عدوي المكورات الرئوية من خلايا بطانة الإنسان الاساسيه في التدفق المستمر
Summary
تصف هذه الدراسة الرصد المجهري للالتزام بالمكورات الرئوية لسلاسل عامل فون ويلبراند المنتجة علي سطح الخلايا البطانية الاساسيه البشرية المتمايزة تحت ضغط القص في ظروف التدفق المحددة. ويمكن توسيع نطاق هذا البروتوكول ليشمل التصور التفصيلي للهياكل الخلوية المحددة والقياس الكمي للبكتيريا عن طريق تطبيق إجراءات المناعة التفاضلية.
Abstract
يتم التوسط في تفاعل العقديه الرئوية مع سطح الخلايا البطانية في تدفق الدم عن طريق البروتينات الميكانيكية مثل عامل فون ويلبراند (vwf). هذا البروتين السكري يغير التشكيل الجزيئي الخاص به استجابه للإجهاد القص ، التالي تعريض مواقع ملزمه لمجموعه واسعه من التفاعلات المضيف-ligand. بشكل عام ، من المعروف ان زراعه الخلايا البطانية الاوليه تحت تدفق القص محدده لتعزيز التمايز الخلوي محدده وتشكيل طبقه بطانية مستقره ومرتبطة باحكام تشبه فسيولوجيا البطانة الداخلية للاوعيه الدموية . وهكذا ، فان التحليل الوظيفي للتفاعلات بين مسببات الامراض البكتيرية والاوعيه الدموية المضيفة التي تنطوي علي البروتينات الميكانيكية يتطلب إنشاء أنظمه ضخ التي يمكن محاكاة قوي تدفق الفسيولوجية المعروف ان تؤثر علي سطح خلايا الاوعيه الدموية.
ويتيح الجهاز المجهري المستخدم في هذه الدراسة أعاده تدوير مستمرة ونبضه للسوائل بمعدل تدفق محدد. يطبق نظام مضخة ضغط الهواء الذي يتحكم فيه الكمبيوتر ضغطا محددا للقص علي أسطح الخلايا البطانية عن طريق توليد تدفق متوسط مستمر وأحادي الاتجاه ومتحكم فيه. يمكن رصد التغيرات المورفولوجية للخلايا والملحقات البكتيرية مجهريا وتحديدها كميا في التدفق باستخدام شرائح قناه خاصه مصممه لتصور مجهري. علي النقيض من العدوى الخلوية الساكنة ، والتي تتطلب بشكل عام تثبيت العينات قبل وضع العلامات المناعية والتحاليل المجهرية ، فان الشرائح الصغيرة تتيح الكشف القائم علي الفلورية للبروتينات والبكتيريا والمكونات الخلوية بعد تثبيت العينة ؛ المسلسل تلطيخ المناعي. والكشف المباشر القائم علي الفلورية في الوقت الحقيقي. في تركيبه مع البكتيريا الفلورية والأجسام المضادة المسمية الفلورية المحددة ، يوفر هذا الاجراء العدوى نظام التصور مكون متعددة فعاله لطيف ضخم من التطبيقات العلمية المتعلقة بعمليات الاوعيه الدموية.
Introduction
وتتميز الاصابه بالتهابات المكورات الرئوية بتفاعل متعدد الأوجه مع تنوع مركبات مصفوفة خارج الخلية ومكونات الأرقاء البشري ، مثل البلازمينوجين و vwf1،2، 3،4،5،6،7،8. البروتين السكري متعدد المجالات VWF بمثابه منظم الرئيسية من الأرقاء متوازنة عن طريق التوسط في التوظيف الجلطات والتاسيس الفيفيبين في موقع تشكيل خضيه الاوعيه الدموية9. ويتجلى اهميه الوظيفية ، VWF النشطة للسيطرة علي النزيف والتئام الجروح من قبل المرض فون ويلبراند ، وهو اضطراب النزيف الموروثة المشتركة10.
