Pneumococcus-infectie van primaire humane endotheliale cellen in constante stroming
Summary
Deze studie beschrijft de microscopische monitoring van pneumococcus hechting aan Von Willebrand factor snaren geproduceerd op het oppervlak van gedifferentieerde menselijke primaire endotheliale cellen onder shear stress in gedefinieerde stromingsomstandigheden. Dit protocol kan worden uitgebreid naar gedetailleerde visualisatie van specifieke celstructuren en kwantificering van bacteriën door differentiële immunokleurings procedures toe te passen.
Abstract
Interactie van Streptococcus pneumoniae met het oppervlak van endotheel cellen wordt gemedieerd in de bloedstroom via mechanosensitieve eiwitten zoals de Von Willebrand factor (vwf). Deze glycoproteïne verandert de moleculaire conformatie in reactie op shear stress, waardoor binding sites bloot voor een breed spectrum van gastheer-ligand interacties. In het algemeen is het kweken van primaire endotheel cellen onder een gedefinieerde schuif stroom bekend om de specifieke celdifferentiatie te bevorderen en de vorming van een stabiele en strak gekoppelde endotheellaag die lijkt op de Fysiologie van de binnenbekleding van een bloedvat . Zo vereist de functionele analyse van interacties tussen bacteriële pathogenen en de gastheer-vasculatuur met mechanogevoelige eiwitten de oprichting van pompsystemen die de fysiologische stroom krachten kunnen simuleren die bekend zijn om het oppervlak van vasculaire cellen.
Het microfluïdische apparaat dat in deze studie wordt gebruikt, maakt een continue en pulseloze recirculatie van vloeistoffen met een gedefinieerde stroomsnelheid mogelijk. Het computergestuurde luchtdruk pompsysteem past een gedefinieerde shear stress op endotheliale celoppervlakken toe door een continue, unidirectionele en gecontroleerde gemiddelde stroom te genereren. Morfologische veranderingen van de cellen en bacteriële gehechtheid kunnen microscopisch worden bewaakt en gekwantificeerd in de stroom door gebruik te maken van speciale kanaal dia’s die zijn ontworpen voor microscopische visualisatie. In tegenstelling tot statische celkweek infectie, die in het algemeen een monster fixatie vereist voorafgaand aan immuun labeling en microscopische analyses, maken de microfluïdische dia’s zowel de fluorescentie-gebaseerde detectie van eiwitten, bacteriën en cellulaire componenten mogelijk na monster fixatie; seriële immunofluorescentie kleuring; en directe fluorescentiedetectie in real-time. In combinatie met fluorescerende bacteriën en specifieke fluorescentie-gelabelde antilichamen, deze infectie procedure biedt een efficiënte meervoudige component visualisatie systeem voor een groot spectrum van wetenschappelijke toepassingen met betrekking tot vasculaire processen.
Introduction
De pathogenese van pneumococcus-infecties wordt gekenmerkt door een veelzijdige interactie met een diversiteit aan extracellulaire matrix verbindingen en componenten van de menselijke hemostase, zoals plasminogeen envwf1,2, 3,4,5,6,7,8. De multi Domain glycoproteïne VWF fungeert als een belangrijke regulator van een evenwichtige hemostase door middel van bemiddeling van trombocyten werving en fibrinincorporatie op de plaats van vasculaire trombus formatie9. Het belang van functionele, actieve VWF voor bloedings beheersing en wondgenezing wordt aangetoond door de ziekte van Von Willebrand, een veelvoorkomend erfelijke bloedingsstoornis10.
Bolvormige vwf circuleert in het humaan bloedsysteem bij een concentratie van maximaal 14,0 μg/ml11,10. Als reactie op vasculaire letsels is de lokale afgifte van vwf door endotheliale Weibel Palade Bodies (WBP) aanzienlijk toegenomen11,12. Eerdere studies tonen aan dat de hechting van pneumococcus aan humane endotheelcellen en de productie van de Pore vormende toxine pneumolysine de Luminale VWF secretie13aanzienlijk stimuleert. De hydrodynamische krachten van de bloedstroom induceren een structurele opening van de mechanoresponsive VWF domeinen. Bij stroomsnelheden van 10 dyn/cm2 de vwf multimerizes tot lange eiwit snaren tot enkele honderden micrometers in lengte die blijven gehecht aan het subendothelium10,12.
