Zinc Finger Nuclease-Based Genome Editing: A Technique for Modifying Genome in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells by Double-Stranded Homology Dependant Repair Mechanism
Abstract
Source: Blair, J. D., et al. Establishment of Genome-edited Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines: From Targeting to Isolation. J. Vis. Exp. (2016).
This video demonstrates a technique of zinc-finger nuclease-based genome editing in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). As hPSCs can potentially be differentiated into various cell types, this technology is helpful for in vitro pathological and pharmacological studies in a patient-specific manner.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Prepare Stem Cells for Editing
- Grow and culture human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) on a 6-well plate containing 2.4 × 106 cells/plate of mitomycin C-inactivated mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) feeders grown on gelatin. Maintain hPSCs in 3 ml of human embryonic stem cell media per well (hESC media) and grow in a 37 °C incubator with 3% O2/5% CO2.
NOTE: For the success of this protocol, it is not necessary to maintain hPSCs in a low-oxygen incubator; however it is important to note that hPSCs proliferate faster in a high O2 environment, so times and cell numbers should be adjusted accordingly. It should also be noted that hPSCs maintained in low oxygen have lower rates of spontaneous differentiation.- To make 500 ml hESC media combine 380 ml DMEM/F12, 75 ml Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS), 25 ml KnockOut Serum Replacement (KSR). Add Glutamine (1 mM final concentration), 5 ml 100x Non-essential Amino Acids, 100 units/ml Penicillin-Streptomycin (P/S), basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF) (4 ng/ml final concentration), and 2-mercaptoethanol (5.5 µM final concentration).
- Change media by removing entire volume of media (3 ml) using a glass pipette and vacuum. Replace with 3 ml warm hESC media using a serological pipette. Repeat media change every day until hPSCs are approximately 50% confluent (Day-1).
- One day before targeting (Day-1), change hESC media, removing the old media and adding warm hESC media supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632.
- Also on Day -1, prepare one to two 6-well or 10 cm plates of drug resistant MEF feeder cells from DR4 mice (2.4 × 106 cells/plate).
Note: In general, 6 well plates are advantageous over 10 cm plates, as they accommodate more media. 6 well plates also ensure that different clones from different wells are independent. However, a 10 cm plate will allow easier picking, depending on the microscope available for this process.
2. Editing Pluripotent Stem Cells
- Prepare transfection solutions by pipetting 5 µg each of ZFN 1 and 2 (Figure 1) into a 1.5 ml tube. Pipette 30 µg of the repair plasmid into this tube as well. Finally, pipette 1x Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) into the tube to bring the volume up to 300 µl.
NOTE: Prepare plasmids as a midiprep (any kit is suitable) with a minimum concentration of 300 ng/µl in order to keep the total volume of the transfection solution under 300 µl. It is not necessary to perform phenol/chloroform extraction, to linearize the plasmid, or to use an endotoxin free plasmid prep kit. - Remove media from hPSCs using a glass pipette and vacuum. Pipette 2 ml warm 1x PBS into each well to wash the cells.
- Remove the PBS immediately using a glass pipette and vacuum. Add 0.5 ml 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA solution directly onto cells in each well. Place in the incubator (37 °C/5% CO2/3% O2) for approximately 10 min. or until feeder layer starts to lift off the plate.
- Add 2 ml warm esWash media (470 ml DMEM/F12, 25 ml FBS, 100 units/ml P/S) to each well to stop the trypsin reaction.
- Ensure that feeder cells come off as a sheet. Pipette the contents of each well into a single 50 ml conical tube, combining all wells. Triturate cells using a 10 ml serological pipette. It is not necessary to break up the feeder layer; hPSCs will come off of the feeder layer by gentle trituration. There should be about 15 ml of the cell suspension.
- Add 25 ml of esWash media to the tube to bring the volume up to 40 ml total. Allow large feeder chunks to settle at the bottom of tube for 1-2 min. Remove the supernatant (~38 ml) from the tube using a serological pipette and deposit into a new 50 ml conical tube.
