17.6:
Gibbs Free Energy
28,632 Views
•
•
One of the challenges of using the second law of thermodynamics to determine if a process is spontaneous is that it requires measurements of the entropy change for the system and the entropy change for the surroundings. An alternative approach involving a new thermodynamic property defined in terms of system properties only was introduced in the late nineteenth century by American mathematician Josiah Willard Gibbs. This new property is called the Gibbs free energy (G) (or simply the free energy), and it is defined in terms of a system’s enthalpy and entropy as the following:
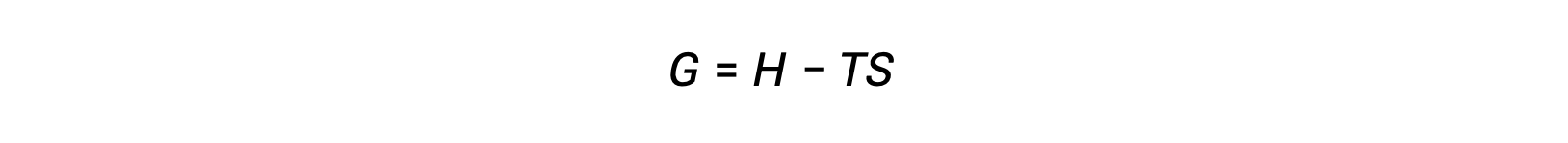
Free energy is a state function, and at constant temperature and pressure, the free energy change (ΔG) may be expressed as the following:
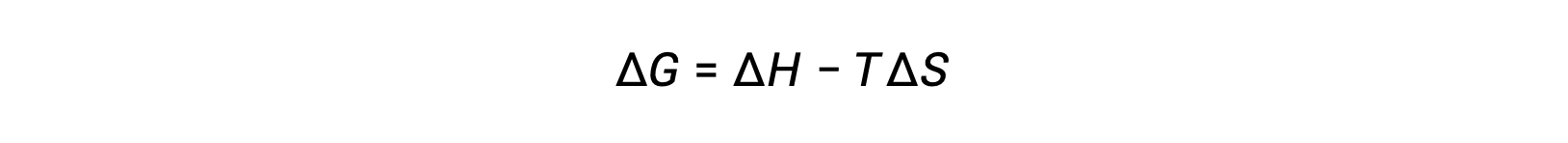
The relationship between this system property and the spontaneity of a process may be understood by recalling the previously derived second law expression:
