Ex Vivo Culture and Imaging of Oculomotor Slices from Transgenic Mouse Embryos
Abstract
Source: Whitman, M. C., et al. Ex Vivo Oculomotor Slice Culture from Embryonic GFP-Expressing Mice for Time-Lapse Imaging of Oculomotor Nerve Outgrowth. J. Vis. Exp. (2019)
This video demonstrates the ex vivo culture and imaging of oculomotor slices from transgenic mouse embryos. The embryos are isolated and embedded in agarose. Using a vibratome, slices containing the oculomotor nuclei and eyes are obtained. The slices are maintained in culture and imaged using a fluorescence microscope.
Protocol
All animal model procedures have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board has reviewed all animal model procedures.
1. Timed matings
- Place ISLMN:GFP (Islet Motor Neuron Green Fluorescent Protein; MGI: J:132726; Jax Tg(Isl-EGFP*)1Slp/J Stock No: 017952) male and female mice together overnight. Weigh the females and record weights prior to mating.
NOTE: ISLMN:GFP specifically labels motor neurons with a farnesylated GFP that is not cytotoxic, localizes to the cell membrane of motor neurons and their axons, and allows the nerves to be visualized during development. Other fluorescently labeled lines could also be used. - Check for vaginal plugs in early morning. The date a plug is identified is designated as E0.5.
- Confirm pregnancy using weight gain and/or ultrasound at embryonic day 10.5 (E10.5). Pregnant dams should have gained at least 1 g. Embryos can be seen on ultrasound at E10.5.
2. Preparation of reagents and vibratome for slice culture
- Prepare 500 mL of slicing buffer: add 5 mL of HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) and 5 mL of penicillin/streptomycin to 500 mL of Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) without Ca2+ and Mg2+. Chill to 4 °C.
NOTE: Extra slicing buffer should be stored at 4 °C and can be used for future slice culture experiments. - Prepare 50 mL of culture media: In a sterile hood, add 12.5 mL of HBSS, 12.5 mL of fetal bovine serum (FBS), 250 µL of glucose, 250 µL of L-glutamine, 125 µL of HEPES to 24.4 mL of Fluorobright DMEM (Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium). (Final concentrations: FlouroBright DMEM with 25% HBSS, 25% FBS, 0.5% glucose, 1 mM glutamine, and 2.5 mM HEPES.). Warm the culture media to 37 °C in a sterile water bath.
NOTE: Culture media can be stored at 4 °C for up to 3 weeks.- In a sterile hood, add 1.5 mL of culture media to each well of a 6-well plate. Add a cell culture insert (Table of Materials) to each well. Place in a sterile 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator.
- Prepare 4% low-melting temperature agarose: dissolve 2 g of low-melting temperature agarose in 50 mL of sterile PBS. Microwave in 30-60 s intervals until fully dissolved. Place in a 40 °C water bath to keep liquid.
NOTE: Extra agarose can be stored at room temperature (RT) and melted for future slice culture experiments. - Set up vibratome: Place a new blade on vibratome. Check settings: thickness 400-450 µm. Pre-chill the vibratome stage. Place some ice in the outer chamber. Use a chamber and stage dedicated to live slices. Do not use the same vibratome chamber for fixed tissue as residual fixative could be damaging to slices.
- Prepare the microscope stage top incubator to 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Prepare for dissection: Clean surgical instruments and spray with 70% ethanol. Fill two Petri dishes with HBSS, place on ice. Open a 12 well tissue culture plate and place the lid on ice with the underside facing up. Open a 6 well tissue culture plate and place cell culture membrane inserts and 1.5 mL cell culture media in each well. Pre-warm the plate in a 37 °C and 5% CO2 incubator.
3. Harvesting E10.5 embryos and preparing slices
NOTE: All steps from this point should be done as quickly as possible. Keep the embryos on ice at all times.
- Euthanize the pregnant dam (E10.5) in a CO2 chamber. Perform cervical dislocation.
- Spray the abdomen with 70% ethanol. Cut open the abdomen with scissors, remove the uterus and place it in a Petri dish with ice cold HBSS to quickly wash away blood. Move the washed uterus to a second Petri filled with dish ice cold HBSS.
- Under a dissecting scope, remove the embryos from the uterine horn and individual amniotic sacs. Place the embryos on the underside of the lid of a 12 well plate. Keep on ice.
- Under a dissecting scope, use filter paper to remove any liquid surrounding each embryo.
NOTE: Embryos will stick to the filter paper if touched. - Embed embryos in agarose. Pour melted agarose over each embryo to cover it. Keep on ice. As soon as the agarose has hardened, flip each embryo and pour additional agarose on the other side. Keep on ice.