- Spin down for 5 min at 190 x g. Remove the supernatant from the tube using a glass pipette and vacuum. Be sure to not disturb the cell pellet. Resuspend the cells in 500 µl 1x PBS. Combine with plasmid transfection solution prepared earlier. Count the cells at this step. Use 5-10 million cells per electroporation.
- Pipette the entire 800 µl suspension into a 4 mm electroporation cuvette, place on ice for 3-5 min. Electroporate cells using the exponential program on the electroporation system with the following parameters: 250 V, 500 µF, ∞ resistance, and 4 mm cuvette size. After electroporation, place cuvette back on ice for 3 min.
NOTE: Observe the time constant of the electroporation on the electroporation system. The time constant varies with cell number and DNA purity. Successful transfections usually have a time constant between 10-14 msec when using the listed conditions and a gene pulser II. Lower electroporation efficiencies can occur when time constants varies from these values. - Resuspend electroporated cells in 18 ml warm hESC Media supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632. Plate 3 ml of this single cell suspension into each well of a 6 well plate with DR4 feeder cells. Return to incubator (37 °C/5% CO2/3% O2).
3. Selection of Positive Colonies
- Day 2, remove all media using a glass pipette and vacuum. Replace with 3 ml of warm hESC media supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632. Day 3, remove all media using a glass pipette and vacuum. Replace with 3 ml of warm hESC media without including Y-27632. Day 4, remove all media using a glass pipette and vacuum. Replace with 3 ml warm hESC media supplemented with antibiotics for selection. Return to incubator (37 °C/5% CO2/3% O2).
NOTE: The type of antibiotic used will depend on the resistance cassette included in the repair template. When working with WIBR#3 hPSCs (NIH registry 0079), 0.5 µg/ml puromycin, 70 µg/ml G418 (geneticin), and 35 µg/ml hygromycin have been used successfully. Concentrations for selection should be determined empirically by establishing the minimal concentration of antibiotic needed to kill wild-type cells within approximately one week. - Days 5-12, change media daily, replacing old media each time with warm hESC media supplemented with antibiotics.
NOTE: Expect a large amount of cell death. Individual colonies will become apparent around day 8-10. Regular hESC media without antibiotics can be used after 12-14 days of continuous selection. If cell density is high or cell death is slow, acidification of the media should be avoided and it may be necessary to increase the media volume (up to 4-5 ml) during the first few days of selection.
Representative Results
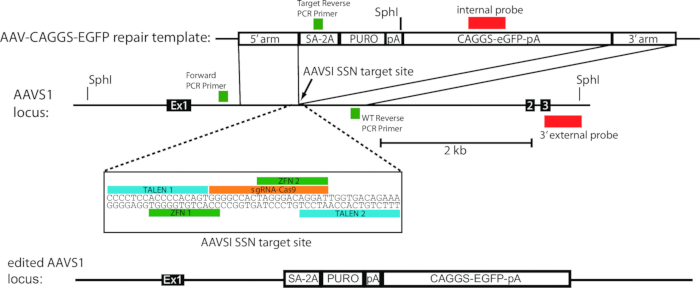
Figure 1. Schematic of gene edited AAVS1 locus using the AAV-CAGGS-EGFP repair template. Modified from Hockemeyer et al., 2009.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Materials
| DMEM/F12 | Life Technologies | 11320082 | |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (HI) | Life Technologies | 10082-147 | |
| Knockout Serum | Life Technologies | 10828-028 | |
| Fibroblast Growth Factor – basic | Life Technologies | PHG0261 | |
| Pen/Strep | Life Technologies | 15140-122 | |
| Glutamine | Life Technologies | 25030-081 | |
| MEM NEAA | Life Technologies | 11140-050 | |
| 2-mercaptoethanol | Life Technologies | 21985-023 | |
| Y-27632 | Calbiochem | 688000 | |
| 6-well plates | Corning | 3506 | |
| 4 mm Electroporation cuvettes | Bio-rad | 165-2081 | |
| X-cel gene pulser II | Bio-rad | 165-2661 | |
| 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA | Life Technologies | 25200-056 | |
| 10× Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH7.4 | Life Technologies | 70011-044 | |
| Puromycin | Life Technologies | A11138-02 |