Om te begrijpen van de functie van multimerized VWF snaren gegenereerd onder shear stress in de interactie van pneumococcus met het endotheliale oppervlak, een microfluidic gebaseerde cel cultuur infectie aanpak werd vastgesteld. Een microfluïdisch apparaat met een software-gestuurde luchtdruk pompsysteem werd gebruikt. Hierdoor kon een continue, unidirectionele recirculatie van het celkweekmedium met een gedefinieerde stroomsnelheid worden ingeschakeld. Daardoor paste het systeem een gedefinieerde shear stress op het oppervlak van endotheliale cellen, die bleef bevestigd in gespecialiseerde kanaal dia’s. Deze aanpak stelde de simulatie van de dwarskracht binnen de bloedstroom van het menselijke vasculaire systeem, waarbij VWF snaren worden gegenereerd op gedifferentieerde endotheliale cellen onder gedefinieerde constante stroom omstandigheden. Voor dit doel werden de endotheelcellen gekweekt in specifieke kanaal glaasjes (Zie tabel van materialen), die tijdens de stroming werden aangepast voor microscopische analyses. Het microfluïdische pompsysteem voorzag in de sterk gedefinieerde en gecontroleerde shear stresssituatie die nodig was voor de vorming van verlengde VWF snaren op de confluente endotheliale cellaag. Na de stimulatie van VWF-afscheiding van de door de mens geteelde humane navelstreng endotheliale cellen (HUVEC) door histamine suppletie, werd de snaar vorming geïnduceerd door het aanbrengen van een shear stress (ԏ) van 10 dyn/cm2. De shear stress wordt gedefinieerd als de kracht die op de cellaag optreedt. Het wordt ongeveer berekend volgens Cornish et. al.14 met vergelijking 1:
Waarbij ԏ = afschuif spanning in dyn/cm2, η = viscositeit in (DYN ∙ s)/cm2, h = helft van de kanaal hoogte, w = de helft van de kanaal breedte en Φ = debiet in ml/min.
Het resultaat van vergelijking 1 is afhankelijk van de verschillende hoogtes en breedten van de verschillende gebruikte dia’s (Zie tabel met materialen). In deze studie werd een Luer-kanaal glijbaan van 0,4 μm gebruikt, resulterend in een kamer glijbaan factor van 131,6 (zie formule 2).
Viscositeit van het medium bij 37 °C is 0,0072 dyn ∙ s/cm ² en een shear stress van 10 dyn/cm ² werd gebruikt. Dit resulteerde in een debiet van 10,5 mL/min (Zie Formule 3).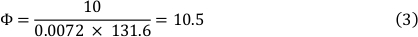
Hier wordt de aanpassing en vooruitgang van een microfluïdische celculturing procedure met behulp van een unidirectioneel laminaire stroomsysteem voor het onderzoek en visualisatie van bacteriële infectiemechanismen in de gastheer-vasculatuur gedetailleerd beschreven. Het genereren van VWF-snaren op endotheliale lagen kan ook worden gestimuleerd door gebruik te maken van andere pompsystemen die in staat zijn om een continue en stabiele shear stress15toe te passen.
Na de teelt van primaire endotheelcellen tot samenvloeiing in stroming en stimulatie van VWF-snaar vorming, werden pneumokokken die rood fluorescentie-eiwit (RFP)16 uitdrukken, toegevoegd aan de endotheelcellaag onder constante microscopische controle. Het gehechtheid van bacteriën aan VWF-snaren op het oppervlak van endotheelcellen werd microscopisch gevisualiseerd en gedurende maximaal drie uur in real-time gemonitord door gebruik te maken van VWF-specifieke antilichamen met fluorescentie-label. Met deze aanpak werd de rol van VWF als adhesie cofactor voor het bevorderen van bacteriële gehechtheid aan het vasculaire endotheel bepaald8.
Naast de microscopische visualisatie van eiwit secretie en conformationele veranderingen, deze methode kan worden gebruikt voor het bewaken van enkele stappen van bacteriële infectie processen in real time en kwantificeren van de hoeveelheid bijgevoegde bacteriën op verschillende tijdstippen van Infectie. Het specifieke software-gestuurde pompsysteem biedt ook de mogelijkheid om de endotheelcellen in gedefinieerde constante stromingsomstandigheden gedurende maximaal enkele dagen te kweken en maakt een gedefinieerde gepulseerde-medium stroom incubatie mogelijk. Bovendien kan deze methode worden toegepast met behulp van verschillende celtypen. Het aanpassen van het kleurings protocol maakt ook de detectie en visualisatie van bacteriën geïnternationaliseerd in eukaryotische cellen mogelijk.
