siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in Neural Stem Cells
Abstract
Source: Nguyen, B. H., et al. Culturing and Manipulation of O9-1 Neural Crest Cells. J. Vis. Exp (2018)
This video demonstrates the use of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to silence specific genes of interest in neural stem cells and differentiate them into desired cell types using appropriate differentiation medium. This procedure enables the study of the critical role of specific genes in the differentiation process of neural stem cells.
Protocol
1. Manipulation of O9-1 cells
- Performing siRNA knockdown in O9-1 cells
- Thaw and coat a 24-well plate with a basement membrane matrix before starting the experiment. Recover and seed O9-1 cells, allowing them to grow to 60% to 80% confluency.
- Dilute liposomes in serum-free media according to the appropriate well volume. Dilute siRNA in serum-free media to the final. Add diluted siRNA to diluted liposomes in a ratio recommended by the manufacturer. Mix well by pipetting and then incubate.
NOTE: Follow the manufacturer's guide on the volume used, time, and temperature of incubation. - Add an appropriate volume of siRNA-lipid complex to cells according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Incubate cells for 24 h in a standard cell culture incubator (37 °C, 5% CO2). Perform downstream steps as appropriate (extract RNA, extract proteins, staining, etc.)
NOTE: siRNA knockdown times and concentrations can vary depending on the individual experiment.
2. O9-1 cell differentiation
- Differentiation of O9-1 cells into osteoblasts
- To prepare osteogenic differentiation media, dilute the following in alpha-MEM (final concentrations are indicated): 0.1 μM dexamethasone, 100 ng/mL bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2), 50 µg/mL ascorbic acid, 10 mM b-glycerophosphate, 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin.
- Detect the osteoblast marker, osteocalcin, in differentiated osteoblasts by immunostaining, as shown in Figure 1.
NOTE: Osteogenic differentiation can also be evaluated by using other markers of osteoblasts or with Alizarin red staining or alkaline phosphatase staining.
- Differentiation of O9-1 cells into smooth muscle cells
- To prepare smooth muscle cell differentiation media, dilute the following in DMEM (final concentrations are indicated): 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 10% FBS.
- Asses smooth muscle cell differentiation with immunofluorescence staining by using antibodies against markers of smooth muscle cells, such as smooth muscle actin (SMA), shown as an example in Figure 2.
Representative Results
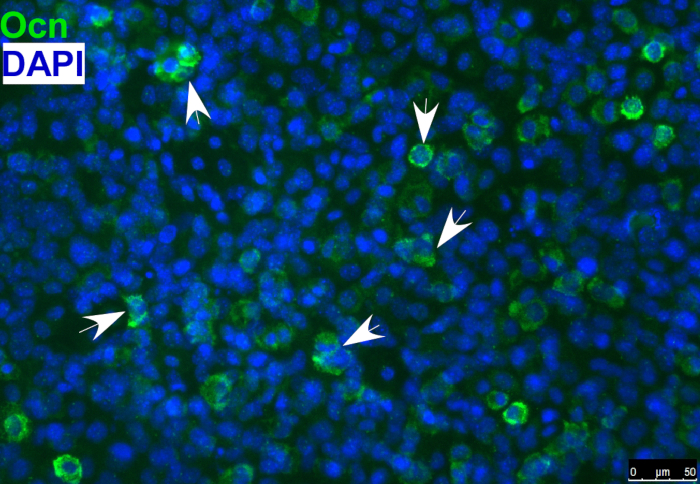
Figure 1: Immunofluorescence staining of osteoblast marker osteocalcin (Ocn) indicating that O9-1 cells gave rise to osteoblast cells under osteogenic differentiation conditions. Cells were stained with osteoblast marker Ocn antibody (green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate Ocn-positive cells. Osteocalcin (Ocn, an osteoblast marker); DAPI (′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole).
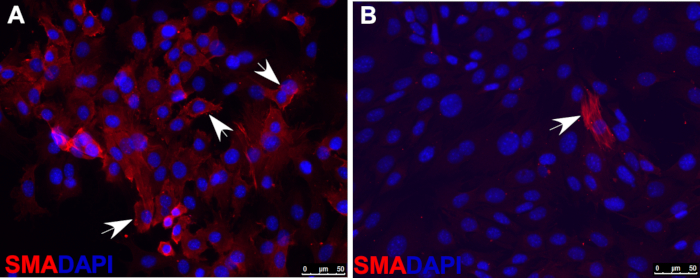
Figure 2: Immunofluorescence staining of smooth muscle actin (SMA) indicating that, under smooth muscle cell differentiation conditions, most wild-type O9-1 cells gave rise to smooth muscle cells (A), whereas Yap-null O9-1 cells failed to differentiate into smooth muscle cells (B). Cells were stained with SMA antibody (red), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate SMA-positive cells.
Divulgaciones
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| O9-1 mouse cranial neural crest cell line | Millipore Sigma | SCC049 | |
| DMEM, high glucose, no glutamine | Gibco | 11960-044 | |
| DMEM, high glucose | Hyclone | SH30243.01 | |
| FBS (fetal bovine serum) | Millipore Sigma | ES-009-B | |
| Penicillin – streptomycin | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| L-glutamine 200mM (100X) | Gibco | 25030-081 | |
| Trypsin-EDTA 0.25% in HBSS | Genesee Scientific | 25-510 | |
| DPBS (Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline) without calcium or magnesium | Lonza | 17-512F | |
| MEM non-essential amino acids (MEM NEAA) 100X | Gibco | 11140-050 | |
| Sodium pyruvate (100mM) | Gibco | 11360-070 | |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | Sigma | M-7522 | |
| Recombinant human fibroblast growth factor-basic (rhFGF-basic) | R&D Systems | 233-FB-025 | |
| Mitomycin C | Roche | 10107409001 | |
| Matrigel matrix | Corning | 356234 | |
| DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide) | Millipore Sigma | MX1458-6 | |
| Lipofectamine RNAiMAX | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 13778-075 | |
| Opti-MEM I (1X) | Gibco | 31985-070 | |
| Minimum essential medium, alpha 1X with Earle's salts, ribonucleosides, deoxyribonucleosides, & L-glutamine | Corning | 10-022-CV | |
| ON-TARGETplus Wwtr1 siRNA | Dharmacon | L-041057 | |
| ON-TARGETplus Non-targeting Pool | Dharmacon | D-001810 | |
| ON-TARGETplus Yap1 siRNA | Dharmacon | L-046247 | |
| FCS (fetal calf serum) | |||
| ITS (insulin-transferrin-selenium ) | |||
| TGF-b3 | |||
| Ascorbic acid | |||
| BMP2 (bone morphogenetic protein 2) | |||
| Dexamethasone | |||
| B-27 supplement |

