זיהום פנאומטי של תאים אנושיים ראשוניים של האדם בזרימה קבועה
Summary
מחקר זה מתאר את הניטור המיקרוסקופית של הדבקות הפנקוקוס על מחרוזות וויללרנד של פון וילבלאנד המיוצר על פני השטח של תאים אנושיים מובחנים ראשוניים תחת לחץ הטיה בתנאי זרימה מוגדרים. פרוטוקול זה יכול להיות מורחב להדמיה מפורטת של מבני תאים ספציפיים וכימות חיידקים על ידי החלת הליכי חיסוני דיפרנציאלי.
Abstract
אינטראקציה של דלקת ריאות סטרפטוקוקוס עם פני השטח של תאים אנדותל מתווך בזרימת הדם באמצעות חלבונים מכניביים מרכיב כגון מקדם וויללמותג פון (vwf). גליקופרוטאין זה משנה את המבנה המולקולרי שלה בתגובה למתח ההטיה, ובכך חושף אתרי כריכה לקשת רחבה של מארחים ואינטראקציות. באופן כללי, הקפדה על תאי האנדותל הראשוניים תחת זרימת הטיה מוגדרת לקדם את הבידול התאי המסוים ואת היווצרות של שכבת אנדותל יציבה ומקושרת היטב הדומה לפיזיולוגיה של הציפוי הפנימי של כלי הדם . לפיכך, ניתוח פונקציונלי של אינטראקציות בין פתוגנים חיידקיים לבין הפונדקאי המארח מעורבים חלבונים מכנימים רגישים דורש הקמת מערכות משאבה שיכולות לדמות את כוחות הזרימה הפיסיולוגיים הידועים להשפיע על פני השטח של תאי כלי הדם.
המכשיר המיקרו-פלואידיג המשמש במחקר זה מאפשר הפעלה מתמשכת ורציפה של נוזלים עם קצב זרימה מוגדר. מערכת משאבת לחץ האוויר מבוקרת המחשב מחיל לחץ הטיה מוגדר על משטחי תא אנדותל על ידי יצירת זרימה רציפה, חד כיווני, בינונית ומבוקרת. שינויים מורפולוגיים של התאים והקבצים המצורפים החיידקיים יכולים להיות מנוטרים באופן מיקרוסקופי ולכמת בזרימה באמצעות שקופיות ערוץ מיוחדות המיועדות להדמיה מיקרוסקופית. בניגוד לזיהום התרבות התא סטטי, אשר באופן כללי דורש קיבעון לדוגמה לפני תיוג החיסונית ניתוחים מיקרוסקופיים, שקופיות microflu, מאפשר הן איתור מבוססי-פלואורסצנטית של חלבונים, חיידקים, ורכיבים סלולריים לאחר קיבעון דגימה; כתמים מוחיסורתיים; וגילוי מבוסס-פלואורסצנטית ישיר בזמן אמת. בשילוב עם חיידקים פלורסנט ונוגדנים ספציפיים המסומנים בקרינה פלואורסצנטית, זה הליך זיהום מספק מערכת יעילה מרובת רכיבים מרובים עבור ספקטרום עצום של יישומים מדעיים הקשורים תהליכים כלי דם.
Introduction
הפתוגנזה של זיהומים פנאומטי מאופיין באינטראקציה רבת-פנים עם מגוון של תרכובות מטריצות ורכיבים של המטאוסטזיס האנושי, כגון פלמיננוגן ו vwf1,2, . שלוש,ארבע,חמש,שש,שבע, שמונה רב התחומים גליקופרוטאין VWF משמש כרגולטור מפתח של הומוסטאזיס מאוזנת על ידי גיוס thrombocyte מדיה ו התאגדות פיאין באתר של היווצרות כלי דם הטרובוס9. החשיבות של הפונקציונלי, VWF פעיל עבור שליטה דימום וריפוי הפצע הוא הפגינו על ידי המחלה של פון Willebrand, הפרעת דימום משותף הפרעה10.
כדורי vwf מסחררת במערכת הדם האנושי בריכוז של עד 14.0 μg/mL11,10. בתגובה לפציעה וסקולרית, שחרורו המקומי של vwf על ידי הגופים האלה של weibel palade (wbp) גדל במידה ניכרת11,12. מחקרים קודמים מראים כי הדבקות האנטי-קוקוס לתאי האנדותל של האדם והייצור של הנקבוביות היוצרות משאבה משמעותית מעוררת באופן משמעותי את הפרשת הלומיאל (VWF)13. הכוחות ההידרודינמיים של זרימת הדם גורמים לפתיחת מבנה של תחומים VWF מכנימים. בקצב זרימה של 10 דינמיקה/ס”מ2 vwf multimerizes למחרוזות חלבון ארוך של עד כמה מיקרומטר באורך הנותרים מחוברים subאנדותל10,12.
