Analyzing Purkinje Cell Survival in Organotypic Cerebellar Slice Cultures
Abstract
Source: Rakotomamonjy, J., et al. Purkinje Cell Survival in Organotypic Cerebellar Slice Cultures. J. Vis. Exp. (2019)
This video illustrates a technique for obtaining cerebellar organotypic slices from a mouse pup's brain and culturing the slices in media supplemented with nutrients and growth factors to mimic cerebellar development in vitro. Additionally, specific cerebellar slices are treated with a test compound, and the compound's neuroprotective ability is analyzed using an immunofluorescence staining technique.
Protocol
1. Preparation prior to organotypic cerebellar slice cultures
- In a cell culture hood sprayed with 70% ethanol beforehand, prepare 200 mL of culture medium in a 250 mL bottle-top vacuum filter attached to a sterile bottle receiver. Add 100 mL of Basal Medium Eagle (BME), 50 mL of Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS), 50 mL of heat-inactivated horse serum, 1 mL of 200 mM L-Glutamine (final concentration 1 mM), and 5 mL of 200 g/L glucose (final concentration 5 mg/mL). Vacuum-filter the culture medium and keep it at +4 °C for up to a month.
- In the sterilized biosafety cabinet, take out a 6-well culture plate from its package. Fill each well with 1 mL of culture medium. If a treatment is tested, add the pharmacological agent to the treated well, and the same volume of vehicle solution for the control well. In the present study, we added 1 μL of sterile 3 M KCl solution to the treated well (30 mM final) and 1 μL of sterile water to the control wells.
- Bring inside the cell culture hood the needed number of individually wrapped cell culture inserts with hydrophilic polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane (pore size = 0.4 μm). Carefully unwrap them and take out the cell culture inserts with sterile forceps. Drop them one by one in a well of a 6-well plate, avoiding bubbles at the interface between the insert membrane and the cell culture medium. Let the inserts equilibrate in the medium in a 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator for at least 2 h before culture.
NOTE: The tissue chopper permanently resides in the cell culture hood. - Prepare two 200 mL beakers, one filled with 150 mL sterile water, and the other filled with 150 mL 70% ethanol. Dip the surgical tools in the 70% ethanol bath and then in water prior to using them.
NOTE: Do not use surgical tools immediately following contact with ethanol. - Disinfect the double-edged blade in the 70% ethanol beaker. Place it on the blade holder using sterile forceps and hold it into place using the blade clamp wrench. Let it dry until use.
- Disinfect the plastic disc provided with the tissue chopper in the 70% ethanol beaker. Spray the cutting table with 70% ethanol prior to placing the disc on it. Let dry until use.
2. Dissection and Cerebellar Organotypic Slice Cultures
- Bring the mouse pup inside the cell culture hood to perform the dissection.
- Decapitate the pup quickly using straight operating scissors (Figure 1A).
- While holding the pup's head by the nose with straight dressing forceps, cut open the scalp using straight eye scissors, starting from the posterior end, and going lateral to midline.
- Proceed identically for the skull.
NOTE: Make sure to point scissor tips outwards to avoid damaging the cerebellum during dissection. - Take out the brain and transfer it to a 60-mm dish filled with cold HBSS + 5 mg/mL glucose.
- Carefully dissect out the cerebellum using sterile straight fine forceps (Figure 1B). Transfer it onto the plastic disc placed on the cutting table of the tissue chopper using sterile curved fine forceps.
- Orient the tissue by rotating the cutting table to perform parasagittal sections.
- Move the cutting table by pulling the table release knob to the right, so the blade is positioned at the edge of the tissue.
- Adjust the slice thickness to 350 µm and the blade speed to medium.
- Start the chopper. Once the whole cerebellum has been sliced (Figure 1C), turn off the chopper.
- Remove the plastic disc with sterile forceps.
- Carefully bring the plastic disc close to a 60-mm dish containing HBSS + 5 mg/mL glucose. Pipette cold HBSS + 5 mg/mL glucose onto the tissue using a sterile transfer pipette to allow harvesting of cerebellar slices in the buffer-filled dish.
- Separate the cerebellar slices from each other using a microprobe. Take out good quality sections with the transfer pipette (it is recommended to use tissue sections that are close to the vermis) and drop them off in a pre-equilibrated cell culture insert (Figure 1D).
- Position the cerebellar slices on the cell culture insert using the microprobe, then carefully remove the excess HBSS + 5 mg/mL glucose solution with the transfer pipette.
NOTE: At this stage the tissue is extremely tender and prone to physical damage. The maximum number of cerebellar slices per cell culture insert depends on the age of the donor animal. 6–8 slices can be cultured for a P0–P4-old animal, and 4–6 slices for animals older than P5. - Place the culture dish in the incubator, changing the medium completely every 2–3 days.