يدور vwf الكروي في نظام الدم البشري بتركيز يصل إلى 14.0 ميكروغرام/مل11,10. ردا علي أصابه الاوعيه الدموية ، والإفراج المحلي من vwf بواسطة الهيئات البطانية weibel palade (wbp) زيادة ملحوظة11،12. وتبين الدراسات السابقة ان التصاق بالمكورات الرئوية للخلايا البطانية البشرية وإنتاجها من السموم التي تشكل المسام بنيوموليسين بشكل كبير يحفز التلالؤ VWF إفراز13. القوي الهيدروديناميكية لتدفق الدم للحث علي فتح الهيكلية للمجالات VWF الألى المستجيبة. في معدلات التدفق من 10 داين/سم2 و vwf multimerizes إلى سلاسل البروتين طويلة تصل إلى عده مئات ميكرومتر في الطول التي لا تزال تعلق علي سوبيندوثيليوم10,12.
لفهم وظيفة السلاسل VWF multimerized المتولدة تحت الضغط القص في التفاعل من المكورات الرئوية مع سطح بطانية ، تم تاسيس نهج العدوى ثقافة الخلية القائمة علي ميكروفلويديك. تم استخدام جهاز ميكروفلويدريك مع نظام مضخة ضغط الهواء التي تسيطر عليها البرمجيات. وقد مكن ذلك من أعاده التدوير المستمرة أحاديه الاتجاه لمتوسط ثقافة الخلية بمعدل تدفق محدد. التالي ، طبق النظام إجهادا محددا للقص علي سطح الخلايا البطانية ، والذي ظل ملتصقا داخل شرائح القناات المتخصصة. وقد مكن هذا النهج من محاكاة قوه القص داخل مجري الدم لنظام الاوعيه الدموية البشرية ، الذي تولد فيه سلاسل VWF علي خلايا بطانية متباينة تحت ظروف تدفق ثابته محدده. لهذا الغرض ، تم زراعه الخلايا البطانية في شرائح قناه محدده (انظر جدول المواد) ، والتي تم تكييفها للتحليلات المجهرية اثناء التدفق. وقد وفر نظام المضخة ميكروفلويديك وضع الإجهاد القص المحدد بدرجه عاليه والمتحكم به والمطلوب لتشكيل سلاسل vwf الموسعة علي طبقه الخلايا البطانية المتموجة. بعد تحفيز VWF-إفراز خلايا الوريد الحبل السري البشري كونفلوينتلي نمت (HUVEC) بواسطة مكملات الهيستامين ، وكان المستحث تشكيل سلسله من خلال تطبيق الضغط القص (ԏ) من 10 داين/سم2. يتم تعريف الإجهاد القص كقوة تعمل علي طبقه الخلية. وتحسب تقريبا وفقا لكورنيش et. al.14 مع المعادلة 1:
حيث ԏ = القص الإجهاد في داين/سم2، η = اللزوجة في (داين ∙ s)/سم2، h = نصف ارتفاع القناة ، ث = نصف عرض القناة ، و Φ = معدل الجريان في مل/دقيقه.
تعتمد نتيجة المعادلة 1 علي الارتفاعات والعروض المختلفة للشرائح المختلفة المستخدمة (انظر جدول المواد). في هذه الدراسة تم استخدام شريحة قناه Luer من 0.4 μm الناتجة في عامل الشريحة الغرفة من 131.6 (انظر الصيغة 2).
اللزوجة من الوسط عند 37 درجه مئوية هو 0.0072 داين ∙ s/cm ² وتم استخدام الضغط القص من 10 داين/سم ². ونتج عن ذلك معدل تدفق 10.5 مل/دقيقه (انظر الصيغة 3).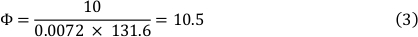
هنا ، يتم وصف التكيف والتقدم من الخلية ميكروفلويدريك اجراء التنظير باستخدام نظام تدفق الصفعي أحادي الاتجاه للتحقيق والتصور من أليات العدوى البكتيرية في الاوعيه الدموية المضيف بالتفصيل. يمكن أيضا تحفيز توليد سلاسل VWF علي طبقات بطانية باستخدام أنظمه المضخات الأخرى التي هي قادره علي تطبيق الإجهاد القص مستمرة وثابته15.
