Wireless Electrophysiological Recording of Neurons by Movable Tetrodes in Freely Swimming Fish
Summary
A novel wireless technique for recording extracellular neural signals from the brain of freely swimming goldfish is presented. The recording device is composed of two tetrodes, a microdrive, a neural data logger, and a waterproof case. All parts are custom-made except for the data logger and its connector.
Abstract
The neural mechanisms governing fish behavior remain mostly unknown, although fish constitute the majority of all vertebrates. The ability to record brain activity from freely moving fish would advance research on the neural basis of fish behavior considerably. Moreover, precise control of the recording location in the brain is critical to studying coordinated neural activity across regions in fish brain. Here, we present a technique that records wirelessly from the brain of freely swimming fish while controlling for the depth of the recording location. The system is based on a neural logger associated with a novel water-compatible implant that can adjust the recording location by microdrive-controlled tetrodes. The capabilities of the system are illustrated through recordings from the telencephalon of goldfish.
Introduction
Fish are the largest and most diverse group of vertebrates, and like other vertebrates they exhibit complex cognitive abilities such as navigating, socializing, sleeping, hunting, etc. Nevertheless, the neural mechanisms governing fish behavior remain for the most part unknown.
In the past few decades, extracellular recordings from immobilized fish have primarily been implemented to investigate different aspects of the neural basis of behavior1,2. Although this technique is appropriate for some sensory systems, investigation of the full spectrum of the neural basis of behavior is difficult if not impossible in immobilized animals. The first advances involved recording from the Mauthner cells of tethered swimming fish3,4. However, Mauthner cells are disproportionately large and the recorded action potential amplitudes, which can go as high as a few mV, facilitate recording. Later, Canfield et al. described a proof of concept when using a tethered animal to record from the telencephalon of fish5. Another recent technique for recording neural activity from fish is calcium imaging (see reviews by Orger and de Polavieja6, and Vanwalleghem et al.7). This technique was developed for use with zebrafish larvae because the skin and skull are transparent during the larval stage. However, this technique cannot be used to study complex behaviors in later stages of development.
Here, we present a novel technique for recording extracellular neural activity from the brains of freely swimming fish. This is a modified version of the protocol described in Vinepinsky et al.8. The main innovation is the addition of a microdrive that makes it possible to control the position of the electrodes after surgery. The technique is designed for recording from the telencephalon of goldfish using a set of tetrodes that are connected to a neural data logger via a microdrive. The whole setup is wireless and anchored to the fish's skull. The specific weight of the system is equalized to the water-specific weight by adding a small float that allows the fish to swim freely.
The technique is based on the use of a neural data logger that amplifies, digitizes, and stores the signal in an onboard memory device. The logger telemetry system is used to start and stop the recordings, and for synchronization with the video camera. In this protocol, a 16-channel neural logger is used, embedded in a waterproof box together with the microdrive.
The microdrive assembly is fabricated from two main components: the microdrive itself and the microdrive housing (Figure 1A,B). The housing holds the microdrive and the tetrodes, and also acts as the anchor between the skull and the logger box (Figure 1C). The PVC logger box is fabricated using a machine process and is sealed using an O-ring (Figure 1E-G, see also Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2, and Supplementary Figure 3 for a three-dimensional [3D] diagram). At one end, a piece of polystyrene foam is attached to the logger box to compensate for the weight of the implant and provide the fish with a buoyancy-neutral implant. The construction of the microdrive described in the protocol follows the procedure presented by Vandecasteele et al.9 with a modification to attach the microdrive to the housing (Figure 1A). All major steps are presented.
The procedure described in the protocol to prepare the fish skull is similar to the one presented in Vinepinsky et al.8 and is described briefly in the protocol. One day after surgery, the fish are normally fully recovered from the effects of anesthesia and are ready for the behavioral experiments. Note that the tetrode location can be adjusted by turning the microdrive screw. The screw has a spacing of 300 µm per full rotation and an advancement of 75 µm is recommended until the target brain location is reached. An appropriate brain atlas should be consulted to target the specific brain region of interest. It is advisable to test the electrode impedance each time the fish is anesthetized for battery or memory card replacement.
Protocol
All surgery procedures must be approved by the local ethics committees on animal welfare (e.g., IACUC).
1. Construction of the Microdrive Housing
- To construct the housing, cut a 1 mm wide brass plate into a 19 mm x 29 mm x 1 mm plate using a saw. Cut two 5.5 mm slits on each of the long sides perpendicular to the edge, such that each slit is 6.5 mm away from the narrow sides (Figure 2A).