- To assess Purkinje cell survival, slices can be collected as early as 5 days in vitro. For other purposes, they can be maintained in culture for several weeks (Figure 1F).
NOTE: In the case of Purkinje cell survival experiments, there is no need to renew the pharmacological treatment when changing cell culture medium (Figure 1F).
3. Immunofluorescence
- Take out the 6-well plate from the incubator. Remove cell culture medium, wash the cell culture insert with 1x PBS, and fix the slices with cold 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 1 h, with 1 mL under the cell culture insert and 500 µL on top of the cell culture insert.
- Wash the inserts 4x 10 min with 1x PBS, with 1 mL under and 500 µL on top of the insert, on an orbital shaker.
- With a brush, transfer the cerebellar slices from 1 cell culture insert to 1 well of a 24-well pre-filled with 1x PBS, 0.25% Triton X-100, and 3% BSA (PBS-TB), 500 µL/well.
- Permeabilize and block the slices by incubation in PBS-TB for 1 h at room temperature.
- Incubate with primary antibodies diluted in the PBS-TB solution, overnight at + 4 °C, on an orbital shaker, 200 µL/well.
- On the following day, perform four washes of 10 min with 1x PBS, on an orbital shaker, 500 µL/well.
- Incubate with secondary antibodies diluted in the PBS-TB solution, two hours at room temperature, on an orbital shaker, and protected from light, 200 µL/well.
- Perform four washes of 10 min with 1x PBS, on an orbital shaker, 500 µL/well.
- Counterstain the slices using Hoechst 33342, diluted in 1x PBS (2 µg/mL), for 10 min at room temperature, protected from light, 500 µL/well.
- Mount the cerebellar slices on a microscopy slide with a transfer pipette. Let them air-dry completely, protected from light. Re-humidify them with 1x PBS and apply a coverslip covered with few drops of mounting medium (~80 µL). Avoid making any bubbles.
- Once the mounting medium has cured, cerebellar sections are ready to be imaged.
4. Imaging and Quantification of Cell Survival
- Turn on the microscope and lasers according to the manufacturer.
- Start the acquisition software.
- Using a 10X objective, locate non-altered cerebellar slices that present 9–10 lobules (usually cerebellar sections close to the vermis).
- Activate z-stack acquisition. Define the range of the z-stack to include all Purkinje cells present in the cerebellar slice. Set a 2 µm step size and start the acquisition. Save the acquired picture in the format of the acquisition software manufacturer to preserve the associated metadata.
- Open the acquired file in ImageJ using the Bio-formats plugin.
- Go to Image > Stacks > Z-project… (Figure 2A).
- Choose Max Intensity in the Projection type dropdown menu and click OK (Figure 2B).
- A flattened 2-D image will be generated. Double click on the Multi-point tool to let the Point Tool window appear. Uncheck the Label points option to ease counted cells visualization. Then, click directly on a soma of a Purkinje cell to begin counting (Figure 1E). The total number of counted cells will be indicated at the bottom of the Point Tool window (Figure 3).
NOTE: Usually, at least 3 non-damaged sections containing 9–10 lobules per cell culture insert can be quantified. To assess the neuroprotective effect of a pharmacological agent, at least 3 independent experiments should be performed.
Representative Results
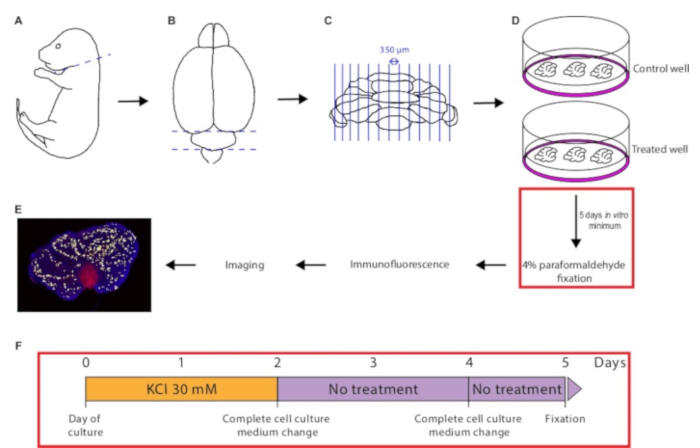
Figure 1: Illustration of the protocol from dissection to Purkinje cell survival quantification. The mouse pup is quickly decapitated (A). Following brain dissection, the cerebellum is isolated (B), and then chopped into 350 µm-width slices (C). The cerebellar sections are placed onto a control or treated cell culture insert (D) and maintained in culture for at least 5 days in vitro. The tissue is then fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, immunostaining is performed, and pictures are acquired with a confocal microscope. Lastly, Purkinje cell number is quantified in each slice using the Multipoint Tool in ImageJ (E). (F) Schematic of the time course of KCl treatment during culture.