כדי להבין את הפונקציה של מחרוזות VWF מולטימzed שנוצר תחת לחץ הטיה באינטראקציה של אבקת הקוקוס עם משטח אנדותל, מבוססי microfluidic מבוסס תרבות התא הגישה זיהום הוקמה. התקן מיקרופלואידיג עם מערכת משאבת הלחץ על התוכנה בקרת האוויר שימש. פעולה זו איפשרה הפעלת מבנה חד-כיווני ורציף של מדיום תרבות התא עם קצב זרימה מוגדר. ובכך, המערכת החלה להדגיש הטיה מוגדרת על פני השטח של תאים אנדותל, אשר נשאר מחובר בתוך שקופיות הערוץ המקצועית. גישה זו אפשרה את הסימולציה של כוח ההטיה בתוך זרם הדם של מערכת כלי הדם של האדם, שבו מחרוזות VWF מופקים על תאים אנדותל מובחנים בתנאי זרימה קבועים מוגדרים. לצורך זה, תאי האנדותל מעובדים בשקופיות מסוימות של ערוצים (ראו טבלת חומרים), שהותאמה לניתוחים מיקרוסקופיים במהלך הזרימה. מערכת המשאבה microflu, מספק את המצב מאוד מוגדר ומבוקר לחץ להטות הנדרש עבור היווצרות של מחרוזות VWF המורחבת על שכבת התאים שוטפת של הרשת. לאחר הגירוי של VWF-הפרשה של האדם בוגר הטבור וריד בתאי הטבורי (HUVEC) על ידי תוספי היסטמין, היווצרות מחרוזת המושרה על ידי החלת מתח הטיה (ԏ) של 10 דינמיקה/cm2. לחץ ההטיה מוגדר ככוח הפועל על שכבת התא. הוא מחושב בקירוב על פי הקורנית. אל14 עם משוואה 1:
כאשר ԏ = להטות את המתח בדינמיקה/cm2, η = צמיגות ב (דינמיקה ∙ s)/cm2, h = מחצית גובה הערוץ, w = חצי רוחב הערוץ, ו Φ = שיעור flowrate-mL/min.
התוצאה של משוואה 1 תלויה בגבהים וברוחב השונים של השקופיות השונות המשמשות (ראה טבלת חומרים). במחקר זה שקופית ערוץ luer של 0.4 יקרומטר והתוצאה היא גורם שקופית קאמרית של 131.6 שימש (ראה נוסחה 2).
צמיגות של המדיום ב 37 ° c הוא 0.0072 דינמיקה ∙ s/cm ² ו להטות את הלחץ של 10 דינמיקה/cm ² שימש. זה הביא לקצב הזרימה של 10.5 mL/min (ראה פורמולה 3).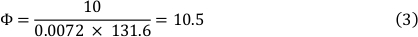
כאן, הסתגלות וקידום של הליך מיקרופלואידיג תא culturing באמצעות מערכת זרימה חד-כיוונית למינארי עבור החקירה ויזואליזציה של מנגנוני זיהום חיידקי בתוך המארח המארחים מתואר בפירוט. הדור של מחרוזות VWF על שכבות אנדותל יכול להיות גם מגורה באמצעות מערכות משאבה אחרות, כי הם מסוגלים להחיל לחץ מתמשך ויציב להטות15.
לאחר הטיפוח של תאי האנדותל הראשוניים למפגש בזרימה וגירוי של היווצרות מחרוזות VWF, הבעת הופעת חלבון פלואורסצנט אדום (RFP)16 נוספו לשכבת התא האנדותל תחת שליטה מיקרוסקופית מתמדת. ההחזקה של חיידקים כדי vwf מחרוזות על פני השטח של תאים אנדותל היה מאכל דמיין והפיקוח עד שלוש שעות בזמן אמת על ידי שימוש ב-vwf ספציפי נוגדנים מתויג-פלורסנט. עם גישה זו, התפקיד של VWF כמו קופקטור הדבקה לקידום ההחזקה החיידקית של כלי הדם אנדותל היה נחוש8.