- Using pliers, fold the area between the slits on the long sides inward, then fold the bottom part inward and the upper side outward to obtain the housing (Figure 2B,C).
- Using a 3 mm drill bit, make holes for screws in the microdrive housing.
NOTE: These holes will be used later to attach the housing to the logger box (Figure 2D). - Solder the sides of the housing.
- Using a fine circular file, generate a small, 1.5 mm in radius, semicircular slit at the bottom of the housing (Figure 2E).
NOTE: This will be used later to insert the stainless steel tube to guide the electrodes. - Use a 1 mm drill bit to make a hole in the back of the housing for the tetrodes (Figure 2F).
NOTE: A 3D model of the housing is found in the Supplementary housing.stl file.
2. Construction of the Microdrive
- Using a cutter, break off a three-pin piece from a single row male pin header strip (Figure 1H). Using pliers, pull out the middle pin.
- Using a cutter, cut the remaining pins to 10 mm in length (2 mm less than the screw length). Another possibility is to use a longer screw (see step 2.4).
- Drill a hole using a #65 drill bit through the middle pin hole. Drill a thread using a 00−99 tap.
- Assemble the microdrive and the brass plates (7.5 mm x 2.5 mm x 0.6 mm, see Supplementary Figure 4) such that the brass plates are touching the pins. Insert a screw (#00-90 round head, 12 mm, brass) through the first brass plate, then through the pin header thread and the second brass plate. Finally, place a nut on the screw and gently tighten the assembled microdrive.
- Solder the pins together with the brass plates, and the nut with the tip of the screw.
- Solder the microdrive into the microdrive housing at four points on the sides of the microdrive brass plates.
- Cut one stainless steel tube 6 mm long with an inner diameter of 1.5 mm and another stainless steel tube 3 mm long with an inner diameter of 1.2 mm. Polish the ends of the tubes to avoid sharp ends.
- Glue the 6 mm long tube to the small semicircular slit at the bottom of the microdrive housing using epoxy. Glue the 3 mm long stainless steel to the pin header, lined up with the 6 mm long tube on the housing.
- Cut two 5 cm long silicone tube segments with diameter of 0.64 mm and one 5 cm long polyimide tube with diameter of 0.250 mm.
- Insert the three tubes into the two stainless steel tubes. Glue the tubes to the stainless steel tube attached to the pin header using cyanoacrylate glue. Screw the microdrive all the way up and cut off the excess tubing from the top and bottom of the two steel tubes.
NOTE: The microdrive with the housing is now ready for use (Figure 1C).
3. Preparing the Tetrode Array
- To fabricate a two-tetrode implant with four electrodes on each tetrode, prepare eight wires, each 12 cm long, Formvar insulated, out of 25 µm diameter tungsten wire.
NOTE: The same design can accommodate four tetrodes. - Place a holder for a 16-channel electrode interface board (EIB-16) PCB (see Table of Materials) under the microscope.
- Using a soft tipped tweezer and a lighter, remove the coating off each of the eight wires on one side using the flame.
NOTE: This is to ensure that the wire will be properly connected to the PCB connector later on. - Push a wire into one of the holes in the EIB-16 with the coated side in the hole. Place a pin and press it using pliers. Check the connectivity by measuring the resistance between the pin and the uncoated side of the wire.
NOTE: The resistance is on the order of tens of Ohms. - Repeat step 3.4 with all eight wires.
- Tape two groups of four wires together using duct tape at the end of each wire.
NOTE: Each group will be glued together later to form a tetrode. - Cut one piece of tungsten wire 12 cm long with a 50 µm diameter. Connect it to one of the EIB-16 connections.
NOTE: This wire will serve as the reference electrode. - Cut two bare silver wires 12 cm long with a 75 µm diameter that will serve as grounds for the recording logger. Solder the two wires to the ground connection in the EIB-16.
- Hold the EIB-16 above a motorized turning device and place the duct tape end of one group of four wires on the motorized tuning device. Apply 130 rounds clockwise followed by 20 counter- clockwise rotations. Apply cyanoacrylate glue to cover the tetrode.
- Wait for the glue to cure. Cut the tetrode close to the duct tape.
- Repeat steps 3.9 and 3.10 with the second tetrode.
NOTE: This produces the finished two-tetrode array (Figure 1D).
4. Assembling the Implant
- Screw the microdrive all the way down.
- Using 1 x 3M Phillips round head screws, attach the EIB-16 to the PVC plate.
