In Vivo Measurement of the Compound Muscle Action Potential in a Rat
Abstract
Source: Wild, B. M., et al. In Vivo Electrophysiological Measurement of the Rat Ulnar Nerve with Axonal Excitability Testing. J. Vis. Exp. (2018)
This video demonstrates the procedure for recording compound muscle action potential (CMAP) in rats by applying electrical stimuli to the ulnar nerve, adjusting electrodes for optimal signal, and increasing stimulation to assess nerve functionality. This method enables the in vivo investigation of the peripheral nerve functions in neurological disorders.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Experimental Set Up
NOTE: 12-week-old female Long-Evans rats were used in this procedure.
- Anesthetize the rat in an induction chamber using 4% isoflurane and 1 L per min oxygen (O2) flow rate. Confirm sufficient anesthesia by testing for the righting reflex and ensuring its absence before removing the animal from the induction chamber. Note that various anesthetic agents have differential effects on nerve excitability.
- Securely place the animal's snout in the nose cone attachment and deliver a maintenance dose of 2.5% isoflurane and 1 L per min O2 flow rate.
- Confirm adequate anesthesia by checking for both pedal withdrawal and corneal reflexes by pinching the animal's toes and gently touching its eye.
NOTE: Application of vet ointment on eyes, to prevent dryness while under anesthesia, is recommended but not essential as the procedure typically takes 30 min per animal. - Maintain the body temperature of the rat at 37 °C with the use of a feedback-controlled heating mat and a rectal thermometer probe. Set the heating mat and integrated body temperature sensor to 40 °C to prevent any skin damage that occurs with higher temperatures.
NOTE: It is recommended to monitor and record physiological measures (heart rate, oxygen saturation, body temperature and respiratory rate) every 10s with the use of an animal physiological monitoring system. Optimal recording procedures should include local measurement of the limb temperature as the peripheral temperature can be colder than that of the core temperature (Figure 1). - Wear antiseptic gloves and always use instruments that have been cleaned with 70% ethanol, to maintain a pathogen-free environment throughout the procedure.
2. Electrophysiological Set Up
- Use low impedance platinum electroencephalogram (EEG) needle electrodes for this procedure.
- Prepare the recording needle electrodes by inserting the recording needle electrode (Figure 1; indicated in purple) through the hypothenar muscle and the reference electrode through the dorsal aspect of the 4th digit (Figure 1; indicated in orange) to record compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs).
- Place the ground electrode through the skin on the superior aspect of the forearm between stimulating and recording electrodes (Figure 1; indicated in green). Take care when inserting the electrodes to avoid muscle tissue.
- Prepare the percutaneous stimulating needle electrodes by inserting the cathode (Figure 1; labeled in blue) approximately 4 mm distal to the cubital tunnel at the elbow. Insert the anode (Figure 1; labeled in red) approximately 1 cm proximally through the skin of the axillar region.
3. Axonal Excitability Procedures
- Perform the rodent motor nerve TRONDNF protocol using a semi-automated, computer controlled axonal excitability program (see the Table of Materials) linked to a constant current stimulator and an amplifier. Remove excess 50 Hz electrical noise using a 50/60 Hz noise eliminator.
- Record the CMAP from the hypothenar muscle by simultaneously visualizing the CMAP morphology and applying a 1 ms square-wave pulse to the ulnar nerve with the cathode needle electrode.
- To achieve optimal recordings, carefully adjust the angle and/or position of the cathode until an optimal biphasic response curve with constant amplitude is achieved (Figure 2A.). Once the optimal position has been determined, stabilize the cathode with a repositionable electrode holder.
NOTE: The software used automatically delivers the test stimuli described below and increases or decreases the current required to achieve the threshold.
- To achieve optimal recordings, carefully adjust the angle and/or position of the cathode until an optimal biphasic response curve with constant amplitude is achieved (Figure 2A.). Once the optimal position has been determined, stabilize the cathode with a repositionable electrode holder.
- Record a stimulus-response curve by incrementally increasing the stimulus intensity of a 1 ms impulse by 1 mA until a maximum response is achieved.
NOTE: The purple and green line in Figures 2B and 2C represents the incremental increase of the stimulus intensity and the automated system, respectively. The target amplitude for threshold tracking is automatically set to 40% of the maximal amplitude corresponding to the area of the steepest slope on the stimulus-response curve. The change in 'threshold' (i.e. stimulus required to elicit 40% CMAP) induced by various test stimuli is the variable obtained throughout the remainder of the protocol.
- Record the CMAP from the hypothenar muscle by simultaneously visualizing the CMAP morphology and applying a 1 ms square-wave pulse to the ulnar nerve with the cathode needle electrode.