Dit manuscript beschrijft dit geavanceerde experimentele protocol, dat kan worden gebruikt als een gedefinieerde, betrouwbare en reproduceerbaar benadering voor een efficiënte en veelzijdige karakterisering van pathofysiologische processen.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
De simulatie van bacteriële interactie met mechanosensitieve gastheer eiwitten zoals VWF vereist een perfbruikbare celcultuursysteem dat het genereren van een gedefinieerde, unidirectionele en continue stroom van vloeistoffen mogelijk maakt, waardoor betrouwbaar shear stress wordt gegenereerd . Verschillende microfluïdische pompsystemen zijn al beschreven. Een uitgebreid overzicht van Bergmann et al. vat de belangrijkste aspecten van verschillende twee-en driedimensionale celcultuurmodellen17sam…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Het project werd gefinancierd door de DFG (BE 4570/4-1) naar S.B.
Materials
| 1 mL Luer-syringe | Fisher Scientific | 10303002 | with 1 mL volume for gelatin injection using the luer-connection of the slides |
| 2 mL Luer-syringe | Sarstedt | 9077136 | For pieptting/injecting fluids into the luer connections of the channel chamber slides |
| Accutase | eBioscience now thermo fisher | 00-4555-56 | protease mix used for gentle detachment of endothelial cells |
| AlexaFluor350-conjugated Phalloidin | Abcam | ab176751 | no concentration available from the manufacturer, stock solution is sufficient for 300 tets, company recommends to use 100 µl of a 1:1000 dilution, blue fluorescence (DAPI-filter settings) |
| AlexaFluor488-conjugated goat-derived anti-mouse antibody | Thermo Fisher Sientific | A11001 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of human VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation, green fluorescence |
| AlexaFluor568-conjugated goat-derived anti-rabbit-antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11011 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of pneumococci in microfluidic slide after pFA fixation, red fluorescence |
| Bacto Todd-Hewitt-Broth | Becton Dickinson GmbH | BD 249210 | complex bacterial culture medium |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma Aldrich | A2153-25G | solubilized, for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Cell culture flasks with filter | TPP | 90026 | subcultivation of HUVEC in non-coated cell culture flasks of 25 cm2 surface |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-12R | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | 392304 | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of > 2mL) |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-30 | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | B06314 | spinning down of eukaryotic cells |
| Centrifuge Z 216 MK | Hermle | 305.00 V05 – Z 216 M | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of less than 2 mL) |
| Chloramphenicol | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3886.2 | used in a concentration of 0.2 /mL for cultivation of pneumococci transformed with genetic construct carrying red fluorescent protein and chloramphenicol resistance cassette |
| Clamp for perfusion tubing | ibidi | 10821 | for holding the liquid in the tube bevor connecting the slide to the pump system |
| CO2-Incubator | Fisher Scientific | MIDI 40 | incubator size is perfectly adapted to teh size of the fluidic unit with connected channel slide and was used for flow cultivation at 37°C and 5% CO2 |
| CO2-Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-18 AIC | for incubation of bacteria and cells in a defined atmosphere at 5% CO2 and 37°C |
| Colombia blood agar plates | Becton Dickinson GmbH | PA-254005.06 | agar-based complex culture medium for S. pneumoniae supplemented with 7% sheep blood |
| Computer | Dell | Latitude 3440 | Comuter with pressure pump software |
| Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) | Leica | DMi8 | An inverse microscope with a stage covered by a heatable chamber and with a fluorescence unit equipped with fluorescence filter, Xenon-light source (SP8, DMi8) and DFC 365 FX Kamera (1392 x 1040, 1.4 Megapixel) |
| Di Potassium hydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3904.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Drying material | Merck | 101969 | orange silica beads for drying used in a glass bottle with a tubing adaptor |
| ECGM supplement Mix | Promocell | C-39215 | supplement mix for ECGM -medium, required for precultivation of endothelial cells: 0.02 mL/mL Fetal calf serum, 0.004 mL/ mL endothelial cell growth supplement, 0.1 ng / mL epidermal growth factor, 1 ng / mL basic fibroblast growth factor, 90 µg / mL heparin, 1 µg / mL Hydrocortisone |
| ECGMS | Promocell | C-22010 | ECGM supplemented with 5 % [w/w] FCS and 1 mM MgSO4 to increase cell adhesion |
| Endothelial Cell growth medium (ECGM, ready to use) | Promocell | C-22010 | culture medium of HUVECs, already supplemented with all components of the supplement mix |