- Using soft end tweezers, pull all the tetrodes and wires through the hole in the front of the logger box cover.
- Using the 2 x 6M Phillips flat head screws, attach the PVC plate to the logger box cover. Keep the EIB-16 connector in the correct orientation so that the logger can be mounted on the EIB-16. Make sure the EIB-16 is fixed in place to avoid motion artifacts in the recorded signal.
- Seal the wires to the box using epoxy. Apply as little as possible because the primary sealing will be done by room temperature vulcanizing (RTV) later on.
- Attach the microdrive housing to the logger box cover using 2 mm screws.
- Thread the tetrodes and all wires through the hole at the back of the microdrive housing. Thread the tetrodes through the two silicone tubes in the microdrive. Thread the 50 µm tungsten wire through the polyimide tube in the microdrive.
- Glue the tetrodes and wires to their tubes by applying cyanoacrylate glue to the top end of the tubes, to ensure the movement is consistent with the microdrive. Screw the microdrive all the way to the top.
- Apply soft petroleum (see Table of Materials) on the exposed tetrode and wires inside the microdrive housing to prevent motion.
- Cut a 12 mm x 14.5 mm Petri dish bottom window using a heated razor blade. Attach the window to the front of the microdrive housing with epoxy. Keep the ground wires outside the window.
- Apply RTV coating to the exposed tetrodes and wires between the logger box cover and the microdrive housing.
- After the RTV is cured, close the box with a small weight inside, and submerge in water overnight to ensure there is no water leakage into the box.
- Cut the tetrodes and reference wire to the desired length using sharp scissors.
- Attach the marked extruded polystyrene foam (see Table of Materials) to the box. Adjust its size so its buoyancy is balanced when submerged in a water bath.
- Dip the tetrode tips in platinum black solution and use a direct current (-0.2 µA) to coat the electrodes and set the electrodes' impedance as desired. Use a multielectrode impedance tester (see Table of Materials) for coating and impedance measurements.
NOTE: In the goldfish pallium, a value of 40 kOhm is best. Depending on the application, the electrode impedance can be adjusted by modifying the platinum black coating10,11.
5. Anesthesia Preparation — 1% MS-222 Stock Solution
CAUTION: Anesthesia preparation includes the use of powdered MS-222, a carcinogen. Hence, steps 5.2 and 5.3 must be done in a chemical hood using gloves.
- Add 100 mL of water to a tube that can contain more than 100 mL.
- In a chemical hood, place a disposable weighting plate on a scale. Add 1 g of MS-222 powder using a spatula, then add the powder to the tube.
- Shake the tube well.
NOTE: In liquid form, MS-222 can be used outside the chemical hood wearing gloves but does not require a mask. - Place a disposable weighting plate on a scale. Add 2 g of sodium bicarbonate using a spatula, then add the powder to the tube. Shake the tube well.
6. Preparing the Fish Skull
NOTE: At this stage, the fish is ready for implant surgery. Prior to surgery, make sure that all components and supplies have been sterilized by the appropriate procedures. For this step, an out of water U-shaped fish holder is needed. In this protocol, an aluminum holder that fits a 15 cm head to tail long goldfish is used. This system holds the fish out of water while perfusing the gills with oxygenated water. For details see Vinepinsky et al.8.
- Place the fish in a 0.02% MS-222 water bath for 20 min until the fish is asleep.
- Using sterile gloves, take the fish out of the water and place it in the holder.
NOTE: The oxygenated water perfusing the fish contains MS-222 at a concentration of 0.02%, so that the fish remains anesthetized during surgery. - Using a sterile spatula, apply lidocaine 5% paste on the skin above the designated place for surgery for 10 min, then remove the lidocaine.
NOTE: Consult an appropriate brain atlas to target the specific brain region. - Using a sterile 15 blade scalpel, remove the skin above the skull in the region of implant.
- Using a dental drill with 0.7 mm drill bits, drill 4 holes in the skull. Insert a 1 mm screw (3 mm long) into each hole and apply cyanoacrylate glue on the holes right before inserting the screw.
- Using a dental burnisher, apply dental cement on the screws and on the periphery of the exposed skull.
- Using the dental drill, make a 5 mm diameter hole in the skull above the brain region of interest. Remove the fatty tissue between the skull and the brain and expose the brain region target using fine tweezers and soft tissue paper. Be careful not to damage the large blood vessels underneath the skull.
NOTE: By the end of this stage, the fish is prepared to implant the probe. Only the main steps specific to this protocol are described here. Several postoperative procedures (such as detailed documentation on the animal's health and sterilization of the surgery tools and area) are not presented or discussed because they are applicable to all surgeries with fish or small animals.
