Differentiation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Neural Progenitor Cells
Abstract
Source: Phillips, A. W., et al. Developing HiPSC Derived Serum Free Embryoid Bodies for the Interrogation of 3-D Stem Cell Cultures Using Physiologically Relevant Assays. J. Vis. Exp. (2017).
The video demonstrates a technique for differentiating human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) into neural progenitor cells (NPCs). Initially, the hiPSCs are cultured on a feeder layer of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Subsequently, the cells are detached and transferred to a biopolymer-coated plate to allow the MEFs to adhere to and separate from the hiPSCs. The suspended hiPSCs are then transferred to a V-bottom plate and centrifuged to form aggregates. Finally, the addition of a differentiation medium induces the differentiation of hiPSCs within the aggregate into NPCs.
Protocol
1. Generation of Neural Progenitor Cells
- Maintain hiPSCs derived from fibroblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in 6-well plates on a γ-irradiated mouse embryonic feeder (MEF) cell layer in human iPSC medium supplemented with small-molecules.
NOTE: Daily maintenance is a modified version of previously reported procedures.- Plate 6 x 105 MEFs onto each well of a 6-well tissue culture grade plate in 300 μL/well recommended medium (following manufacturer's protocol).
- After 48 h, replace MEFs medium with 300 μL/well hiPSC medium for 1 h before adding hiPSCs.
- Quickly thaw hiPSCs in a 37 °C water bath and slowly add 1 mL hiPSC medium dropwise. Transfer the hiPSCs and medium to a 15 mL conical tube. Add medium to bring the total volume to 5 mL. Centrifuge for 4 min at 129 x g, aspirate the supernatant, gently resuspend the pellet in 1 mL hiPSC medium with Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor at 1:1,000 concentration.
- Plate the cell suspension (typically seeded at 300,000 cells/well) onto the MEF cell layer and incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2, 95% humidity.
- Monitor iPSC culture closely using a light microscope. After 48 h, remove cultures that have uneven edges, have grown to become cystic-like or appear yellowish-brown under the light microscope to minimize spontaneous differentiation.
NOTE: After 7 – 10 days, hiPSC colonies should form. Colonies should be round, with clearly defined borders and uniform cell densities, and devoid of loosely packed non-uniform cells. - Manually select round hiPSC colonies to clear the culture of spontaneously differentiated cells. Expand the colonies by placing them on fresh MEF layers. Expand 1:3 every 7 days when cultures near confluency and freeze.
- After expansion and freezing cells (for backup), grow hiPSC colonies on plates until they reach 50 – 75% confluence.
- Seven-days post plating, use mild enzymatic treatment (5-10 min with 300 μL of enzyme solution) and gentle trituration (2-4 times with a 1,000 µL pipet) to harvest and prepare hiPSCs for neural precursor cell differentiation.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension at 129 x g for 4 min, aspirate the supernatant, and resuspend the pellet in 5 mL human iPSC medium. Transfer the cell suspension to a 0.1% gelatin coated 5 cm cell culture dish for 1 h at 37 °C to eliminate MEFs and to maximize the hiPSC yield. Transfer the medium (with non-adherent cells) to another 5 cm gelatin coated dish.
- Transfer the non-adherent cells to a 15 mL centrifuge tube using a transfer pipet. Gently rinse the plates with 3 mL medium and add it to the 15 mL tube.
- Centrifuge the cell suspension at 129 x g for 4 min, aspirate the supernatant, and gently resuspend the pellet in medium. Determine the cell count using an automated cell counter. Plate 9,000 cells/well in a 96-well low-adhesion V-bottom plate.
- Centrifuge the plate at 163 x g for 3 min. Incubate the plate at 37 °C, 95% humidity and 5% CO2. Using a pipette, change 50% medium every other day by removing half of the medium and replacing it with fresh chemically-defined differentiating medium 1 (DM1; Figure 1; Table of Materials) for 14 days.