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) | biochrome now Merck | S 0415 | supplement for cell culture, used for infection analyses |
| FITC-conjugated goat anti-human VWF antibody | Abcam | ab8822 | stock concentration: 10 mg/mL, for immunodetection of globular and multimerized VWF in flow |
| Fluidic Unit | ibidi | 10903 | fluidic unit for flow cultivation |
| Gelatin (porcine) | Sigma Aldrich | G-1890-100g | for precoating of microslide channel surface |
| histamine dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | H-7250-10MG | for induction of VWF secretion from endothelial Weibel Palade Bodies |
| Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) | Promocell | C-12203 Lot-Nr. 396Z042 | primary endothelial cells from pooled donor, stored crypcoserved in liquid nitrogen |
| Human VWF-specific antibody derived from mouse (monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc73268 | stock concentration: 200 µg/mL for immunostaining of VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation |
| Injection Port | ibidi | 10820 | for injection of histamin or bacteria into the reservoir tubing during the flow circulation |
| Light microscope | Zeiss | Axiovert 35M | inverse light microscope for control of eukaryotic cell detachement and cell counting using a 40 x water objective allowing 400 x magnification |
| Luer-slides I0.4 (ibiTreat472microslides) | ibidi | 80176 | physically modified slides for fludic cultivation (μ–Slide I0.4Luer with a channel hight of 0.4 mm, a channel volume of 100 μl, a growth area of 2.5 cm and a coating area of 25.4 cm2) suitable for all kinds of flow assay, the physical treatment generates a hydrophilic and adhesive surface. |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4, unhydrated) | Sigma Aldrich | M7506-500G | For preparation of ECGMS medium |
| Microfluidic Pump | ibidi | 10905 | air pressure pump |
| Neubauer cell counting chamber | Karl Hecht GmbH&Co KG | 40442002 | microscopic counting chamber for HUVECs |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% (PFA) | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710-S | for cross linking of samples |
| Perfusion Set | ibidi | 10964 | Perfusion Set Yellow/Green has a tubing diameter of 1.6 mm, a tube length of 50 cm, a total working volume of 13.6 mL, a dead tube volume of 2.8 mL and a reservoir size of 10 mL. combined with the µ-slide L0.4Luer, at 37°C and a viscosity of 0.0072 dyn x s/cm2 a flow rate range of 3.8mL/min up to 33.9 mL/min and shear stress between 3.5 dyn/cm2 and 31.2 dyn/cm2 can be reached. with 50 cm lenght for microfluidic |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | the solution was prepared using the following chemicals: 0.2 g/L KCl, 1.44 g/L Na2HPO4, 0.24 g/L KH2PO4 , pH 7.4 | ||
| Plastic cuvettes | Sarstedt | 67,741 | (2 x optic) for OD measurement at 600 nm |
| Pneumococcus-specific antiserum | Pineda | raised in rabbit using heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC10319 and D39, IgG-purified using proteinA-sepharose column. | |
| Polystyrene or Styrofoam plate | this is a precaution step to avoid cold stress on the cells seeded in the channel slides. Any type of styrofoam such as packaging box-material can be used. The plate might by 0.5 cm thick and should have a size of 20 cm2. | ||
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 6781.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Pump Control Software (PumpControl v1.5.4) | ibidi | v1.5.4 | Computer software for controlling the pressure pump, setting the flow conditions and start/end the flow |
| reaction tubes 1.5/ 2.0mL | Sarstedt | 72.706/ 72.695.500 | required for antibody dilutions |
| reaction tubes with 50 mL volume | Sarstedt | 6,25,48,004 | |
| RFP-expressing pneumococci | National Collection of Type Cultures, Public Health England | 10,319 | Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 47 expressing RFP fused to ahistone-like protein integrated into the genome |
| serological pipets 5, 10 mL | Sarstedt | 86.1253.025/ 86.1254.025 | for pipeting larger volumes |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3, water free) | Sigma Aldrich | 451614-25G | for preparation of 100 mM Sodium Carbonate buffer |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | P030.2 | used for PBS buffer |
| Spectral Photometer Libra S22 | Biochrom | 80-2115-20 | measurement of optical density (OD) of bacterial suspension at 600 nm |
| Sucrose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389-500G | for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T9284-500ML | Used in 0.1% end concentration diluted in dH20 for eukaryotic cell permeabilization after PFA fixation |
| Yeast extract | oxoid | LP0021 | bacteria are cultivated in THB supplement with 1% [w/w] yeast extract = complete bacterial cultivation medium THY |
References
- Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., Paton, J. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16 (6), 355-367 (2018).
