Combined Recording of Mechanically Stimulated Afferent Output and Nerve Terminal Labelling in Mouse Hair Follicles
Abstract
Source: Bewick, G. et al., Combined Recording of Mechanically Stimulated Afferent Output and Nerve Terminal Labelling in Mouse Hair Follicle Lanceolate Endings. J. Vis. Exp. (2016).
This video demonstrates the combined recording of mechanically stimulated afferent output and nerve terminal labeling in the hair follicles of a mouse pinna. It outlines the steps involved in the mechanical stimulation of hair follicle nerve terminals before and after exposure to a fluorescent membrane dye, electrophysiology recording of the generated action potentials, and visualization of the nerve terminal labeling in the hair follicles.
Protocol
All procedures involving sample collection have been performed in accordance with the institute's IRB guidelines.
1. Electrophysiological Recording Setup
- Pin the mouse external ear (pinna) skin to the PDMS-lined base of a recording chamber with fine insect pins around the edges (~6-8 per ear), placing the cleaned nerves at the base of the ear near two suction electrodes – one for recording (to take the nerve) and the other an indifferent electrode (to provide the neutral signal to a differential amplifier).
- For the recording electrode, carefully match the aperture and internal diameter of the opening to the combined thickness of the two nerves, so they fit as snugly as possible and for as great a length as possible.
- Draw the nerves into the electrode by gentle suction from a 2 ml syringe attached to the other end with silicone rubber tubing. Ensure the nerves are straight, not folded or doubled up.
- Develop a high electrical resistance/impedance fit by using stronger suction to draw connective tissue or adipose tissue to form a plug that tightly seals the aperture around the nerve.
- Fill the other (indifferent) electrode with saline by suction if necessary (it may be filled by capillary action).
- Place identical recording wires (silver or platinum) into the internal bore of the recording electrodes to contact the saline and the nerve (recording) or narrowed, fire-polished end (indifferent) of the electrode. Each electrode is soldered individually to different cores of two-core screened cable. Place the bath (ground) electrode (Ag/AgCl pellet) into the bath and ground it to the screen of the two-core cable connected to the recording electrodes.
- Feed the electrical activity from the two electrodes into the separate channels of a differential amplifier, filter (band-passed 0.2-2 kHz), and view on an oscilloscope screen. Check that channel A (recording) and channel B (indifferent) electrical noise levels look similar. At this stage it may not be possible to see the normal spontaneous action potentials in channel A before the two electrodes are balanced.
- Redress any differences in background noise between electrodes by increasing the impedance of the recording (channel A) or indifferent (channel B) electrodes. Do this by sucking areolar (adipose) connective tissue further into either electrode and/or applying greater suction force on the 50 ml syringe.
- Once 'balanced' in this way, switch back to differential (A-B) recording and look for spontaneous action potentials (APs) in the trace or when stroking hairs at the margin of the pinna. If no activity (spiking) is seen, re-check the tight fit of the nerve in the recording electrode and the areolar connective tissue in the indifferent electrode – usually, the tighter (higher resistance) the seal and the more equal the impedance in the two electrodes, the better. With practice, this will achieve a good quality (>2:1) signal:noise ratio.
- Record the electroneurogram via a lab interface and electrophysiology software running on a computer. An audio output of spiking is very useful and can be achieved by feeding the neurogram through an audio amplifier and associated audio speaker. Adjust the threshold to be just above the baseline noise (identified by the absence of white-noise 'hiss').
- To increase drug or fluorescent styryl dye access to the lanceolate endings, carefully peel away the sub-dermal adipose layer near the pinna margin, opening a window of ~5 mm x 5 mm, exposing the dermis and base of the follicles (Figure 1A, B).
- Pin back a fold of ~1 mm of adipose-cleared ear skin at the leading margin (at the level of the window just produced, if applicable), leaving a clear saline-filled gap between the apposed skin layers. Gently stroke the hairs protruding along the folded edge with a pin or grounded fine forceps, without touching the skin, to locate the area of maximal AP output on the oscilloscope and the distinctive 'clicks' and 'pops' in the audio output.
2. Recording Stimulus-evoked Action Potentials
- Position the mechanical stimulation probe – a fire-polished 10 cm borosilicate microelectrode glass attached to a ceramic piezo-electric actuator – so movement is parallel with the skin fold. Place the tip about 0.5-1 mm from the skin fold, so it touches the hairs but not the skin. Verify effective stimulation by slowly moving the probe tip manually to deflect the hairs and observe/listen to the spiking.
- Use the software to drive mechanical stimulation of 1-3 hairs (e.g. 3 sec at 5 Hz sinusoids, every 10 sec. Probe displacement 200-500 µm), and record the stimulation-evoked responses in the nerves.
- Give several identical mechanical stimulation trains at 10 sec intervals. Optimize the probe position for repeatability, then reduce frequency of stimulation according to experimental protocol (e.g. drop repeat rate from 10 sec to 30 sec).
- Use the software to discriminate AP-like activity, e.g., using a simple threshold set to ~2x the high-frequency noise amplitude and ~25% of the largest APs.
- Count the APs crossing the threshold as 'events', quantifying the frequency and characteristics of the APs produced.
3. Recording Stimulus-evoked Firing Combined with N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(4-(dibutylamino) styryl) Pyridinium Dibromide Labeling
- To examine the effects of styryl dyes on stimulus-evoked afferent firing and terminal labeling, add the appropriate concentration of a styryl dye of choice to the bathing solution and continue with the electrical recording.
- After the required exposure time (usually at least 30 min), prepare the preparation for viewing the follicles. Unfold the skin flap by removing the retaining pins, and expose the cleared dermal area to reveal the terminal labeling.