בנוסף להדמיה המיקרוסקופית של הפרשת החלבון והשינויים השונים, ניתן להשתמש בשיטה זו כדי לפקח על צעדים בודדים של תהליכי זיהום חיידקי בזמן אמת, כדי לכמת את כמות החיידקים המצורפים בנקודות זמן שונות של זיהום. מערכת ספציפית מבוקרת תוכנה מספקת גם את האפשרות לתרבות התאים האנדותל בתנאי זרימה קבועה מוגדר למשך עד מספר ימים ומאפשר הדגירה פעמו זרימה בינונית. כמו-כן, ניתן להחיל שיטה זו באמצעות סוגי תאים שונים. התאמת פרוטוקול הצביעת גם מאפשרת איתור והדמיה של חיידקים הפנימו לתוך תאים איקריוטית.
כתב יד זה מתאר את הפרוטוקול הניסיוני המתקדם שניתן להשתמש בו כגישה מוגדרת, אמינה וניתנת ליישום לאפיון יעיל ותכליתי של תהליכים פתופסלוגיים.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
הדמיה של אינטראקציה חיידקית עם חלבונים מארחים רגישים מכונאי כגון VWF דורש מערכת התרבות התא המכונה המאפשרת את הדור של זרימה מוגדרת, חד כיווני, רציפה של נוזלים, ובכך לייצר מאמץ הטיה אמין . כמה מערכות משאבות מיקרופלואידיסי כבר תוארו. סקירה מקיפה של ברגמן ואח ‘ מסכמת את ההיבטים המרכזיים של מודלי?…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
הפרויקט מומן על ידי DFG (להיות 4570/4-1) כדי S.B.
Materials
| 1 mL Luer-syringe | Fisher Scientific | 10303002 | with 1 mL volume for gelatin injection using the luer-connection of the slides |
| 2 mL Luer-syringe | Sarstedt | 9077136 | For pieptting/injecting fluids into the luer connections of the channel chamber slides |
| Accutase | eBioscience now thermo fisher | 00-4555-56 | protease mix used for gentle detachment of endothelial cells |
| AlexaFluor350-conjugated Phalloidin | Abcam | ab176751 | no concentration available from the manufacturer, stock solution is sufficient for 300 tets, company recommends to use 100 µl of a 1:1000 dilution, blue fluorescence (DAPI-filter settings) |
| AlexaFluor488-conjugated goat-derived anti-mouse antibody | Thermo Fisher Sientific | A11001 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of human VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation, green fluorescence |
| AlexaFluor568-conjugated goat-derived anti-rabbit-antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11011 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of pneumococci in microfluidic slide after pFA fixation, red fluorescence |
| Bacto Todd-Hewitt-Broth | Becton Dickinson GmbH | BD 249210 | complex bacterial culture medium |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma Aldrich | A2153-25G | solubilized, for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Cell culture flasks with filter | TPP | 90026 | subcultivation of HUVEC in non-coated cell culture flasks of 25 cm2 surface |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-12R | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | 392304 | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of > 2mL) |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-30 | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | B06314 | spinning down of eukaryotic cells |
| Centrifuge Z 216 MK | Hermle | 305.00 V05 – Z 216 M | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of less than 2 mL) |
| Chloramphenicol | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3886.2 | used in a concentration of 0.2 /mL for cultivation of pneumococci transformed with genetic construct carrying red fluorescent protein and chloramphenicol resistance cassette |
| Clamp for perfusion tubing | ibidi | 10821 | for holding the liquid in the tube bevor connecting the slide to the pump system |
| CO2-Incubator | Fisher Scientific | MIDI 40 | incubator size is perfectly adapted to teh size of the fluidic unit with connected channel slide and was used for flow cultivation at 37°C and 5% CO2 |
| CO2-Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-18 AIC | for incubation of bacteria and cells in a defined atmosphere at 5% CO2 and 37°C |
| Colombia blood agar plates | Becton Dickinson GmbH | PA-254005.06 | agar-based complex culture medium for S. pneumoniae supplemented with 7% sheep blood |
| Computer | Dell | Latitude 3440 | Comuter with pressure pump software |
| Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) | Leica | DMi8 | An inverse microscope with a stage covered by a heatable chamber and with a fluorescence unit equipped with fluorescence filter, Xenon-light source (SP8, DMi8) and DFC 365 FX Kamera (1392 x 1040, 1.4 Megapixel) |
| Di Potassium hydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3904.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Drying material | Merck | 101969 | orange silica beads for drying used in a glass bottle with a tubing adaptor |
| ECGM supplement Mix | Promocell | C-39215 | supplement mix for ECGM -medium, required for precultivation of endothelial cells: 0.02 mL/mL Fetal calf serum, 0.004 mL/ mL endothelial cell growth supplement, 0.1 ng / mL epidermal growth factor, 1 ng / mL basic fibroblast growth factor, 90 µg / mL heparin, 1 µg / mL Hydrocortisone |
| ECGMS | Promocell | C-22010 | ECGM supplemented with 5 % [w/w] FCS and 1 mM MgSO4 to increase cell adhesion |
| Endothelial Cell growth medium (ECGM, ready to use) | Promocell | C-22010 | culture medium of HUVECs, already supplemented with all components of the supplement mix |
