Isolating Microglia from Mouse Brain Demyelinating Lesions Using Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting
Abstract
Source: Zhang, H. et al. Isolation of Mouse Primary Microglia by Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting in Animal Models of Demyelination. J. Vis. Exp. (2022).
This video demonstrates a protocol for extracting microglial cells from demyelinating lesions in mouse brains using magnetic cell sorting. The protocol involves dissecting the lesioned brain tissue containing microglial cells, treating the tissue with specific enzymes to obtain a single-cell suspension, and utilizing microglial receptor-specific magnetic beads to isolate the microglial cells.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal samples have been reviewed and approved by the appropriate animal ethical review committee.
1. Materials
- Prepare the following solutions before beginning the protocol:
- Prepare the loading buffer by adding fetal bovine serum (FBS, 2%) to phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
- Add neutral red (NR) dye (final 1%) to PBS.
- Prepare the following solutions using the commercially available Adult Brain Dissociation Kit (see the Table of Materials).
- To prepare enzyme mix 1, pipette 1.9 mL of Buffer Z and 50 μL of Enzyme P into a 15 mL centrifuge tube.
- To prepare enzyme mix 2, pipette 20 μL of Buffer Y and 10 μL of Enzyme A into a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube.
- Prepare the debris removal solution.
2. Mice perfusion and dissection
- Intraperitoneally (i.p.) inject the mouse with 500 μL of 1% NR dye in PBS 2-3 h before anesthesia.
NOTE: Intraperitoneal injection of NR in demyelinating mouse models helps discern the lesions (Figure 1). - Anesthetize the mouse with pentobarbital (50 mg/kg, i.p.), and ensure that the mouse is successfully anesthetized by examining the pain responses.
- Open the thoracic cavity of the mouse and expose the heart.
- Carefully cut off a small corner of the right atrium and intracardially perfuse the mouse with 20-30 mL of cold PBS from the left ventricle.
- Decapitate the mouse under anesthesia.
- Open the mouse's skull and carefully free the brain from the skull.
- Transfer the brain to the mouse brain slice mold and cut the brain into 0.1 cm slices.
- Remove the brain slices and place them in cold PBS in a Petri dish (60/15 mm). Using microsurgical forceps, microdissect the lesions labeled by NR dye around the corpus callosum under a stereomicroscope.
NOTE: Ensure the dissected tissue is as complete as possible to facilitate the subsequent transfer; the total dissection progress should be completed in 2 h. - Transfer the dissected tissue to 15 mL centrifuge tubes containing the appropriate amount of cold loading buffer.
NOTE: Pool the corpus callosum tissue from 2-3 mice together in one tube as one sample.
3. Tissue dissociation
- Centrifuge the dissected tissue at 300 ×g for 30 s (after reaching this speed) to collect the sample at the bottom of the tube.
- Preheat enzyme mix 1 and 2 to 37 °C in an incubator.
- Add 1,950 μL of preheated enzyme mix 1 to one sample and digest in an incubator at 37 °C for 5 min.
- Add 30 μL of preheated enzyme mix 2 and mix gently.
- Digest in an incubator at 37 °C for 15 min and mix gently every 5 min.
- Add 4 mL of cold PBS to the tube after digestion and shake gently.
- Place 70 μm filters on 50 mL centrifuge tubes and prewet the filters with 500 μL of cold PBS. Filter the dissociated tissue by passing the digested tissue samples through the filters, and transfer the filtered suspension in the 50 mL centrifuge tube to a 15 mL centrifuge tube.
NOTE: Skip this step if the amount of tissue is too small. - Centrifuge the filtered tissue samples at 300 ×g for 10 min at 4 °C and aspirate the supernatant slowly and completely.
NOTE: All the steps should be performed on ice except for the enzymatic digestion.
4. Debris removal
- Resuspend the cell pellet gently with 1,550 μL of cold PBS.
- Add 450 μL of cold solution for debris removal and mix well.
- Overlay the above mixture slowly and gently with 2 x 1 mL of cold PBS using a 1,000 μL pipette.
NOTE: Tilt the centrifuge tube by 45 ° and slowly add PBS along the tube wall with the pipette. - Transfer the tube slowly and gently to a centrifuge and spin at 4 °C and 3,000 × g for 10 min.
- Look for three layers after centrifugation. Aspirate the two top layers completely by using a 1,000 μL pipette (Figure 2).
- Fill the tube up to 5 mL with cold loading buffer and gently invert the tube three times.
- Centrifuge at 4 °C and 1,000 × g for 10 min. Aspirate the supernatant completely and avoid disrupting the cell pellet.
5. Magnetic separation of microglial cells
- Resuspend the cell pellet with 90 μL of loading buffer and add 10 μL of CD11b (Microglia) beads.
- Mix well and incubate for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Add 1 mL of loading buffer and gently pipette the liquid up and down with a 1,000 μL pipette to wash the cells after incubating. Centrifuge the cells at 4 °C and 300 × g for 10 min and aspirate the supernatant completely to remove the unbound beads.
- Resuspend the cells in 500 μL of loading buffer.
- Place the MS column with its separator for positive selection in the magnetic field.