Representative Results
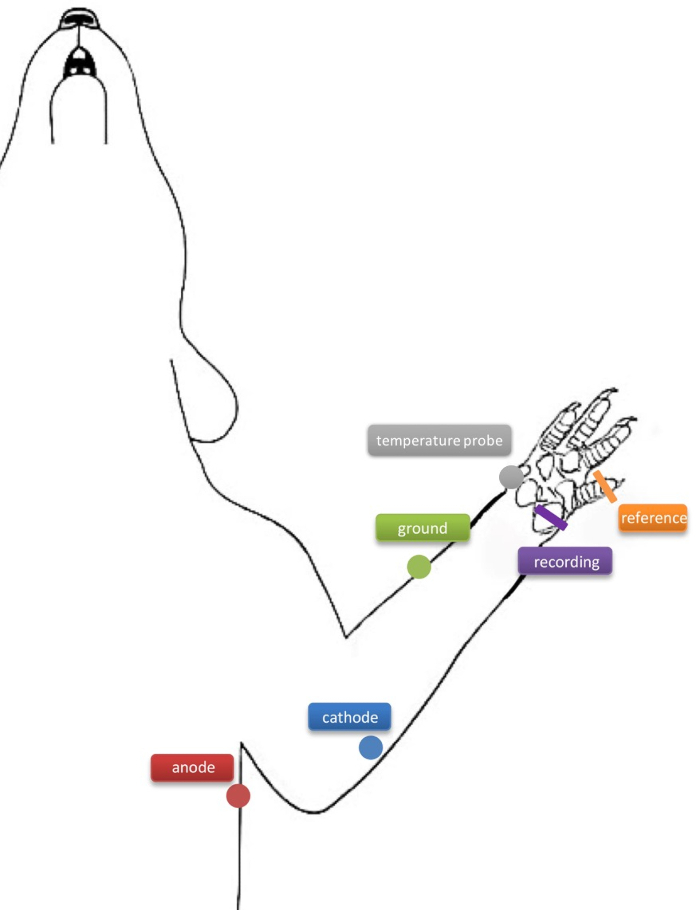
Figure 1: A schematic diagram of the needle electrode placements in the rat forelimb. The cathode (blue) is inserted approximately 4 mm distal to the cubital tunnel at the elbow, and the anode (red) is inserted approximately 1 cm proximally through the skin of the axillar region. The ground needle electrode (green) is inserted through the skin on the superior aspect of the forearm between stimulating and recording electrodes. The recording (purple) and reference (orange) needle electrodes are inserted through the hypothenar muscle and through the dorsal aspect of the 4th digit. The temperature probe (grey) is placed on the superior aspect of the thenar muscle.
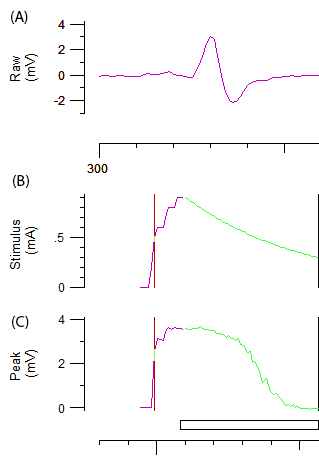
Figure 2: Raw data from an axonal excitability test. Panel A demonstrates a biphasic CMAP response curve after an incremental increase of stimulation to the ulnar nerve. Panels B and C represent the stimulus intensity (mA) and amplitude of CMAP (mV), respectively. The green components of B and C depict the automated incremental decrease in stimulus intensity and the associated sigmoid-shaped decrease in CMAP required for threshold tracking.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| QTracS Program | Digitimer Ltd. | Axonal excitability program | |
| AM-Systems 2200, Analog Stimulus Isolator, 2200V/50Hz | SDR Scientific | 850005 | Stimulator |
| High Performance AC Amplifier Model LP511 | Grass Technologies | Amplifier | |
| Humbug 50/60Hz Noise eliminator | Quest Scientific Instruments | 726310 | Noise eliminator |
| Low Impedance Platinum Monopolar Subdermal Needle Electrodes | Grass Technologies | F-E2-24 | Recording electrodes, 10 mm length, 30 gauge |
| Low Impedance Platinum Electroencephalography Needle Electrodes | Cephalon | 9013L0702 | Stimulating electrodes, 10 mm length, 30 gauge |
| Multifunction I/O Device Model USB-6341 | National Instruments | Multifunction input/output device | |
| Iron Base Plate IP | Narishige Scientific Instrument Laboratory | Used for holding stimulating needle electrode in place | |
| Rotating X-block X-4 | Narishige Scientific Instrument Laboratory | Used for holding stimulating needle electrode in place | |
| Magnetic Stand GJ-8 | Narishige Scientific Instrument Laboratory | Used for holding stimulating needle electrode in place | |
| Micromanipulator M-3333 | Narishige Scientific Instrument Laboratory | Used for holding stimulating needle electrode in place |

