedure for administering intra-prostatic injection of prostate cancer cells into a mouse model. Orthotopic murine models can be used to study the disease origin and response to treatment therapies in a non-invasive and clinically relevant environment.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Pre-operative Mouse Preparation
NOTE: House mice in the university animal facility for at least one week before surgery to allow for adequate adaptation and minimize animal stress. Steps 1.1-1.6 are performed by the surgeon’s assistant. All subsequent surgical steps are performed by the surgeon using sterile gloves and surgical tools with sterile technique.
- Anesthetize the mice with isoflurane (2-5% for induction via chamber, 1-3% for maintenance via nose cone). Verify full induction by the loss of toe pinch reflex.
- Weigh the mice and administer at least 0.05 mg/kg of the analgesic buprenorphine s.c.
NOTE: Mouse weight ≥20 g is ideal for successful intra-prostatic injections. - Apply ophthalmic ointment lubrication to both eyes to prevent corneal drying.
- Shave all fur from the abdomen.
- Sterilize the abdomen by three rounds of circular application of surgical scrub using sterile non-adhering pads followed by sterile alcohol wipes. Allow the abdomen to dry.
NOTE: For the rest of the surgical procedure, only sterile gloves and surgical instruments must be used to contact the sterilized mouse abdomen. - Transfer the mouse supine onto a clean surface on a heating pad directly under the objective of a clean surgical microscope.
- Cover the mouse with a sterile drape with a small hole cut over the abdomen.
2. Intra-prostatic Injection
NOTE: Perform all surgical steps under sterile conditions. Adjusting the microscope, the mouse placement, or any other non-sterile object must be done with additional assistance.
- Perform an approximately 1 cm incision of the outer skin along the midline of the abdomen superior to the penis and the preputial glands (Figure 1D).
- Separate the connective tissue between the outer abdominal skin and the inner abdominal musculature by opening the scissors between the layers.
- Perform a similar incision on the inner abdominal muscles, using forceps to raise the muscles to avoid puncturing the intestines or bladder (Figure 1D).
- Locate one of the bilateral seminal vesicles (Figure 1A, white)/anterior prostate lobes (Figure 1A, black), which are often posterior, lateral, and slightly superior to the bladder (Figure 1A, yellow), but this may vary between mice. The anterior prostate lobes are translucent and attached to the lesser curvature of the white seminal vesicles.
- Gently raise the tip of the seminal vesicle using the Graefe tissue forceps to create tension on the tissue without puncturing the seminal vesicle (Figure 1E).
- Mix the Myc-CaP matrigel solution by gentile pipetting (performed by the surgeon assistant), as cells may have pelleted, and slowly aspirate 30 µL (1×106 cells) into the needle to avoid air bubbles.
- Carefully insert the bevel of the needle parallel to the long axis of the anterior prostate lobe. Slowly inject 30 µL into the lobe and then slowly retract the needle to prevent leakage (Figure 1F). Verify adequate injection by engorgement of the anterior prostate lobe (Figure 1G).
- Carefully hold the seminal vesicle and the prostate lobe outside of the mouse for approximately 30 s to allow the matrigel to partially solidify within the lobe. During this time, collect any cell solution leakage in the abdomen using a sterile polyester-tipped applicator to prevent non-orthotopic tumor development without pressing on the injected prostate lobe.
- Carefully return the seminal vesicle and the injected prostate lobe into the abdomen without putting pressure on the lobe. Replace any externalized tissues.
- Perform continuous sutures to close the inner abdominal muscles with 5-0 vicryl absorbable reverse cutting needle sutures.
- Perform interrupted sutures to close the outer abdominal skin with 4-0 nylon monofilament non-absorbable reverse cutting needle sutures. NOTE: Sterilized 9 mm staples can also be used to close the outer abdominal skin. However, in contrast to sutures, they interfere with any subsequent bioluminescent and fluorescent tumor imaging signal.
- Clean all tools with sterile ethanol wipes (opened by the surgeon's assistant) and place them in a glass bead sterilizer for 30 s. Allow the tools to dry before use on the next mouse.
- Flush the syringe and needle in sterile saline (opened by the surgeon's assistant) to prevent clogging by remnant matrigel.
NOTE: A surgeon assistant should be present for all operations, performing all non-sterile pre-operative mouse preparation and post-operative mouse care, as well as mixing the Myc-CaP matrigel solution before injections. To minimize time, as each intra-prostatic mouse procedure will require 20-30 min, the surgeon assistant can begin preparing the next mouse as the surgeon is suturing the current mouse.
