Isolation of Schwann Cells from Mouse Spinal Roots
Abstract
Source: He, Q., et al., & Ding, F. Purification of fibroblasts and schwann cells from sensory and motor nerves in vitro. J. Vis. Exp. (2020)
This video outlines the isolation and culturing of Schwann cells from mouse spinal roots. Isolated cells are then cultured in specific media. Schwann cells are isolated via differential digestion and adherence. They are subsequently transferred to extracellular matrix-coated coverslips for attachment and proliferation.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Isolation and culture of motor and sensory nerve fibroblasts and SC (Schwann cells)
- Use seven-day-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (n=4) from the Experimental Animal Center of Nantong University of China. Place the rats in a tank containing 5% isoflurane for 2-3 minutes, allow the animals to breathe slowly and have no independent activity, and then sanitize using 75% ethanol before decapitation.
- Use scissors to cut the back skin for about 3 cm and remove the spinal column. Open the vertebral canal carefully to expose the spinal cord.
- Maintain the spinal cord in a 60 mm Petri dish with 2-3 mL of ice-cold D-Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS).
- Based on the anatomical structure, excise the ventral root (motor nerve) and then the dorsal root (sensory nerve) under a dissecting microscope. Next, place them in an ice-cold D-Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS).
- After removing the HBSS, slice the nerves into 3-5 mm pieces with scissors and digest with 1 mL of 0.25% (w/v) trypsin at 37 °C for 18-20 min. Next, supplement with 3-4 mL of DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) to stop the digestion.
- Pipette the mixture up and down gently about ten times and centrifuge at 800 x g for 5 min. After that, discard the supernatant and suspend the precipitate in 2-3 mL of DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS.
- Filter the cell suspension using a 400 mesh filter, then inoculate the cells in a 60 mm Petri dish and culture at 37 °C in 5% CO2. After 4-5 days of culturing, isolate the passage 0 (p0) fibroblasts and SCs after reaching 90% confluence.
- Isolation and culture of SCs (Figure 1)
- Wash the cells once using 1x PBS. Add 1 mL of 0.25% (w/v) trypsin (37 °C) per 60 mm Petri dish to digest the cells for 8-10 s at room temperature. After that, 3 mL of DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS was added to stop the digestion.
- Gently blow the mixture with a pipette to detach the SCs. Then, collect and centrifuge the SCs at 800 x g for 5 min.
- Discard the supernatant and suspend the residue in 3 mL of DMEM with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 2 µM forskolin, and 10 ng/mL HRG, and then inoculate the cells in an uncoated 60 mm Petri dish. After culturing at 37 °C for 30-45 min, the fibroblasts (a few fibroblasts are digested with SCs) attach to the bottom of the dish.
- Transfer the supernatant (including the SCs) to another poly-L-lysine (PLL)–coated medium dish and culture at 37 °C for 2 days.
Representative Results
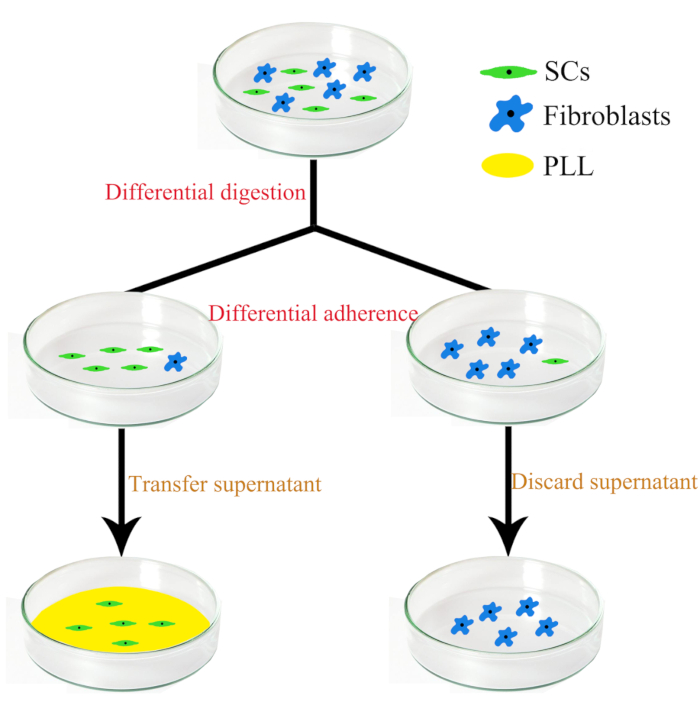
Figure 1: The schematic diagram showing the separation and purification steps of sensory and motor Fibroblasts and SCs.
開示
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| D-Hank's balanced salt solution | Gibco | 14170112 | |
| DMEM | Corning | 10-013-CV | |
| Dissecting microscope | Olympus | SZ2-ILST | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Gibco | 10099-141C | |
| Forskolin | Sigma | F6886-10MG | |
| 0.25% (w/v) trypsin | Gibco | 25200-072 | |
| Culture dishes | |||
| Centrifuge tubes | |||
| Coverslips | |||
| Poly-L-Lysine | |||
| CO2 incubator |

