Generating a Coronal Brain Slice Exposing the Amygdala Regions from a Mouse Brain
Abstract
Source: Bosch, D., et al. Ex Vivo Optogenetic Dissection of Fear Circuits in Brain Slices. J. Vis. Exp. (2016).
This video demonstrates the preparation of thin coronal brain slices from a murine brain, exposing the amygdala regions rich in synaptic connections from the medial prefrontal cortex. The slices are then recovered in oxygenated artificial cerebrospinal fluid to maintain neuronal viability.
Protocol
1. Preparation of Acute Slices
- Prepare ACSF, cutting solution, tools (scissors, scalpel, forceps, spatula, Pasteur pipette), and agar blocks.
NOTE: 1 L of artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) is required per experiment. As previously published, ACSF is prepared by dissolving chemicals in double-distilled H2O. The cutting solution is prepared by supplementing 200 ml of ACSF with 0.87 ml of 2 M MgSO4 stock solution. - Oxygenate ACSF and cutting solution throughout the experiment with 95% O2 and 5% CO2.
- Deeply anesthetize the mouse using a small animal anesthesia machine, using isoflurane (3% oxygen). Check the anesthesia depth using the limb withdrawal reflex before continuing.
- Decapitate the mouse using large scissors and immediately chill the head in an ice-cold cutting solution.
- Open the skull by a single midline incision from caudal to rostral and gently push pieces of the skull to the sides using forceps. Rapidly remove the brain by gently lifting it out of the skull using a small rounded spatula. Cut off cerebellum with scalpel. Place the brain in an ice-cold cutting solution.
- For mPFC injection sites, use a scalpel to cut off the anterior part of the brain (containing mPFC) and put it in an ice-cold cutting solution until slicing.
- Remove the excess cutting solution with filter paper and glue the posterior part of the brain onto the vibratome stage.
- For coronal amygdala slices, MGm/PIN injection sites, and mPFC injection sites, glue the brain directly on stage (Figure 1D, left and right). Place an additional agar block behind the brain for stability while slicing.
- Place the stage in a cutting chamber with an ice-cold oxygenated cutting solution maintained at 4 °C using a cooling unit. Using a sapphire blade, prepare coronal slices of the amygdala. Place the slices in an interface chamber supplied with oxygenated ACSF at RT.
Representative Results
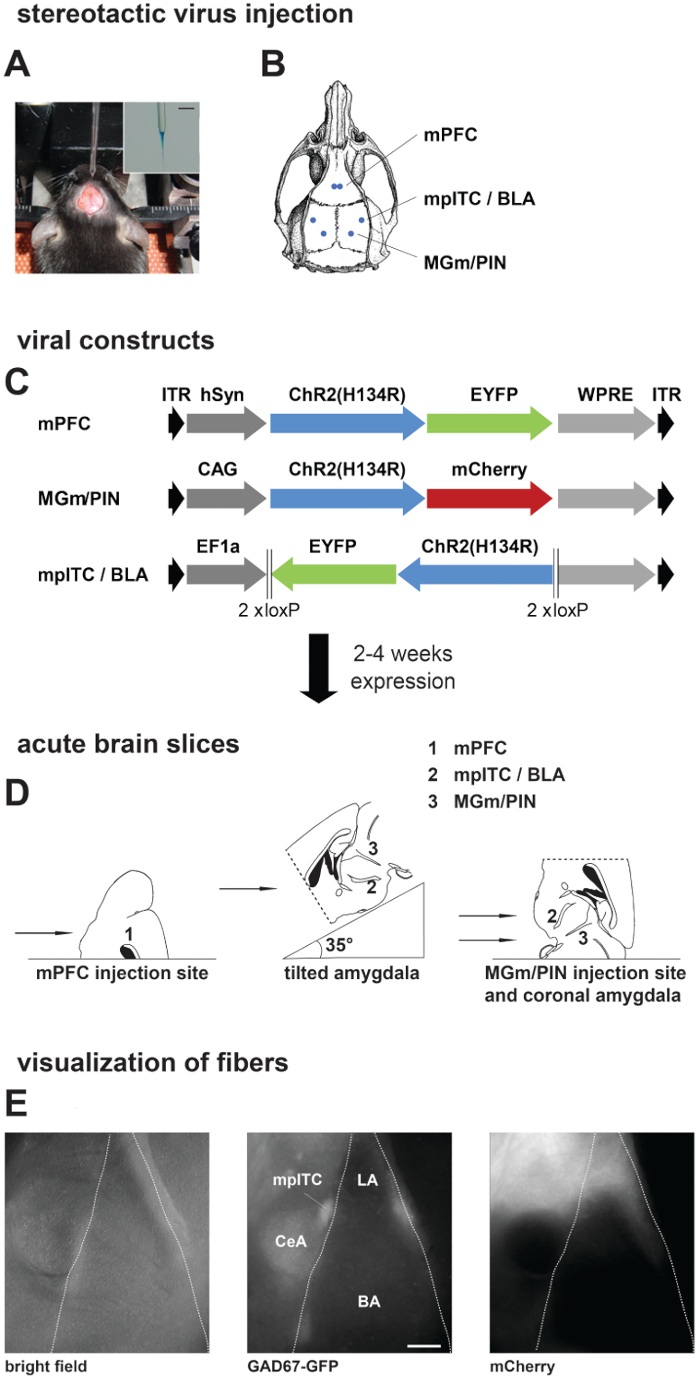
Figure 1. Stereotactic Injections, Preparation of Acute Brain Slices, and Visualization of Presynaptic Fibers. (A, B) Stereotactic virus injection. A) Picture of an anesthetized mouse placed in a stereotactic frame with the skull exposed and the injection pipette. Inset: Zoom in the picture of the injection pipette filled with virus solution mixed with fast green. Scale bar: 3 mm. (B) Schematic of a mouse skull with marked positions of drill holes for different injection areas. (C) Scheme showing different viral constructs used in this study. Dark grey: promoter sequence; blue: Channelrhodopsin2 (ChR2 (H134R)); green/red: fluorescent protein. Expression time was 2 weeks for local amygdala projections and 4 – 6 weeks for projections from mPFC and MGm/PIN. (D) Preparation of acute brain slices: Scheme showing placement of mouse brain on slicer stage for obtaining slices from different injection and projection areas. (E) Visualization of fibers in acute brain slices from a GAD67-GFP mouse injected with ChR2-mCherry virus in MGm/PIN. Pictures are taken on the upright patch microscope with different filter sets: GAD67-GFP expression, middle; MGm/PIN fibers labeled with mCherry, right. Scale bar: 200 µm. mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; mpITC, medial paracapsular intercalated cells; BLA, basolateral amygdala; MGm, medial geniculate nucleus, medial part; PIN, posterior intralaminar thalamic nucleus; LA, lateral amygdala; BA, basal amygdala; CeA, central nucleus of the amygdala.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) | for composition see references #16 and #23 | ||
| Internal patch solutions | for composition see references #16 and #23 | ||
| Slicer, Microm HM650V | Fisher Scientific, Germany | 920120 | |
| Cooling unit for tissue slicer, CU65 | Fisher Scientific, Germany | 770180 | |
| Sapphire blade | Delaware Diamond Knives | ||
| Stereoscope, SZX2-RFA16 | Olympus, Japan |