- Wash away external dye with dye-free saline, making 3 complete changes of saline.
- Incubate in the final change of gassed dye-free saline for 10-15 min to allow the most persistent dye contamination to leach from exposed/external membranes.
- Remove non-internalized dye remaining on membranes with a sequestering agent (sulfobutylated beta-cyclodextrin, 1 mM, 5 min) in saline.
- Transfer the recording chamber to the stage of an upright epifluorescence microscope and engage the chamber with the stage/slide movement mechanism.
- Illuminate the preparation with excitation light appropriate for the styryl dye. Use a 10X or 25X fluorescence microscope objective to observe the follicle labeling (Figure 1).
Representative Results
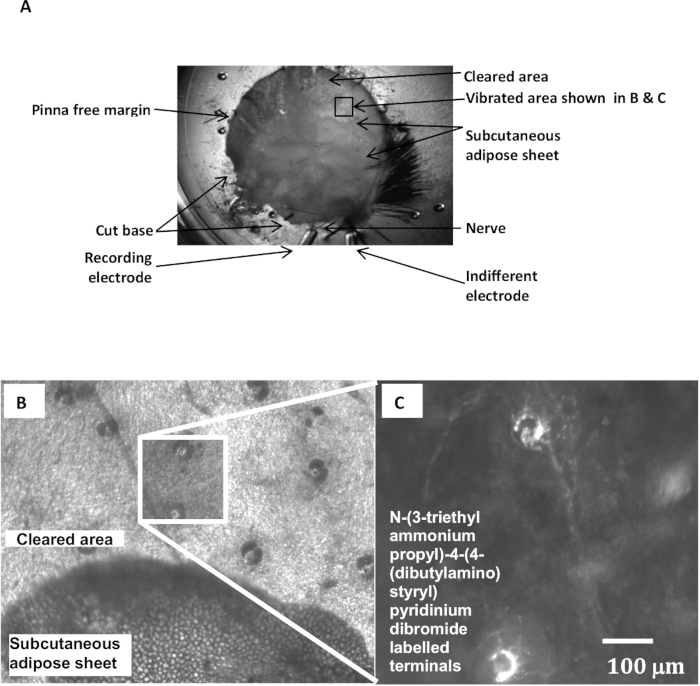
Figure 1: Electrophysiological Recording Arrangement and N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(4-(dibutylamino) styryl) Pyridinium Dibromide Labeling of Hair Follicle Afferent Lanceolate endings. (A) A pinna preparation set up for an electrophysiological experiment showing the pinna orientation, the location of the nerves, the recording electrodes and the exposed area of follicle innervation after adipose tissue removal. (B) Several hair follicles are visible in bright field illumination in the area cleared of overlying adipose tissues down to the dermis. The dark, usually bilobed, shapes are sebaceous glands. (C) Enlarged view of the boxed area in B) showing two lanceolate endings labelled with the styryl dye N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(4-(dibutylamino) styryl) pyridinium dibromide and imaged after mechanical stimulation by epifluorescence microscopy.
Offenlegungen
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| PDMS – Sylgard 184 | Dow Corning | Flexible, inert, translucent solid silicone polymer. | |
| No. 3 Dumont forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11231-20 | |
| Austerlitz Insect pins | Fine Science Tools | 26002-10 | Very fine pins to attach pinna preparation securely to the PDMS with minimal damage. |
| AC Differential Preamplifier | Digitimer | Neurolog NL104A | Amplifying the size of the incoming afferent electroneurogram. Differential recording minimises the extraneous electrical noise and baseline drift. |
| High/Low-pass Filter | Digitimer | Neurolog NL125 | Signal conditioning, by reducing extraneous electrical noise to ensure best signal to noise ratio. |
| Spike Trigger | Digitimer | Neurolog NL201 | Sets the event detector threshold and displays it on the oscilloscope. This shows the action potential detection efficacy. |
| Audio Amplifier & speakers | Digitimer | Neurolog NL120S | Useful audio monitoring for the presencec of electrical firing of the sensory endings while adjusting the mechanical stimulation preparation down the microscope |
| Oscilloscope | Digitimer | PM3380A | We use this old model but any standard oscilloscope will suffice. |
| Piezo electroceramic wafer | Morgan Electroceramics, Southampton UK | PZT507 | Electrophysiology/computer interface |
| Piezo electroceramic powersupply | Home made | 0-200V DC output to drive the ceramic wafer displacement, with variable electronic control of output via recording/stimulation software and computer interface. We use Spike2 software and 1401micro computer interface. | |
| Electrophysiology Software | Cambridge Electronic Design (CED) | Spike2 v7 | Electrophysiology recording, stimulation and data analysis software |
| Laboratory interface | Cambridge Electronic Design (CED) | 1401 micro | Electrophysiology interface, between the amplifier/filters and the computer. It inputs the electroneurogram and also drives the electroceramic movement. |
| FM1-43/Synaptogreen C4 | Biotium/Cambridge Bioscience | BT70020 | Fluorescent membrane probe that reversibly partitions into the outer leaflet of cell membranes. Used predominantly for monitoring vesicle membrane endo-/exocytosis. |
| Advasep 7 | Biotium/Cambridge Bioscience | BT70029 | A sulfonated b-cyclodextrin derivative that chelates FM1-43 (& other styryl pyridinium dyes) out of the exposed membranes, leaving internalised dye to be seen more clearly by lowering the background labelling/fluorescence. |
| Retiga Exi Fast 1394 | Qimaging | Monochrome, cooled CCD camera – basic model | |
| Volocity 3D Image Analysis Software | Perkin Elmer | Volocity 6.3 | Image capture and analysis software. |