7. Implanting the Probe
NOTE: To complete the final step in the protocol, a manipulator that can hold the implant in place while it is inserted into the brain is needed.
- Use the manipulator to hold the logger box cover with the tetrodes pointing down toward the fish brain.
- Bend the reference electrode such that when the tetrodes are lowered into the brain, the reference stays outside the brain.
- Cut the grounds such that they fit into the skull. Optionally, connect one ground wire to one of the skull screws.
- Lower the implant such that the electrodes are inserted into the brain while the bottom part of the microdrive housing is near the skull.
- Start attaching the implant to the skull by applying a small quantity of dental cement between the housing and the nearest skull screw.
- After the first part of the dental cement is cured, apply dental cement and close the hole above the skull and the entire exposed skull.
NOTE: Usually several rounds of dental cement applications are needed in order to cover the entire exposed skull. - Install the logger and the battery in the box and seal the box with all the screws.
- Apply antibiotics and local painkillers according to the type of fish used for the experiments.
- Flush the fish's gills with fresh water until the fish starts to wake up. Remove the fish from the holder and place it back in its home tank.
NOTE: The fish is fully recovered within 60 min after surgery. - Make sure the fish is able to swim freely with the implant (Figure 3, Supplementary Video 1). If needed, readjust the size of the extruded polystyrene foam above the logger box such that the fish can balance easily.
Representative Results
During a recording session the goldfish swam freely in a square water tank while the neural activity in its telencephalon was recorded. The goal of these experiments was to study how the neural activity of single cells determines the fish's behavior. To do so, spiking activity needed to be identified in the recorded data. The brain activity, while being recorded, was digitized at 31,250 Hz and high-pass filtered at 300 Hz by the data logger. Then, offline, a band-pass filter (300−5,000 Hz) was applied to the signals, and the presorted raw data were separated into each tetrode's channels and the reference channel (Figure 4A). Next, common spike sorting algorithms12 were used to characterize single cell activity. First, each channel was manually filtered by the minimal spike amplitude threshold (relative to the noise levels of each channel). Then, because the tetrodes' tips are not in the same site, and the reference electrode was outside the brain, spikes that appeared in more than one tetrode or in the reference channel were also filtered. The filtered data were then manually clustered and filtered by shape, length, inter-spike interval (the time between subsequent action potentials must adhere to the refractory period of neurons), and by principal component analysis (PCA). Examples of single cell clustering vs. multiunit and noise clusters are presented in Figure 4.