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) | biochrome now Merck | S 0415 | supplement for cell culture, used for infection analyses |
| FITC-conjugated goat anti-human VWF antibody | Abcam | ab8822 | stock concentration: 10 mg/mL, for immunodetection of globular and multimerized VWF in flow |
| Fluidic Unit | ibidi | 10903 | fluidic unit for flow cultivation |
| Gelatin (porcine) | Sigma Aldrich | G-1890-100g | for precoating of microslide channel surface |
| histamine dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | H-7250-10MG | for induction of VWF secretion from endothelial Weibel Palade Bodies |
| Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) | Promocell | C-12203 Lot-Nr. 396Z042 | primary endothelial cells from pooled donor, stored crypcoserved in liquid nitrogen |
| Human VWF-specific antibody derived from mouse (monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc73268 | stock concentration: 200 µg/mL for immunostaining of VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation |
| Injection Port | ibidi | 10820 | for injection of histamin or bacteria into the reservoir tubing during the flow circulation |
| Light microscope | Zeiss | Axiovert 35M | inverse light microscope for control of eukaryotic cell detachement and cell counting using a 40 x water objective allowing 400 x magnification |
| Luer-slides I0.4 (ibiTreat472microslides) | ibidi | 80176 | physically modified slides for fludic cultivation (μ–Slide I0.4Luer with a channel hight of 0.4 mm, a channel volume of 100 μl, a growth area of 2.5 cm and a coating area of 25.4 cm2) suitable for all kinds of flow assay, the physical treatment generates a hydrophilic and adhesive surface. |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4, unhydrated) | Sigma Aldrich | M7506-500G | For preparation of ECGMS medium |
| Microfluidic Pump | ibidi | 10905 | air pressure pump |
| Neubauer cell counting chamber | Karl Hecht GmbH&Co KG | 40442002 | microscopic counting chamber for HUVECs |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% (PFA) | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710-S | for cross linking of samples |
| Perfusion Set | ibidi | 10964 | Perfusion Set Yellow/Green has a tubing diameter of 1.6 mm, a tube length of 50 cm, a total working volume of 13.6 mL, a dead tube volume of 2.8 mL and a reservoir size of 10 mL. combined with the µ-slide L0.4Luer, at 37°C and a viscosity of 0.0072 dyn x s/cm2 a flow rate range of 3.8mL/min up to 33.9 mL/min and shear stress between 3.5 dyn/cm2 and 31.2 dyn/cm2 can be reached. with 50 cm lenght for microfluidic |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | the solution was prepared using the following chemicals: 0.2 g/L KCl, 1.44 g/L Na2HPO4, 0.24 g/L KH2PO4 , pH 7.4 | ||
| Plastic cuvettes | Sarstedt | 67,741 | (2 x optic) for OD measurement at 600 nm |
| Pneumococcus-specific antiserum | Pineda | raised in rabbit using heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC10319 and D39, IgG-purified using proteinA-sepharose column. | |
| Polystyrene or Styrofoam plate | this is a precaution step to avoid cold stress on the cells seeded in the channel slides. Any type of styrofoam such as packaging box-material can be used. The plate might by 0.5 cm thick and should have a size of 20 cm2. | ||
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 6781.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Pump Control Software (PumpControl v1.5.4) | ibidi | v1.5.4 | Computer software for controlling the pressure pump, setting the flow conditions and start/end the flow |
| reaction tubes 1.5/ 2.0mL | Sarstedt | 72.706/ 72.695.500 | required for antibody dilutions |
| reaction tubes with 50 mL volume | Sarstedt | 6,25,48,004 | |
| RFP-expressing pneumococci | National Collection of Type Cultures, Public Health England | 10,319 | Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 47 expressing RFP fused to ahistone-like protein integrated into the genome |
| serological pipets 5, 10 mL | Sarstedt | 86.1253.025/ 86.1254.025 | for pipeting larger volumes |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3, water free) | Sigma Aldrich | 451614-25G | for preparation of 100 mM Sodium Carbonate buffer |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | P030.2 | used for PBS buffer |
| Spectral Photometer Libra S22 | Biochrom | 80-2115-20 | measurement of optical density (OD) of bacterial suspension at 600 nm |
| Sucrose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389-500G | for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T9284-500ML | Used in 0.1% end concentration diluted in dH20 for eukaryotic cell permeabilization after PFA fixation |
| Yeast extract | oxoid | LP0021 | bacteria are cultivated in THB supplement with 1% [w/w] yeast extract = complete bacterial cultivation medium THY |
References
- Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., Paton, J. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16 (6), 355-367 (2018).