- Rinse the column with 500 μL of loading buffer to protect the cells and ensure the efficiency of magnetic sorting, following the manufacturer's protocol.
- Apply the cell suspension onto the MS column and discard the flowthrough containing unlabeled cells.
- Add 500 μL of loading buffer to the column three times to wash away cells that adhere to the column wall and discard the flowthrough.
NOTE: Only add a new loading buffer for washing when the column reservoir is empty. - Remove the column from the separator after washing the column and place it on a 15 mL centrifuge tube.
- Add 1 mL of loading buffer into the column and push the plunger to the bottom to flush out the magnetically labeled cells. Repeat this step three times to completely collect the magnetically labeled cells.
Representative Results
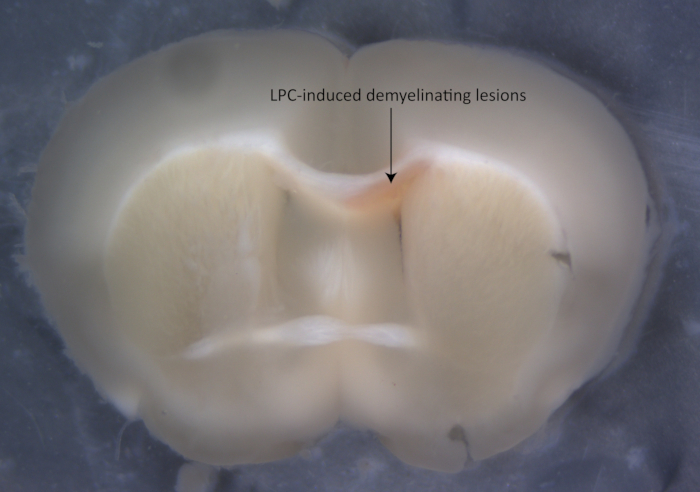
Figure 1: Images of the focal demyelinating lesions labeled by the neutral red dye.
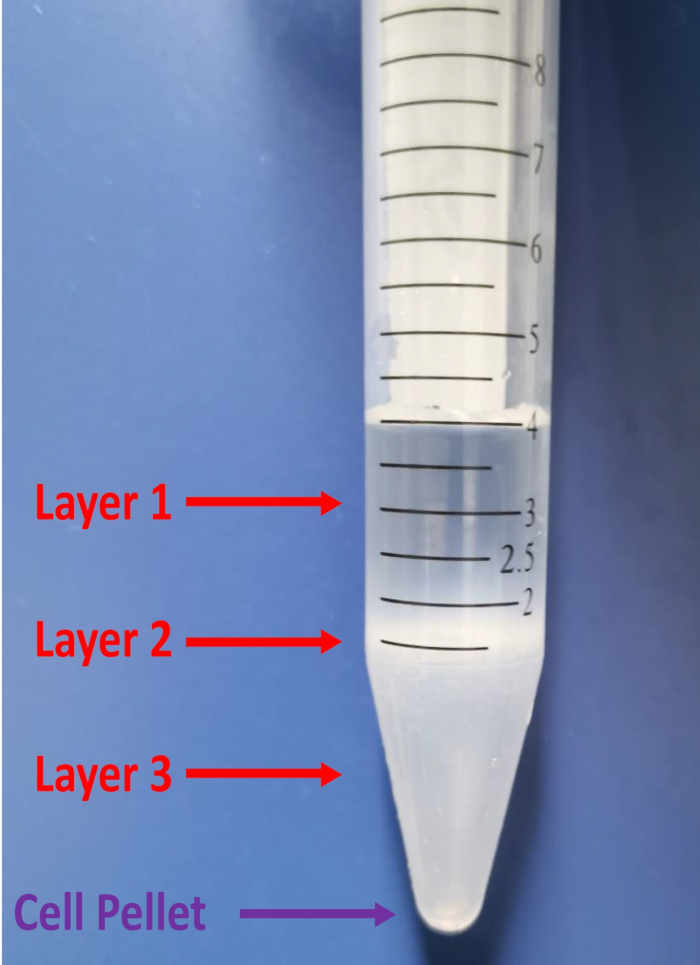
Figure 2: Images of the three layers formed by centrifugation. The top two layers (layer 1 + layer 2) must be removed in the debris removal process (see protocol step 4.5).
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| 1.5 mL Micro Centrifuge Tubes | BIOFIL | CFT001015 | |
| 15 mL Centrifuge Tubes | BIOFIL | CFT011150 | |
| 50 mL Centrifuge Tubes | BIOFIL | CFT011500 | |
| 70 µm Filter | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-095-823 | |
| Adult Brain Dissociation Kit, mouse and rat | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-107-677 | |
| C57BL/6J Mice | SJA Labs | ||
| CD11b (Microglia) Beads, human and mouse | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-093-634 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum | BOSTER | PYG0001 | |
| MACS MultiStand | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-303 | |
| MiniMACS Separator | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-102 | |
| MS columns | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-042-201 | |
| Neutral Red | Sigma-Aldrich | 1013690025 | |
| PBS | BOSTER | PYG0021 | |
| Pentobarbital | Sigma-Aldrich | P-010 | |
| Stereomicroscope | MshOt | MZ62 |