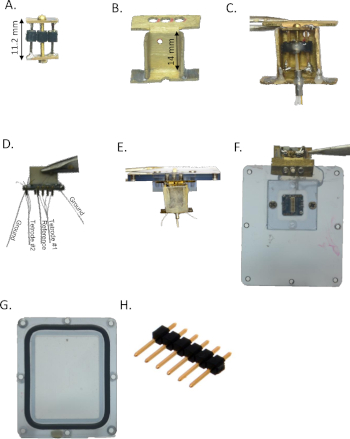
Figure 1: Implant assembly. (A) Microdrive, made out of a pin header, brass plates, and a screw. (B) Microdrive housing, made from a single brass plate by folding. (C) Microdrive assembly made with the microdrive (A) and the housing (B). (D) The tetrode array was made using EIB-16, two tetrodes, a reference electrode, and grounds connected to a connector (see Table of Materials). (E) and (F) The microdrive implant assembly is connected to the waterproof logger box cover. The tetrode assembly connector is located inside the box and the tetrodes are glued to the microdrive. (G) The logger box base where the logger and the battery are located. The O ring around the base is used for sealing. (H) Single row male pin headers strip. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
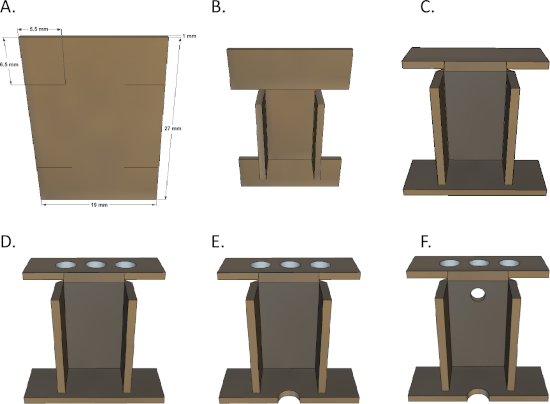
Figure 2: Microdrive housing folding technique. (A) Start with a 1 mm wide brass plate and make four slits. (B) Fold the middle part of the side inward. (C) Fold the upper part backward and the bottom part inward. (D) Drill three 3 mm holes in the top. (E) Engrave a 1 mm semicircle on the bottom. (F) Drill a 1 mm hole in the middle of the upper side. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
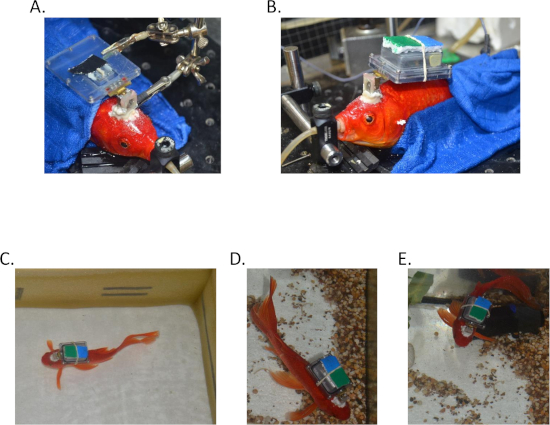
Figure 3: Recording from a freely behaving goldfish. (A) The tetrodes are implanted in the fish brain and the assembly is connected to the fish's skull. (B) The box is sealed with the logger inside. (C-E) A fish swimming freely with the assembly after surgery. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
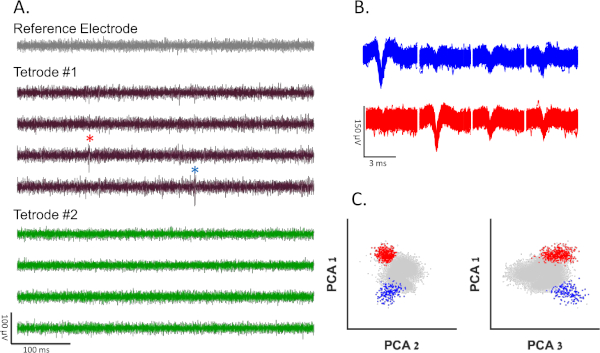
Figure 4: Representative results. (A) Recording 0.5 s long from a freely swimming fish 24 h after surgery. The signal is filtered using a band-pass filter (300−10,000 Hz). There is no high amplitude noise in the reference electrode, indicating a lack of motion artifacts. There are no action potentials in the second tetrode (green channels). The first electrode data are shown in the brown channels. Blue and red stars indicate spikes from blue and red clusters shown in panels B and C, respectively. (B) Spike shapes of two different clusters of single neurons, recorded from tetrode 1. (C) Projection on the first three principal components of the data from the first tetrode of all spike candidates that crossed the threshold. Blue and red clusters correspond to blue and red spike shapes from panel B. Gray dots represent neural noise or multiunit activity. