Co-culturing of Ventral Hippocampal and Nucleus Accumbens
Abstract
Source: Zhong, C., et al. Live Imaging of Nicotine Induced Calcium Signaling and Neurotransmitter Release Along Ventral Hippocampal Axons. J. Vis. Exp. (2015)
This video demonstrates the process of preparing ventral hippocampal and nucleus accumbens tissues from mouse brains for co-culture. Neurons extend projections to form synaptic connections between the ventral hippocampal and nucleus accumbens tissues. This method allows studying neuronal interactions between these two brain regions, offering insights into cognition, behavior, and neurological disorders.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. vHipp-nAcc Synaptic Co-cultures
- Sacrifice mice (postnatal day 0 – 3, from wild-type (WT) or α7 nAChRs transgenic mouse line) with CO2. Decapitate each pup and save the tail in a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube for post facto genotyping. Perform the following steps in a sterilized hood.
- Remove the top of the skull with scissors and forceps to expose the whole brain. Starting at the juncture where the cerebral cortices part from each other caudally, obtain a coronal section that contains the posterior cortices, including the ventral hippocampal (vHipp), under a dissecting microscope.
- Dissect vHipp tissue strips containing the cornu ammonis 1 (CA1)-subiculum region out according to a developing mouse brain atlas (Figure 1A). Transfer to a 35 mm culture dish containing cold culture media (4 °C), and cut into small thin slices (around 100 µm × 100 µm microslices).
- Pre-incubate 12 mm poly-D-lysine/laminin-coated glass coverslips inside 24 well tissue culture plates with culture media (~ 500 μl) for at least 30 min in the incubator at 37 °C. Remove media before plating microslices.
- Plate with a fire-polished Pasteur pipette at the center of the coverslip with a minimal amount of media (~ 50 μl, containing ~ 20 pieces of microslices) to facilitate attachment of the explants. Plate vHipp microslices originating from a single animal (either the +/+ or the -/- genotype of the transgenic α7 line) on each coverslip.
- After the explants settle onto the coverslip, gently add additional media (~ 100 μl) by the wall so that the level of the media is high enough to completely cover the explants on the periphery but not those at the center of the coverslip.
- After an O/N incubation in 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator, disperse nucleus accumbens (nAcc) neurons from embryonic days 18 to postnatal day 1 WT mice and add to the explants.
- Dissect out nAcc tissues according to a developing mouse brain atlas (Figure 1B).
- Cut into small pieces (around 500 µm × 500 µm microslices) and transfer to a 15 ml tube.
- Treat with 0.25% trypsin (2 ml) for 15 min at 37 °C. Wash tissue chunks three times with cold washing media (5 ml, 4 °C) followed by one wash in cold culture media (5 ml, 4 °C). Allow suspension to rest for 5 min in each wash step, and then pour off supernatant carefully.
- Dissociate cells by gentle trituration in 2 ml of culture media with a lightly fire-polished Pasteur pipette.
- Transfer cell suspension to another 15 ml tube and centrifuge at 2,000 x rpm for 5 min. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the cells in culture media at 1 ml per 6 pups. Disperse cells by gently pipetting in media several times with a fire-polished Pasteur pipette.
- Add 0.25 ml of dispersed nAcc cells to each coverslip with vHipp explants.
- Maintain the cultures in a humidified 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator. Place culture plates on dampened sterile gauze pads to mechanically stabilize and maintain humidity, facilitating synapse formation.
Representative Results
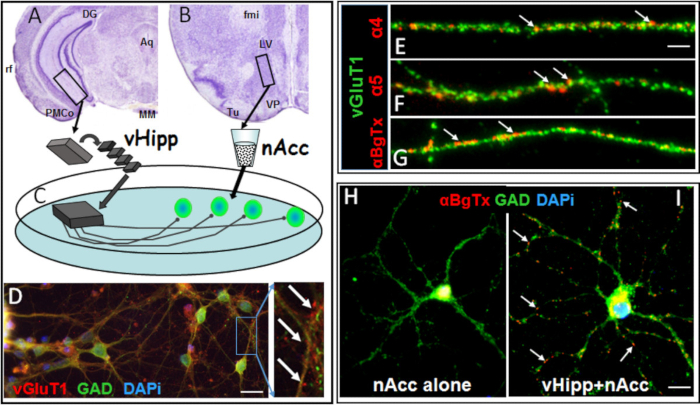
Figure 1. Synaptic co-culture of vHipp with nAcc allows examination of pre-synaptic localization of nAChRs. (A-C) Schematic cartoon of genotype-specific in vitro circuits (C) prepared by separate plating of ventral hippocampus/subiculum (A). slices from an individual WT or α7 -/- mouse and dispersed neurons from WT nucleus accumbens (B). Aq, aqueduct (Sylvius); DG, dentate gyrus; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; PMCo, posteromedial cortical amygdaloid nucleus; rf, rhinal fissure, fmi, forceps minor of the corpus callosum; LV, lateral ventricle; Tu, olfactory tubercle; VP, ventral pallidum. (D) vHipp microslices extend vGluT1 positive (red) axonal projections that contact GAD65 positive (green) nAcc neurons (white arrows are examples of those contact sites). Scale bar: 10 µm. (E-G) Representative micrographs of WT vHipp axons (staining with vGluT1, green) are shown for α4*nAChR (E), α5*nAChR (F), and surface α7*nAChR (nicotinic acetylcholine receptors) (G) staining in red clusters (white arrows). Scale bar: 5 μm. (H) There are no surface α7*nAChR clusters on dispersed GABA(gamma-aminobutyric acid)ergic neurons (GAD65 positive) from nAcc alone. (I) Red "clusters" of surface α7*nAChR (white arrows) can be seen in those dispersed neurons co-cultured with vHipp microslices. Scale bar: 5 μm.
Divulgations
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Culture Media (50 ml) | |||
| Neurobasal | GIBCO | 10888022 | 48 ml |
| B-27 Supplements | GIBCO | 0080085-SA | 1 ml |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | GIBCO | 10908-010 | 0.5 ml |
| GlutaMAX Supplement | GIBCO | 35050-061 | 0.5 ml |
| Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) | GIBCO | 15140-122 | 20 ng/ml |
| washing media (HBSS, 100 ml) | |||
| HBSS, no calcium, no magnesium, no phenol red | GIBCO | 14175-095 | 99 ml |
| HEPES ( 1M) | GIBCO | 15630-130 | 1 ml |
| HEPES buffered saline (HBS) pH=7.3 | |||
| NaCl | Sigma | S9888 | 135 mM |
| KCl | Sigma | P9333 | 5 mM |
| MgCl2 | Sigma | M8266 | 1 mM |
| CaCl2, | Sigma | C1016 | 2 mM |
| HEPES | Sigma | H3375 | 10 mM |
| Glucose | Sigma | G0350500 | 10 mM |
| HBS Cocktail for live imaging pH=7.3 | |||
| NaCl | Sigma | S9888 | 135 mM |
| KCl | Sigma | P9333 | 5 mM |
| MgCl2 | Sigma | M8266 | 1 mM |
| CaCl2, | Sigma | C1016 | 2 mM |
| HEPES | Sigma | H3375 | 10 mM |
| Glucose | Sigma | G0350500 | 10 mM |

