Preparation of Colliculo-Thalamocortical Slices from a Mouse Pup Brain
Abstract
Source: Slater, B. J., et al., Modification of a Colliculo-thalamocortical Mouse Brain Slice, Incorporating 3-D printing of Chamber Components and Multi-scale Optical Imaging. J. Vis. Exp. (2015)
The video demonstrates the preparation of colliculo-thalamocortical brain slices from mouse pup brains. An isolated brain is aligned on a marked slide and cut at an angle to align the auditory midbrain and forebrain in the same plane. The brain is then sliced using a vibratome, and the slices containing the major auditory midbrain and forebrain structures are transferred to a holding chamber for preservation.
Protocol
All procedures involving sample collection have been performed in accordance with the institute's IRB guidelines.
1. Preparation for and Removal of Brain from Mouse for Slicing
- Prepare for perfusion and slice incubation.
- Approximately 30 min before slicing, prepare high sucrose cutting solution and low calcium artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) for incubation of the slice prior to recording or imaging.
- Lay out all necessary tools (large blunt end scissors, small spring scissors, anatomic forceps, large scissors or guillotine, iris scissors, jewelers forceps, 10 ml syringe with 27G x 1/2 inch needle, small piece of 1 cm x 2 cm filter paper, and a broken tipped Pasteur pipette for slice transfer) for perfusion and slicing, and prepare perfusion tray.
- Set up incubating chamber with oxygenated aCSF in a 32 oC water bath and a culture dish filled with cutting solution.
- Prepare cutting stage for slicing.
- Cut a small piece of 3% agar approximately 1 cm3 to use as a backstop for the brain and 1.5 cm x 1.5 mm x 3 mm for a bump to be used to prop up the inferior colliculus (IC).
- Glue the backstop onto the stage with cyanoacrylate adhesive as well as the bump on the right side of the backstop such that they form an 80o angle.
- Remove the brain.
- Deeply anesthetize a postnatal day 12- postnatal day 20 (p12-p20, ideally p14-18) mouse with ketamine 100 mg/kg and xylaxine 3 mg/kg (or comparable ethics committee approved procedure).
Note: Confirm proper anesthesia level via lack of response to toe pinch. As the animal is under anesthesia briefly, ophthalmic ointment is unnecessary. - Using blunt end scissors, expose the ribcage from the xiphoid process to the neck.
- Find the xiphoid process, and make a horizontal cut of approximately 1.5 cm.
- Make two vertical cuts from the ends of the previous horizontal cut to the shoulders, approximately 1.5 cm each.
- Cut through the diaphragm and the costochondral junctions to expose the heart.
- With small spring scissors, make a small, 2-5 mm cut in the right atrium, from the ventral to dorsal side of the heart.
- Using a 10 ml syringe with a 27G x 1/2 inch needle, inject the left ventricle and quickly perfuse the animal with high sucrose cutting solution.
- Once the blood runs clear, use larger scissors to remove the head.
Note: We have not systematically assessed the utility of perfusion. However, in our experience, transcardiac perfusion in mice this young can be done with nearly 100% success, and does have the benefit of eliminating red blood cells, which can fluoresce and interfere with imaging. - Cut the skin down the midline to expose the skull.
- Using bent iris scissors, cut the skull between the eyes, then starting from the cut between the eyes, carefully cut from anterior to posterior along the midline suture taking care not to damage the brain underneath.
Note: The dura usually comes off with the skull. If necessary, remove the dura before carefully removing the brain. - Using jewelers forceps, pry open the skull and carefully remove the brain, then place the brain in cutting solution. Take care to avoid damaging the cortices.
- Deeply anesthetize a postnatal day 12- postnatal day 20 (p12-p20, ideally p14-18) mouse with ketamine 100 mg/kg and xylaxine 3 mg/kg (or comparable ethics committee approved procedure).
2. Preparing Brain for Slicing
- Preparing brain for mounting on vibratome stage.
- Using a slide marked with two lines at 90o and a diagonal line at 17o from the top left to bottom right, intersecting where the two lines meet, place the brain dorsal side up, using a razor blade, remove 2-4 mm of the rostral end brain creating a flat surface.
- Place the brain caudal side up on the newly created flat surface, and align the dorsal surface of the brain with the horizontal and the midline of the brain with the vertical line.