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Supplementary Video 1: Swimming patterns: example of goldfish a day before implantation surgery (left) and a day after (right). Video shows similar swimming patterns, indicating that the fish is not impeded by surgery. Video speed is x1.8. Please click here to view this video (Right click to download).
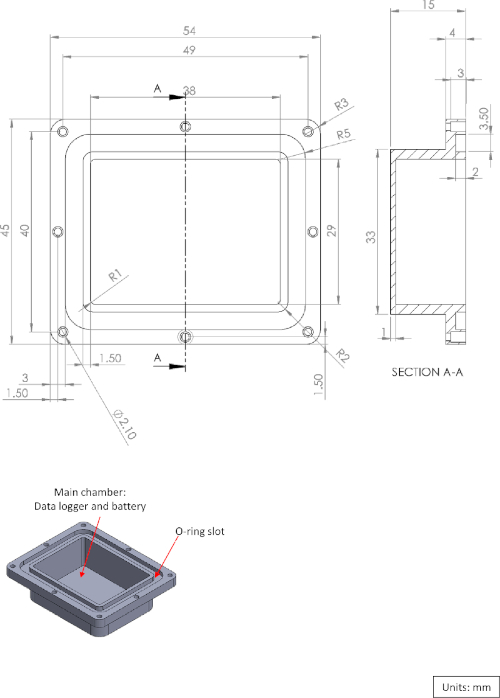
Supplementary Figure 1: Diagram of the logger box main chamber. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
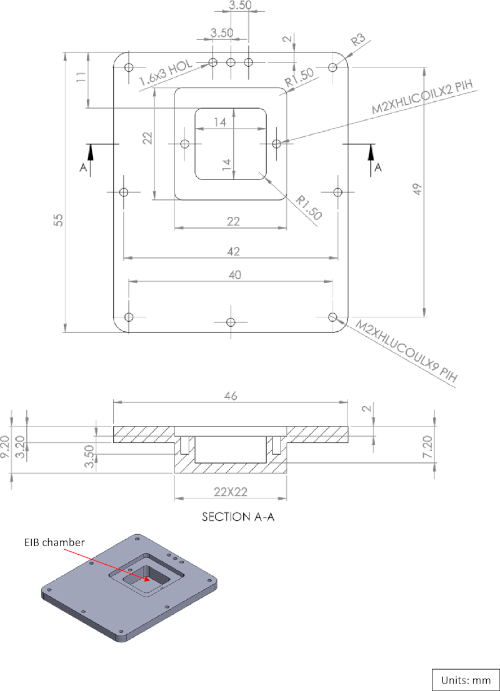
Supplementary Figure 2: Diagram of the logger box cover. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
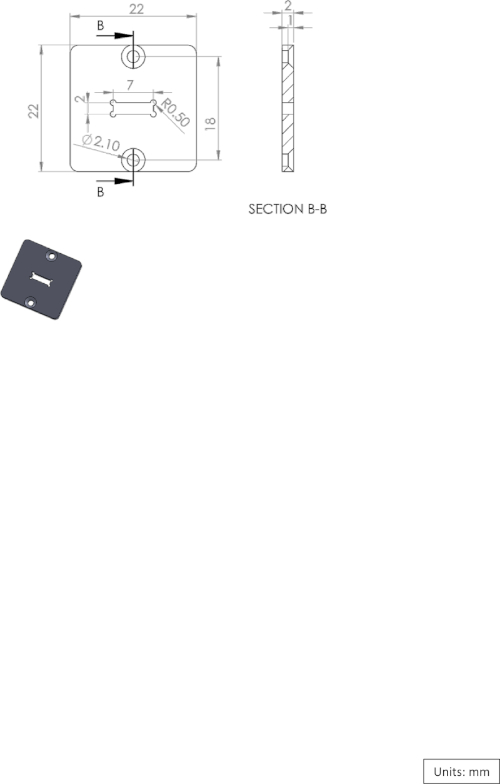
Supplementary Figure 3: Diagram of the EIB-16 chamber cover. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
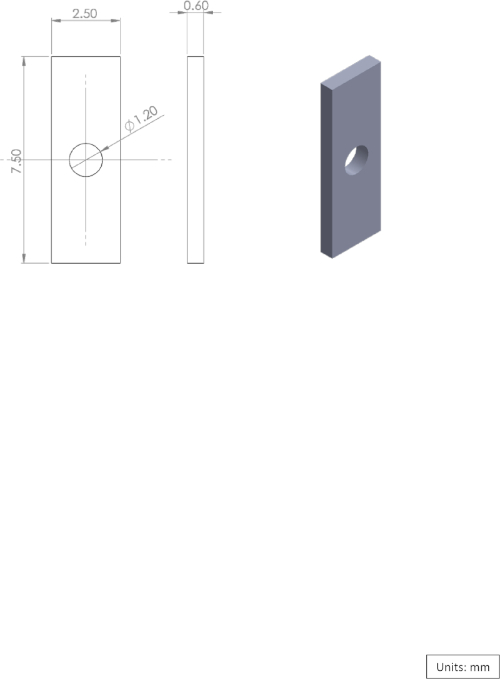
Supplementary Figure 4: Diagram of the brass plate used for the microdrive. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Supplementary File 1: Housing Diagram. Please click here to view this file (Right click to download).
Discussion
This protocol details the steps involved in implanting a tetrode array into the telencephalon of freely swimming goldfish. This technique implements a neural logger that amplifies and records the signals acquired from up to 16 channels along with a microdrive that can adjust the tetrode position in the brain. The microdrive makes it possible to adjust the position in the brain to optimize the recording.
This protocol can easily be modified for recording from other brain regions (see Vinepinsky et al.8 for recording from the optic tectum using a similar technique) or any other aquatic animal 15 cm long or larger (approximately equal to a goldfish head to tail, ~100 grams weight). In addition, the protocol can be modified to work with any data logger as long as it communicates at a frequency that can penetrate water. The logger used here communicates using a radio frequency of 900 MHz and can communicate through about 20 cm of water. A radio frequency of 2.4 GHz can also penetrate through ~15 cm of fresh water. Lower frequencies and other alternatives might give even better results13,14,15. The protocol presented here used a two-tetrode array with eight recording channels. In addition, the protocol can be modified to incorporate other probe geometries such as a wire array16 or silicone probes9.