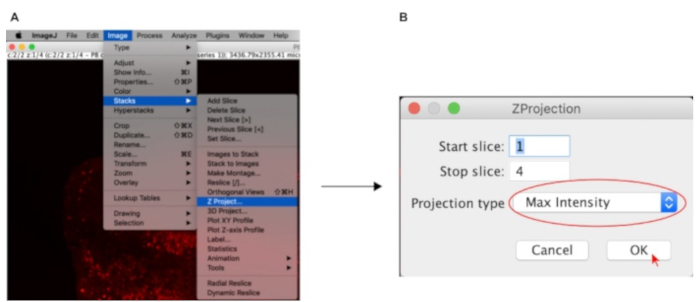
Figure 2: ImageJ settings used to flatten the 3D-stack prior to quantification.
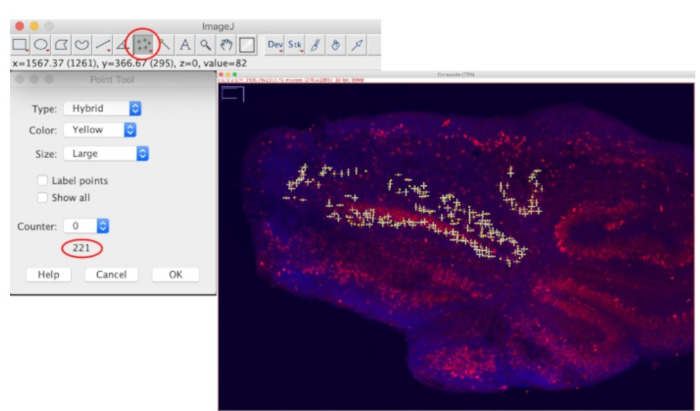
Figure 3: Settings used to count Purkinje cell number using the Multipoint tool in ImageJ with an example of a cerebellar slice being quantified.
Offenlegungen
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| Alexa Fluor 594 Donkey anti- Mouse IgG secondary antibody | ThermoFisher scientific | A21203 | |
| Basal Medium Eagle (BME) | ThermoFisher scientific | 21010046 | |
| Biosafety cabinet Class II, Type A2 | NuAire | NU-540-400 | |
| Bovine serum albumin | Millipore Sigma | A2153 | |
| Brush | |||
| Anti-Calbindin D-28K antibody (CB-955) | Abcam | ab82812 | |
| CO2 Incubator | NuAire | NU-5700 | |
| Corning Costar Flat Bottom 6-well Cell Culture Plates | Fisher Scientific | 07-200-83 | |
| Coverslips, 22 x 50 mm | Fisher Scientific | 12-545-E | |
| Dressing forceps, straight | Harvard Apparatus | 72-8949 | |
| Double edge blades | Fisher Scientific | 50949411 | |
| Ethanol 200 proof | Decon Labs, Inc | 2701 | |
| Eye Scissors, straight | Harvard Apparatus | 72-8428 | |
| Fine forceps | Fisher Scientific | 16-100-127 | |
| L-Glutamine 100X | ThermoFisher scientific | 25030149 | |
| Glucose solution | ThermoFisher scientific | A2494001 | |
| Hanks' Balanced Salt Solution | ThermoFisher scientific | 14025092 | |
| Hoechst 33342, Trihydrochloride, Trihydrate | Fisher Scientific | H21492 | |
| Horse Serum, heat inactivated, New Zealand origin | ThermoFisher scientific | 26050088 | |
| ImageJ | |||
| McIlwain Tissue Chopper | Fisher Scientific | NC9914528 | |
| Microprobes | Fisher Scientific | 08-850 | |
| Millicell Cell Culture Inserts | Millipore Sigma | PICM0RG50 | |
| Nalgene Rapid-Flow Sterile Disposable Filter Units with PES Membrane, 250 mL | ThermoFisher scientific | 168-0045 | |
| Nikon A1R confocal laser microscope system | Nikon | ||
| NIS-Elements Imaging Software | Nikon | ||
| Paraformaldehyde | Acros Organics | 41678-0010 | |
| Pasteur pipets | Fisher Scientific | 13-678-20D | |
| Potassium Chloride | Fisher Scientific | BP366-500 | |
| ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant | ThermoFisher scientific | P10144 | |
| Operating Scissors, straight | Harvard Apparatus | 72-8403 | |
| Orbital shaker Belly Dancer | IBI Scientific | BDRLS0003 | |
| Prism 8 | GraphPad | ||
| Superfrost Plus Microscope Slides | Fisher Scientific | 12-550-15 | |
| Tissue Culture Dish, 60 mm w/ grip ring | Fisher Scientific | FB012921 | |
| Tissue culture plate, 24 well | Falcon/Corning | 353047 | |
| Transfer pipettes, sterile | ThermoFisher scientific | 13-711-21 | |
| Triton X-100 | ThermoFisher scientific | BP151-500 |