- Using a fluorescent dissecting scope, trim the agarose around each embryo so it will be oriented properly when glued to the vibratome stage. The oculomotor nucleus and early axon outgrowth are fluorescent. Align the embryo so that the nucleus, outgrowing axons, and eye form a line, and trim the agarose with a razor blade cut parallel to this line (dorsal to the embryo, see Figure 1A).
NOTE: This will be the side glued to the vibratome stage (the embryo will be positioned on its back, head closest to the vibratome blade). A line between the oculomotor nucleus and eye should be parallel to the vibratome blade. - Fill the vibratome chamber with ice-cold slice buffer. Superglue the embryo to the vibratome stage so that the blade will be parallel with the oculomotor nucleus and eyes. Once the superglue is dry, submerge the vibratome stage so the embryo is oriented facing away from blade.
- Slice 400-450 µm slices. Collect each slice with a sterile transfer pipet. Place into cold slicing buffer.
- Under the dissecting scope, choose the slice containing the oculomotor nuclei and eyes. Using a sterile transfer pipet, place it on the cell culture insert in the 6 well plate. Return the plate to the 37 °C incubator. Alternatively, have one person slicing and another placing the slices. Minimize the time between slicing and placing into incubator.
NOTE: Slices should be oriented in a way that the maximum fluorescence emitted from the nuclei and axons is closest to the imaging microscope objective. On an inverted microscope, the slices should be placed on the membrane with the nuclei and axons closest to the objective underneath the plate. - Remove the residual agarose from the vibratome stage, superglue the next embryo to the stage and repeat steps 3.7-3.9 until all embryos have been sliced and plated.
- Add inhibitor or recombinant molecule of choice to media in each well to create a dose-response curve. Dilute in appropriate solvent.
NOTE: If using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), use only tissue culture grade DMSO. Alternatively, protein-eluting beads can be placed in specific locations on the slice. - Place on the microscope in the 37 °C and 5% CO2 chamber. Set the microscope to take phase contrast and fluorescent photographs of each slice every 30 min (or more often if desired). Slices can be maintained for 48-72 h.
Representative Results
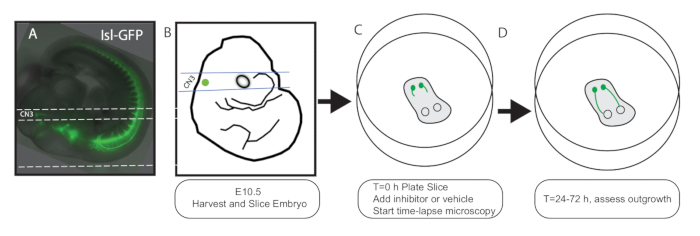
Figure 1: Schematic. E10.5 IslMN:GFP embryos (A: photo, B: schematic) are sliced on a vibratome (400-450 µm thick) so that sections include both the oculomotor nucleus and the orbit. Parallel dashed lines in A and B denote the location of the vibratome cuts. The lower dashed line in A shows where the agarose should be trimmed and glued to the vibratome stage. (C) Sections are laid flat on a tissue-culture membrane, allowing exchange of nutrients and gases, and placed in a stage-top incubator for time-lapse microscopy. At this stage, inhibitors can be added to the growth media. (D) Cultures can be maintained for 24-72 h, and the oculomotor axons can be seen growing to the eye.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 24-Well Tissue Culture Plate G | Genesee Scientific | 25-107 | |
| 6-Well Tissue Culture Plate | Genesee Scientific | 25-105 | |
| Disposable Pasteur Pipet (Flint Glass) | VWR | 14672-200 | |
| Fine Forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11412-11 | |
| Fluorobrite DMEM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A1896701 | |
| Glucose (200 g/L) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A2494001 | |
| Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (1X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 14175-095 | |
| Heat Inactivated Fetal Bovine Serum | Atlanta Biologicals | S11550H | |
| HEPES Buffer Solution (1M) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15630106 | |
| L-Glutamine (250 nM) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25030081 | |
| Loctite Superglue | Loctite | ||
| Low Melting Point Agarose | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 16520050 | |
| Millicell Cell Culture Insert (30mm, hydrophilic PTFE, 0.4 um) | Millipore Sigma | PICM03050 | |
| Moria Mini Perforated Spoon | Fine Science Tools | 10370-19 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin (10,000 U/ mL) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15140122 | |
| Petri Dish (100 x 15mm) | Genesee Scientific | 32-107G | |
| Phosphate Buffered Saline (1X, pH 7.4) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 10010049 | |
| Razor Blades | VWR | 55411-050 | |
| Surgical Scissors – Blunt | Fine Science Tools | 14000-12 | |
| Ti Eclipse Perfect Focus with TIRF | Nikon | ||
| Vibratome (VT 1200S) | Leica | 1491200S001 | |
| Vibratome Blades (Double Edge, Stainless Steel) | Ted Pella, Inc | 121-6 |