- Bergmann, S., Hammerschmidt, S. Versatility of pneumococcal surface proteins. Microbiology. 152, 295-303 (2006).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Integrin-linked kinase is required for vitronectin-mediated internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae by host cells. Journal of Cell Science. 122, 256-267 (2009).
- Bergmann, S., Schoenen, H., Hammerschmidt, S. The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and endothelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 303, 452-462 (2013).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Chhatwal, G. S., Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin(ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Molecular Microbiology. 40, 1273-1287 (2001).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Microbiology. 49, 411-423 (2003).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Preissner, K. T., Hammerschmidt, S. The nine residue plasminogen-binding motif of the pneumococcal enolase is the major cofactor of plasmin-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix, dissolution of fibrin and transmigration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 94, 304-311 (2005).
- Jagau, H., et al. Von willebrand factor mediates pneumococcal aggregation and adhesion in flow. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10, 511 (2019).
- Tischer, A., et al. Enhanced local disorder in a clinically elusive von willebrand factor provokes high-affinity platelet clumping. Journal of Molecular Biology. 429, 2161-2177 (2017).
- Ruggeri, Z. M. Structure of von willebrand factor and its function in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. Best Practice Research Clinical Haematology. 14, 257-279 (2001).
- Spiel, A. O., Gilbert, J. C., Jilma, B. Von willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117, 1449-1459 (2008).
- Springer, T. A. Von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood. 124, 1412-1425 (2014).
- Luttge, M., et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies in pulmonary endothelial cells. Cellular Microbiology. 14, 210-225 (2012).
- Cornish, R. J. Flow in a Pipe of Rectangular Cross-Section. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 786, 691-700 (1928).
- Michels, A., Swystun, L. L., Mewburn, J., Albánez, S., Lillicrap, D. Investigating von Willebrand Factor Pathophysiology Using a Flow Chamber Model of von Willebrand Factor-platelet String Formation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 14 (126), (2017).
- Kjos, M., et al. fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions. Journal of Bacteriology. 197, 807-818 (2015).
- Bergmann, S., Steinert, M. From single cells to engineered and explanted tissues: New perspectives in bacterial infection biology. International Reviews of Cell and Molecular Biology. 319, 1-44 (2015).
- Harrison, D. J., et al. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science. 261 (5123), 895-897 (1993).
- Magnusson, M. K., Mosher, D. F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 18, 1363-1370 (1998).
- Zerlauth, G., Wolf, G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (4), 685-689 (1984).
- Li, X. J., Valadez, A. V., Zuo, P., Nie, Z. 2012. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 4, 1509-1525 (2019).
- Fiddes, L. K., et al. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials. 31, 3459-3464 (2010).
- Schimek, K., et al. Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3588-3598 (2013).
- Pappelbaum, K. I., et al. Ultralarge von willebrand factor fibers mediate luminal Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to an intact endothelial cell layer under shear stress. Circulation. 128, 50-59 (2013).
- Schneider, S. W., et al. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von willebrand factor fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104, 7899-7903 (2007).
- Reneman, R. S., Hoek, A. P. G. Wall shear stress as measured in vivo: consequences for the design of the arterial system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 46 (5), 499-507 (2008).
- Valentijn, K. M., Sadler, J. E., Valentijn, J. A., Voorberg, J., Eikenboom, J. Functional architecture of Weibel- Palade bodies. Blood. 117, 5033-5043 (2011).
- Freshney, R. I. . Culture of animal cells: A manual of basic Technique, 5th edition. , (2005).
- Shaw, J. A., Shaw, A. J. . Epithelial cell culture- a practical approach. , 218 (1996).
- Elm, C., et al. Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR) mediate invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into the epithelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (8), 6296-6304 (2004).
- Nerlich, A., et al. Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (30), 20319-20328 (2009).
- Ho, C. T., et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3578-3587 (2013).
- Huh, D., et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 328, 1662-1668 (2010).
- Harink, B., Le Gac, S., Truckenmuller, R., van Blitterswijk, C., Habibovic, P. Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3512-3528 (2013).