There are several advantages to using a data logger over a full telemetry recording system or a tethered system. First, wireless communication adds noise to the recording. Therefore, full transmission of the data will reduce the signal quality. In addition, logging the data ensures no data are lost if communication fails. Furthermore, wireless systems allow the fish to swim freely, unlike in tethered animals. Finally, this protocol was developed to record action potentials but can also be used to record local field potentials by setting the logger analog high-pass filter to 1 Hz instead of 300 Hz. One disadvantage of the logger is the need to physically download the data and replace the battery when it runs down.
The microdrive suggested in the protocol significantly increases the likelihood of recording single cell activity. Without the microdrive device, the implanted tetrodes are placed approximately in the same recording site in the brain for the whole time the fish is being tested. This physically limits the likelihood of recording multiple single neurons from the same fish, and therefore curtails the recording yield per fish. The fact that the specific recording site in the brain remains unknown until after surgery strengthens the need for a movable device that makes it possible to move the electrodes in the brain after fixation as well.
An important feature of this protocol that was omitted for clarity is the determination of the electrode impedance. The electrode impedance can be adjusted by the selection of the wire diameter (i.e., a higher diameter leads to lower impedance), wire composition (e.g., tungsten or nichrome), and electrode coating (e.g., platinum black for tungsten and gold for nichrome) which yields wires with lower diameters and lower impedance. Because all these parameters are critical to the success of neuronal recordings, the reader is strongly encouraged to consult the vast literature on this subject, including Harris et al.17.
Note the importance of the reference electrode in detecting possible external noise sources in the system. The reference electrode is a relatively low impedance electrode that is inserted into the skull but is outside the brain. Because it does not come into contact with brain tissue, it records the signal's signature, which is composed of thermal noise, motion artifacts, and external noise. The major noise sources in this system are motion artifact and communication noises that can be controlled and timed by the logger. These noises can easily be detected by the signature they impose on the signal of the reference electrode.
Divulgaciones
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Nachum Ulanovsky and the members of the Ulanovsky lab for all their help. In addition, we are grateful to Tal Novoplansky-Tzur for helpful technical assistance. We gratefully acknowledge financial support from THE ISRAEL SCIENCE FOUNDATION – FIRST Program (grant no. 281/15), and the Helmsley Charitable Trust through the Agricultural, Biological and Cognitive Robotics Initiative of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev.
Materials
| 0.7 mm round drill bits | Compatible with the drill. | ||
| 15-blade Scalpel | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| 16 channel PCB board | Neurlynx | EIB-16 | |
| 1X3M phillips flat head screws | Stainless steel. Any type. | ||
| 1X3M phillips round head screws | Stainless steel. Any type. | ||
| 27 cm X 19 cm X 1 mm brass plate | See Figure 2 | ||
| 2X6M phillips flat head screws | Stainless steel. Any type. | ||
| 3140 RTV coating | Dow Crowning | 2767996 | |
| 75 µm Silver wire | A-M Systems | ||
| Brass machine screws #00-90 | 947-1006 | ||
| Brass plates 7.5mm X 2.5mm X 0.6mm | A 3D drawing is provided. See supplementary 1 | ||
| Coated Tungsten wire 25µm | California Fine Wire Company | 5000160 | Depending on the appication the tetrodes can be fabricated from any type of wire. Popular wires are nicrome wires that can be found with lower diameters (eg. A-M systems, 762000) |
| Coated Tungsten wire 50µm | A-M Systems | 795500 | Can be replaced with any other wire with low impedance |
| Cyanoacrilic glue | |||
| Dental Burnisher | ComDent UK | Any small sterille stainless-still tool will do. | |
| Dental cement – GCFujiPLUS | GC | 431011 | Other dental cements would probably will work as well although we have never tried any other. |
| Dental drill or nail polish drill | Dental drills are expensive, a nail polish drill can be a cheap replacement. | ||
| Drill bit #65 | 947-65 | ||
| Fast curing epoxy | Any 5 minutes curing epoxy can be used here. | ||
