26.11:
Boundary Conditions for Current Density
552 Views
•
•
Current density becomes discontinuous across an interface of materials with different electrical conductivities. The normal component of the current density is continuous across the boundary.
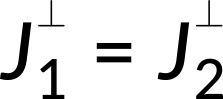
However, the tangential components of the current density are discontinuous across the interface.
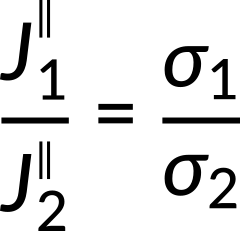
Consider an interface separated by two conducting media with conductivities σ1 and σ2. The steady current density at the interface is ![]() , in medium 1 at a point P1. It makes an angle α1 with the normal. The current density
, in medium 1 at a point P1. It makes an angle α1 with the normal. The current density ![]() at point P2 in medium 2 makes an angle α2 with the normal.
at point P2 in medium 2 makes an angle α2 with the normal.
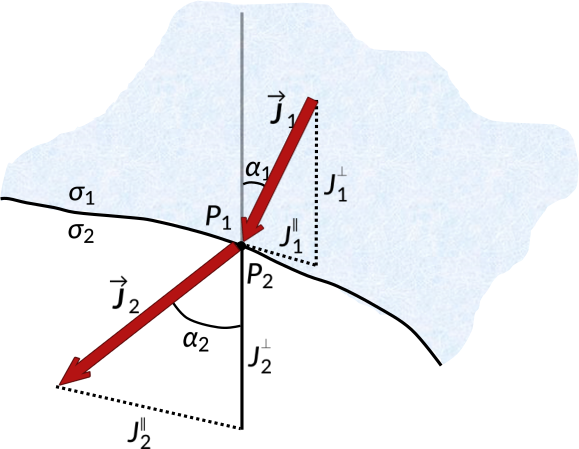
The normal and tangential components of the current density give the equations as follows:
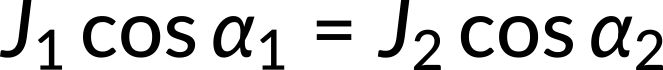
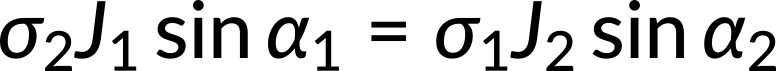
Taking the ratio of the two equations, the expression for the electrical conductivities in both the media is obtained.
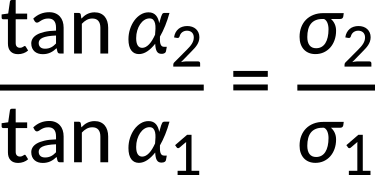
If the electrical conductivity of medium 1 is greater than that of medium 2, the angle α2 approaches zero. This implies that the current density ![]() is normal to the surface of conductor 1.
is normal to the surface of conductor 1.