بعد زراعه الخلايا البطانية الاوليه للتقاء في تدفق وتحفيز تشكيل سلسله VWF ، تمت أضافه المكورات الرئوية التي تعبر عن البروتين الأحمر الفلوري (عروض العروض)16 إلى طبقه الخلايا البطانية تحت السيطرة المجهرية المستمرة. تم مجهريا تصور ومراقبه المرفق من البكتيريا إلى سلاسل VWF علي سطح الخلايا البطانية ورصدها لمده تصل إلى ثلاث ساعات في الوقت الحقيقي باستخدام الأجسام المضادة المحددة بالنيون التي تحمل علامة الفلورسنت. مع هذا النهج ، تم تحديد دور VWF كعامل التصاق تعزيز التعلق البكتيرية لبطانة الاوعيه الدموية8.
بالاضافه إلى التصور المجهري لإفراز البروتين وتغييرات المطابقة ، يمكن استخدام هذه الطريقة لمراقبه الخطوات الفردية لعمليات العدوى البكتيرية في الوقت الحقيقي ولقياس كميه البكتيريا المرفقة في نقاط زمنيه مختلفه من العدوي. كما يوفر نظام المضخات الذي يتم التحكم فيه بواسطة البرامج امكانيه لاستزراع الخلايا البطانية في ظروف التدفق الثابتة المحددة لمده تصل إلى عده أيام وتمكين الحاضنة المتوسطة التدفق المحددة. وعلاوة علي ذلك ، يمكن تطبيق هذه الطريقة باستخدام أنواع مختلفه من الخلايا. تكييف بروتوكول تلطيخ أيضا تمكن من الكشف والتصور من البكتيريا التي تم استيعابها في الخلايا النواة.
تصف هذه المخطوطة هذا البروتوكول التجريبي المتقدم الذي يمكن استخدامه كنهج محدد وموثوق به وقابل للتكرار لتوصيف العمليات الفسيولوجية المرضية بطريقه تتسم بالكفاءة والتنوع.
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
محاكاة التفاعل البكتيري مع البروتينات المضيفة الميكانيكية مثل VWF يتطلب نظام ثقافة الخلية القابلة للاستخدام التي تمكن جيل من تدفق محدده ، أحاديه الاتجاه ، ومستمر من السوائل ، التالي توليد الإجهاد القص موثوق بها . وقد تم بالفعل وصف عده أنظمه ضخ ميكروفلويدريك. ويلخص استعراض شامل من Bergmann وآخر…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
تم تمويل المشروع من قبل DFG (BE 4570/4-1) إلى نشره سورينام
Materials
| 1 mL Luer-syringe | Fisher Scientific | 10303002 | with 1 mL volume for gelatin injection using the luer-connection of the slides |
| 2 mL Luer-syringe | Sarstedt | 9077136 | For pieptting/injecting fluids into the luer connections of the channel chamber slides |
| Accutase | eBioscience now thermo fisher | 00-4555-56 | protease mix used for gentle detachment of endothelial cells |
| AlexaFluor350-conjugated Phalloidin | Abcam | ab176751 | no concentration available from the manufacturer, stock solution is sufficient for 300 tets, company recommends to use 100 µl of a 1:1000 dilution, blue fluorescence (DAPI-filter settings) |
| AlexaFluor488-conjugated goat-derived anti-mouse antibody | Thermo Fisher Sientific | A11001 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of human VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation, green fluorescence |
| AlexaFluor568-conjugated goat-derived anti-rabbit-antibody | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-11011 | stock concentration: 2 mg/mL for immunostaining of pneumococci in microfluidic slide after pFA fixation, red fluorescence |
| Bacto Todd-Hewitt-Broth | Becton Dickinson GmbH | BD 249210 | complex bacterial culture medium |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | Sigma Aldrich | A2153-25G | solubilized, for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Cell culture flasks with filter | TPP | 90026 | subcultivation of HUVEC in non-coated cell culture flasks of 25 cm2 surface |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-12R | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | 392304 | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of > 2mL) |
| Centrifuge Allegra X-30 | Beckman Coulter Life Sciences | B06314 | spinning down of eukaryotic cells |
| Centrifuge Z 216 MK | Hermle | 305.00 V05 – Z 216 M | spinning down of bacteria (volumes of less than 2 mL) |
| Chloramphenicol | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3886.2 | used in a concentration of 0.2 /mL for cultivation of pneumococci transformed with genetic construct carrying red fluorescent protein and chloramphenicol resistance cassette |