| Logger box with O-ring sealing | A 3D drawing is provided. See supplementary 1-3. The box should be machine fabricated (do not use 3D printers). Use transperant material, to be able to see the indicator LEDs on the logger. | ||
| Motorized turning device | Custom made as described in "open ephys" website. Can also be purchusaed from neurolynx ("Tetrode Spinner 2.0") or bulit by other means. | ||
| Mouselog-16 Neural logger | Deuteron Technologies Ltd | There are several neural loggers available on the market, including: SpikeGadget (UH32 32channels) and Neurologger 2/2A/2B of Alexei Vyssotski. It should be noted that weight is not a major contraint since it can be counterbalanced with floating Styrofoam | |
| MS-222 | Sigma Aldrich | E10521 | Ethtl 3-aminobenzoate methanesulfonate 98% |
| Nano-Z plating | White Matter LLC | The nano-Z can be bought from several supllieres. Any impedance meter can be used, e.g. IMP-1 / 6662 / 2788, BAK Electronics. | |
| PCB pins | Neurlynx | Neuralynx EIB Pins | |
| Polymide tubing 250µm | A-M Systems | 822000 | |
| Rechargable battery | 3.7 Lipo battery, 370 mAh. Holds about 6 hours of recording. Smaller or larger battries can be used to reduce the weight or extend recording time. | ||
| Silicone tubing 0.64 mm | A-M Systems | 806100 | |
| Stainless steel 1.5 mm | A-M Systems | 846000 | |
| Sudium Bicarbonate | Sigma Aldrich | S9625 | |
| Tap #00-90 | 947-1301 | ||
| Vaseline | Any type of soft petroleum skin protectant can be used here. |
Referencias
- Jacobson, M., Gaze, R. M. Types of visual response from single units in the optic tectum and optic nerve of the goldfish. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology and Cognate Medical Sciences. 49 (2), 199-209 (1964).
- Ben-Tov, M., Donchin, O., Ben-Shahar, O., Segev, R. Pop-out in visual search of moving targets in the archer fish. Nature Communications. 6, 6476 (2015).
- Zottoli, S. J. Correlation of the startle reflex and Mauthner cell auditory responses in unrestrained goldfish. Journal of Experimental Biology. 66 (1), 243-254 (1977).
- Canfield, J. G., Rose, G. J. Activation of Mauthner neurons during prey capture. Journal of Comparative Physiology A. 172 (5), 611-618 (1993).
- Canfield, J. G., Mizumori, S. J. Methods for chronic neural recording in the telencephalon of freely behaving fish. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 133 (1-2), 127-134 (2004).
- Orger, M. B., de Polavieja, G. G. Zebrafish behavior: opportunities and challenges. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 40, 125-147 (2017).
- Vanwalleghem, G. C., Ahrens, M. B., Scott, E. K. Integrative whole-brain neuroscience in larval zebrafish. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 50, 136-145 (2018).
- Vinepinsky, E., Donchin, O., Segev, R. Wireless electrophysiology of the brain of freely swimming goldfish. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 278, 76-86 (2017).
- Vandecasteele, M., et al. Large-scale recording of neurons by movable silicon probes in behaving rodents. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments). (61), e3568 (2012).
- Ferguson, J. E., Boldt, C., Redish, A. D. Creating low-impedance tetrodes by electroplating with additives. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical. 156 (2), 388-393 (2009).
- Arcot Desai, S., Rolston, J. D., Guo, L., Potter, S. M. Improving impedance of implantable microwire multi-electrode arrays by ultrasonic electroplating of durable platinum black. Frontiers in Neuroengineering. 3, 5 (2010).
- Lewicki, M. S. A review of methods for spike sorting: the detection and classification of neural action potentials. Network: Computation in Neural Systems. 9 (4), R53-R78 (1998).
- Teixeira, F. B., Freitas, P., Pessoa, L. M., Campos, R. L., Ricardo, M. Evaluation of IEEE 802.11 underwater networks operating at 700 MHz, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems. , (2015).
- Sendra, S., Lloret, J., Rodrigues, J. J., Aguiar, J. M. Underwater wireless communications in freshwater at 2.4 GHz. IEEE Communications Letters. 17 (9), 1794-1797 (2013).
- Lloret, J., Sendra, S., Ardid, M., Rodrigues, J. J. Underwater wireless sensor communications in the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band. Sensors. 12 (4), 4237-4264 (2012).
- Hoogerwerf, A. C., Wise, K. D. A three-dimensional microelectrode array for chronic neural recording. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 41 (12), 1136-1146 (1994).
- Harris, K. D., Quiroga, R. Q., Freeman, J., Smith, S. L. Improving data quality in neuronal population recordings. Nature Neuroscience. 19 (9), 1165 (2016).