Representative Results
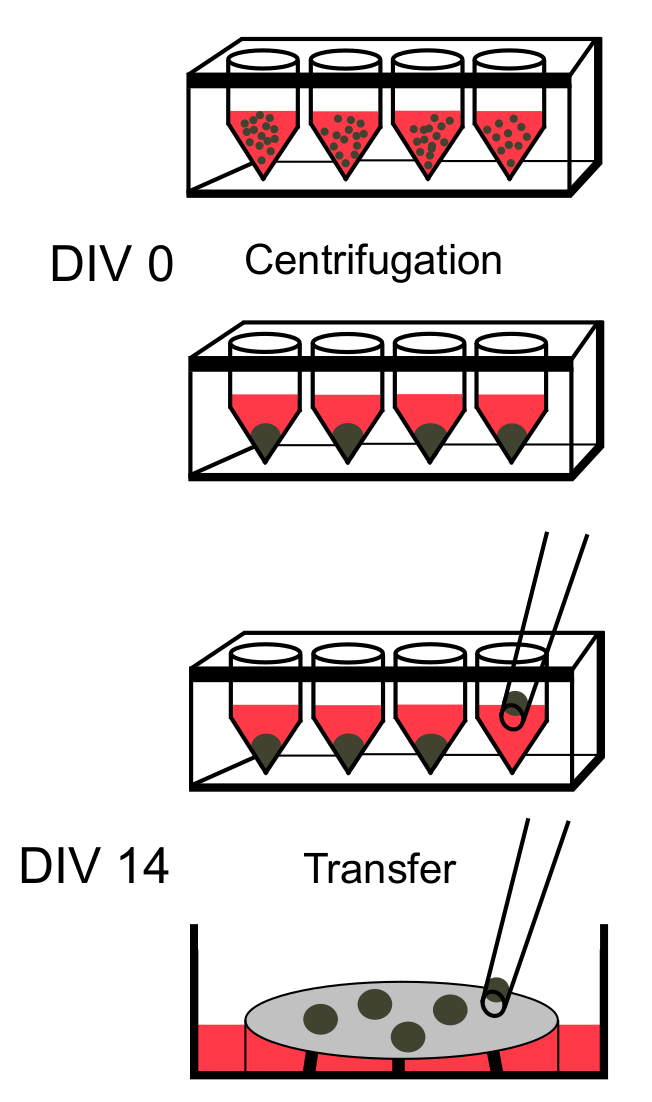
Figure 1: Schematic Outlining the Early Steps in Preparing SFEBs. After iPSCs have been harvested using an enzymatic dissociation, they are plated in 96-well plates and centrifuged at 163 x g for 3 min to induce quick aggregation. After 14 days in vitro (DIV) cell aggregates can be transferred from 96-well plates via wide-bore pipets onto cell culture insert-containing 6-well plates.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| SFEB Neuronal Differentiation Cell culture Media. Reagents. Components | |||
| STEMdiff Neural Induction Medium (hiPSC Media) | STEMCELL Technologies | 0-5835 | 250ml |
| PluriQ ES-DMEM Medium (MEF Media) | GlobalStem | GSM-2001 | |
| DM1 Media Components | |||
| D-MEM/F-12 (1X), Glutamax liquid, 1:1 | Invitrogen | 10565018 | 385ml |
| Knockout Serum Replacement | Invitrogen | 10828028 | 20% 100ml |
| Pen/Strep | Invitrogen | 15140122 | 5ml |
| Glutamax 200mM | Invitrogen | 35050061 | 5ml |
| MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution 10 mM (100X), liquid | Invitrogen | 11140050 | 5ml |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol (1,000X), liquid | Invitrogen | 21985023 | 900ul |
| Small Molecules | |||
| Y27632 (ROCKi) | Stemgent | 04-0012-10 | 10uM |
| Components/Materials | |||
| Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts | GlobalStem | GSC-6301G | |
| 96 well V bottom w/Lids | Evergreen | 222-8031-01V | |
| StemPro Accutase Cell Dissociation Reagent | ThermoFisher | A1110501 | |
| 6 well flat bottom | Falcon | 353046 |