- Align the razor blade with the 17o line, tilt the razor at a 30o angle and remove approximately 3 mm of the right cortex in a double diagonal cut (17o from horizontal plane and 60o from the coronal).
- Mounting brain on vibratome stage.
- Place a small piece of filter paper 1 cm x 2 cm on the ventral side of the brain so that the long dimension is perpendicular to the midline.
- Carefully apply a small amount of cyanoacrylate adhesive to the area in front of the backstop (and to the left of the bump).
- Place the double diagonally-cut brain face on to the glue so that the caudal part of the brain and hindbrain are propped upon the bump and the right side of the brain is against the backstop.
- Delicately press down on the brain, ensuring that the entire surface is in contact with the slicing chamber.
3. Obtaining the Colliculo-thalamocortical Slice
- Quickly take the cutting stage and place in the vibratome, fill the stage with cutting solution.
- Align the blade with the top (ventral side) of the brain.
- Remove 1-1.5 mm from the top of the brain, remove 300-500 µm slices and assess depth after removal.
Note: When the IC, the medial geniculate body (MGB), and the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) are all visible, and the dentate gyrus forms a 'C' shape take one to two 600 µm slices. See Figure 1A. - Place slices in heated (32 oC) holding chamber.
Representative Results
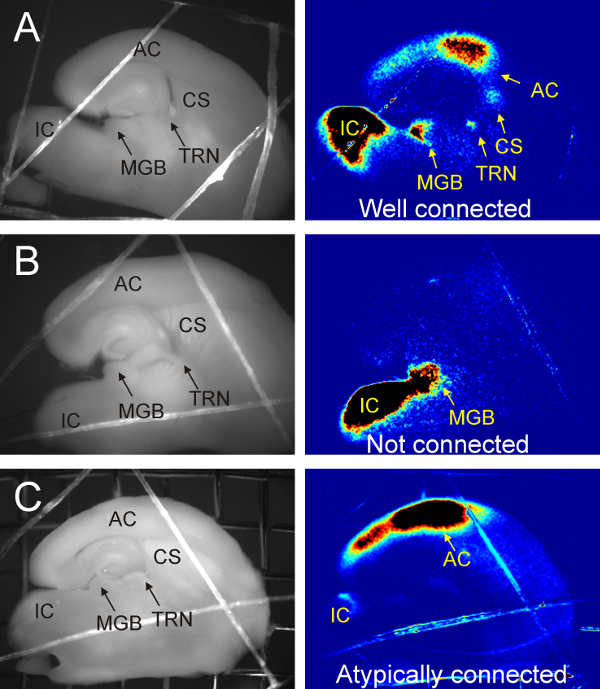
Figure 1. Flavoprotein autofluorescence imaging of colliculo-thalamocortical brain slice. (A) Connected colliculo-thalamocortical brain slice as confirmed by flavoprotein autofluorescence. Electrical stimulation at 0.05 Hz of IC imaged at 4 Hz and Fourier processed to show power at stimulation frequency. Note activation of MGB, thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) and, auditory cortex (AC) as well as the corpus striatum (CS). (B) Unconnected slice. Electrical stimulation of IC with only activation of MGB. Entire pathway was not captured likely due to 17o angle being slightly too steep. (C) Atypical activation of AC. Electrical stimulation of IC with activation of AC without visible signal in the MGB or TRN. Pathway likely intact however the active cells in the MGB are likely on the other side of the tissue.
Offenlegungen
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| High sucrose cutting solution | in mM: 206 sucrose, 10.0 MgCl2, 11.0 glucose, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 0.5 CaCl2, 2.5 KCl, pH 7.4 | ||
| Low calcium aCSF | in mM: 126 NaCl, 3.0 MgCl2, 10.0 glucose, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 1.0 CaCl2, 2.5 KCl, pH 7.4 | ||
| aCSF | in mM: 126 NaCl, 2.0 MgCl2, 10.0 glucose, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 2.0 CaCl2, 2.5 KCl, pH 7.4 | ||
| DMSO | Life Technologies | D12345 | Lot: 1572C502 |
| Large culture dish | Fisherbrand | 08-757-13 | 100x15mm culture dish |
| Small culture dish | Falcon | 353001 | 35x10mm culture dish |
| Raised culture membrane | Millicell | PICMORG50 | Used to maintain oxygenated fluid perfusion on both sides of slice. |
| Agar for blocking brain | 3% by weight in water |