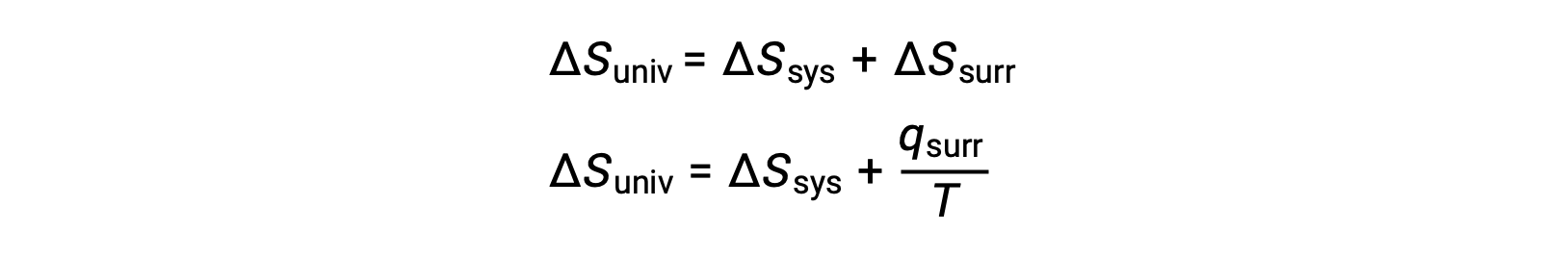
The first law requires that qsurr = −qsys, and at constant pressure qsys = ΔH, so this expression may be rewritten as:
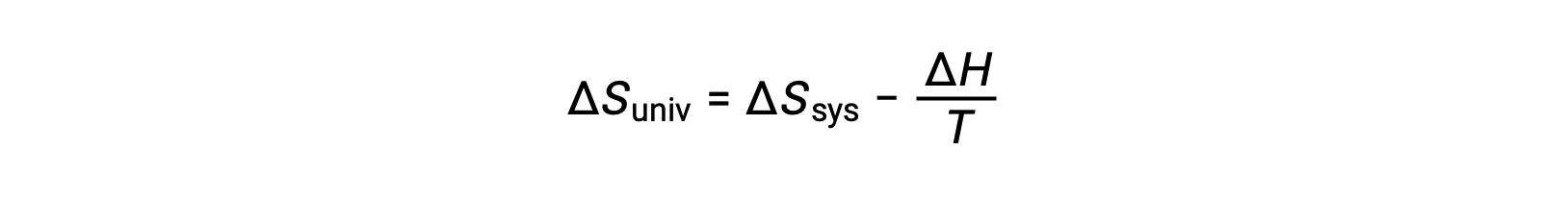
Multiplying both sides of this equation by −T and rearranging yields the following:
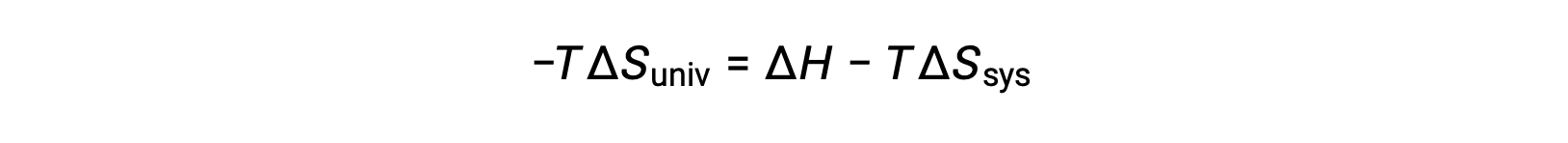
For simplicity’s sake, the subscript “sys” can be omitted, and the expression becomes
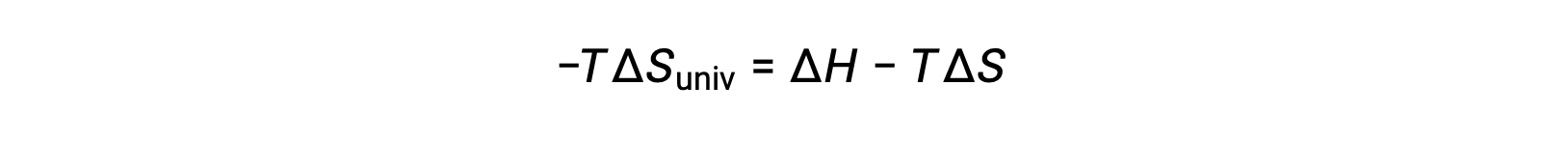
Comparing this equation to the previous one for free energy change shows the following relation:
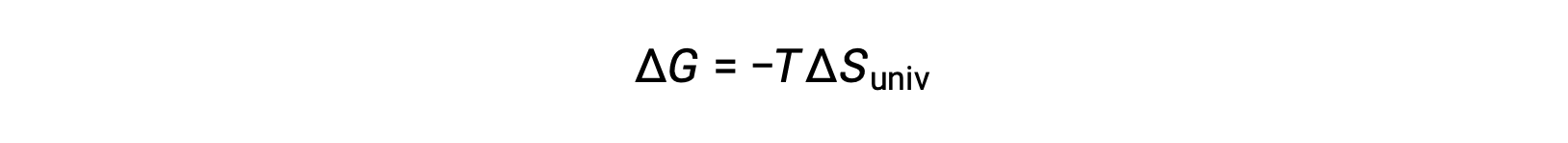
The free energy change is, therefore, a reliable indicator of the spontaneity of a process, as it is directly related to the previously identified spontaneity indicator, ΔSuniv.
If ΔSuniv > 0, ΔG < 0 and the reaction is spontaneous.
If ΔSuniv < 0, ΔG > 0 and the reaction is nonspontaneous.
If ΔSuniv = 0, ΔG = 0 and the reaction is at equilibrium.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Chapter 16.4: Free Energy.