- Bergmann, S., Hammerschmidt, S. Versatility of pneumococcal surface proteins. Microbiology. 152, 295-303 (2006).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Integrin-linked kinase is required for vitronectin-mediated internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae by host cells. Journal of Cell Science. 122, 256-267 (2009).
- Bergmann, S., Schoenen, H., Hammerschmidt, S. The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and endothelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 303, 452-462 (2013).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Chhatwal, G. S., Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin(ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Molecular Microbiology. 40, 1273-1287 (2001).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Microbiology. 49, 411-423 (2003).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Preissner, K. T., Hammerschmidt, S. The nine residue plasminogen-binding motif of the pneumococcal enolase is the major cofactor of plasmin-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix, dissolution of fibrin and transmigration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 94, 304-311 (2005).
- Jagau, H., et al. Von willebrand factor mediates pneumococcal aggregation and adhesion in flow. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10, 511 (2019).
- Tischer, A., et al. Enhanced local disorder in a clinically elusive von willebrand factor provokes high-affinity platelet clumping. Journal of Molecular Biology. 429, 2161-2177 (2017).
- Ruggeri, Z. M. Structure of von willebrand factor and its function in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. Best Practice Research Clinical Haematology. 14, 257-279 (2001).
- Spiel, A. O., Gilbert, J. C., Jilma, B. Von willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117, 1449-1459 (2008).
- Springer, T. A. Von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood. 124, 1412-1425 (2014).
- Luttge, M., et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies in pulmonary endothelial cells. Cellular Microbiology. 14, 210-225 (2012).
- Cornish, R. J. Flow in a Pipe of Rectangular Cross-Section. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 786, 691-700 (1928).
- Michels, A., Swystun, L. L., Mewburn, J., Albánez, S., Lillicrap, D. Investigating von Willebrand Factor Pathophysiology Using a Flow Chamber Model of von Willebrand Factor-platelet String Formation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 14 (126), (2017).
- Kjos, M., et al. fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions. Journal of Bacteriology. 197, 807-818 (2015).
- Bergmann, S., Steinert, M. From single cells to engineered and explanted tissues: New perspectives in bacterial infection biology. International Reviews of Cell and Molecular Biology. 319, 1-44 (2015).
- Harrison, D. J., et al. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science. 261 (5123), 895-897 (1993).
- Magnusson, M. K., Mosher, D. F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 18, 1363-1370 (1998).
- Zerlauth, G., Wolf, G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (4), 685-689 (1984).
- Li, X. J., Valadez, A. V., Zuo, P., Nie, Z. 2012. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 4, 1509-1525 (2019).
- Fiddes, L. K., et al. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials. 31, 3459-3464 (2010).
- Schimek, K., et al. Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3588-3598 (2013).
- Pappelbaum, K. I., et al. Ultralarge von willebrand factor fibers mediate luminal Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to an intact endothelial cell layer under shear stress. Circulation. 128, 50-59 (2013).
- Schneider, S. W., et al. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von willebrand factor fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104, 7899-7903 (2007).
- Reneman, R. S., Hoek, A. P. G. Wall shear stress as measured in vivo: consequences for the design of the arterial system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 46 (5), 499-507 (2008).
- Valentijn, K. M., Sadler, J. E., Valentijn, J. A., Voorberg, J., Eikenboom, J. Functional architecture of Weibel- Palade bodies. Blood. 117, 5033-5043 (2011).
- Freshney, R. I. . Culture of animal cells: A manual of basic Technique, 5th edition. , (2005).
- Shaw, J. A., Shaw, A. J. . Epithelial cell culture- a practical approach. , 218 (1996).
- Elm, C., et al. Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR) mediate invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into the epithelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (8), 6296-6304 (2004).
- Nerlich, A., et al. Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (30), 20319-20328 (2009).
- Ho, C. T., et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3578-3587 (2013).
- Huh, D., et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 328, 1662-1668 (2010).
- Harink, B., Le Gac, S., Truckenmuller, R., van Blitterswijk, C., Habibovic, P. Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3512-3528 (2013).