3. Post-operative Mouse Care
- Administer 1 mg/kg of the analgesic meloxicam s.c. immediately, 24 h, and 48 h after surgery.
- Allow mice to recover in a cage with no bedding placed halfway on a heating pad. Monitor mice for at least 30 min after surgery until they regain normal mobility and activity, after which place them in a clean cage with food on the floor of the cage.
- Further monitor mice daily for proper wound healing, body weight, grooming, and ambulation after surgery. Separate mice into individual cages upon any evidence of fighting.
- Remove any remaining sutures within 14 days after surgery.
Representative Results
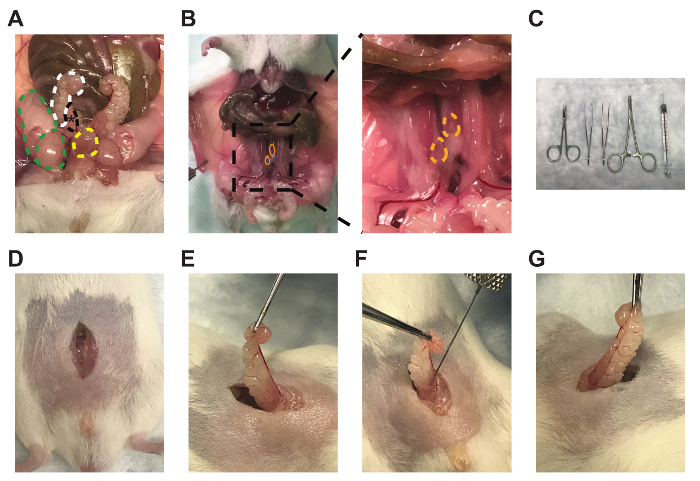
Figure 1: Anterior prostate lobe, draining lymph nodes, and representative technique for intra-prostatic cell injections. Images of the (A) right anterior prostate lobe (black, *), attached right seminal vesicle (white), right testicle and fat pad (green), and bladder (yellow), (B) bilateral prostate-draining para-aortic lymph nodes (orange), (C) micro-dissecting scissors, Graefe forceps, Graefe tissue forceps, a needle holder with suture cutters, and 50 µL syringe with a 28 gauge needle (left to right), (D) midline incisions, (E) seminal vesicle and anterior prostate lobe externalization, (F) intra-prostatic injection, and (G) engorgement of the anterior prostate lobe.
Açıklamalar
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Myc-CaP cell line | ATCC | CRL-3255 | Verify as mycoplasma-free before use |
| Micro-dissecting scissors | Roboz | RS-5910 | |
| Graege forceps | Roboz | RS-5135 | |
| Graefe tissue forceps | Roboz | RS-5150 | |
| Olsen-Hegar needle holder with suture cutters |
FST | 12002-12 | |
| 50 µL Syringe 705 RN SYR | Hamilton | 7637-01 | Sterilize by ethylene oxide gas |
| 28-gauge Needles Small Hub RN H | Hamilton | 7803-02 | Point style 4, Angle 45°, Length 0.75 in. Sterilized by ethylene oxide gas |
| RPMI | Gibco | 18875-093 | |
| FBS | Gibco | 10437-028 | |
| Pencillin/Streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| PBS | Gibco | 14190-144 | |
| Matrigel basement membrane matrix, phenol red-free, LDEV-free |
Corning | 356237 | Thaw on ice in 4°C overnight before use |
| Isoflurane | Henry Schein | 11695-0500-2 | Acquired from Northwestern University Center for Comparative Medicine (CCM) |
| Buprenorphine hyrochloride 0.3 mg/mL |
12496-0757-5 | Controlled substance, acquired from Northwestern University CCM |
|
| 26 5/8-gauge syringe | BD | 309597 | For meloxicam and buprenorphine injections |
| Ophthalmic ointment lubrication | Akron | 17478-162-35 | |
| Betadine surgical scrub (povidoneiodine, 7.5%) | Purdue Products | 67618-151-16 | |
| Sterile non-adhering pads | Moore Medical | 10775 | |
| Sterile alcohol wipes | Fisher Scientific | 22-363-750 | |
| Surgical microscope Stemi DV4 | Zeiss | ||
| Sterile polyester tipped applicators | Puritan | 25-806 1PD | |
| 5-0 vicryl absorbable reverse cutting needle sutures | eSutures | J493G | |
| 4-0 nylon monfilament nonabsorbable reverse cutting needle sutures | eSutures | 699H | |
| Glass bead sterilizer | Fine Science Tools | 18000-45 | |
| Sterile saline 0.9% sodium chloride | Hospira | 0409-4888-02 |