| Clamp for perfusion tubing | ibidi | 10821 | for holding the liquid in the tube bevor connecting the slide to the pump system |
| CO2-Incubator | Fisher Scientific | MIDI 40 | incubator size is perfectly adapted to teh size of the fluidic unit with connected channel slide and was used for flow cultivation at 37°C and 5% CO2 |
| CO2-Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-18 AIC | for incubation of bacteria and cells in a defined atmosphere at 5% CO2 and 37°C |
| Colombia blood agar plates | Becton Dickinson GmbH | PA-254005.06 | agar-based complex culture medium for S. pneumoniae supplemented with 7% sheep blood |
| Computer | Dell | Latitude 3440 | Comuter with pressure pump software |
| Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) | Leica | DMi8 | An inverse microscope with a stage covered by a heatable chamber and with a fluorescence unit equipped with fluorescence filter, Xenon-light source (SP8, DMi8) and DFC 365 FX Kamera (1392 x 1040, 1.4 Megapixel) |
| Di Potassium hydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 3904.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Drying material | Merck | 101969 | orange silica beads for drying used in a glass bottle with a tubing adaptor |
| ECGM supplement Mix | Promocell | C-39215 | supplement mix for ECGM -medium, required for precultivation of endothelial cells: 0.02 mL/mL Fetal calf serum, 0.004 mL/ mL endothelial cell growth supplement, 0.1 ng / mL epidermal growth factor, 1 ng / mL basic fibroblast growth factor, 90 µg / mL heparin, 1 µg / mL Hydrocortisone |
| ECGMS | Promocell | C-22010 | ECGM supplemented with 5 % [w/w] FCS and 1 mM MgSO4 to increase cell adhesion |
| Endothelial Cell growth medium (ECGM, ready to use) | Promocell | C-22010 | culture medium of HUVECs, already supplemented with all components of the supplement mix |
| Fetal Calf Serum (FCS) | biochrome now Merck | S 0415 | supplement for cell culture, used for infection analyses |
| FITC-conjugated goat anti-human VWF antibody | Abcam | ab8822 | stock concentration: 10 mg/mL, for immunodetection of globular and multimerized VWF in flow |
| Fluidic Unit | ibidi | 10903 | fluidic unit for flow cultivation |
| Gelatin (porcine) | Sigma Aldrich | G-1890-100g | for precoating of microslide channel surface |
| histamine dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | H-7250-10MG | for induction of VWF secretion from endothelial Weibel Palade Bodies |
| Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell (HUVEC) | Promocell | C-12203 Lot-Nr. 396Z042 | primary endothelial cells from pooled donor, stored crypcoserved in liquid nitrogen |
| Human VWF-specific antibody derived from mouse (monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc73268 | stock concentration: 200 µg/mL for immunostaining of VWF in microfluidic slide after PFA fixation |
| Injection Port | ibidi | 10820 | for injection of histamin or bacteria into the reservoir tubing during the flow circulation |
| Light microscope | Zeiss | Axiovert 35M | inverse light microscope for control of eukaryotic cell detachement and cell counting using a 40 x water objective allowing 400 x magnification |
| Luer-slides I0.4 (ibiTreat472microslides) | ibidi | 80176 | physically modified slides for fludic cultivation (μ–Slide I0.4Luer with a channel hight of 0.4 mm, a channel volume of 100 μl, a growth area of 2.5 cm and a coating area of 25.4 cm2) suitable for all kinds of flow assay, the physical treatment generates a hydrophilic and adhesive surface. |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4, unhydrated) | Sigma Aldrich | M7506-500G | For preparation of ECGMS medium |
| Microfluidic Pump | ibidi | 10905 | air pressure pump |
| Neubauer cell counting chamber | Karl Hecht GmbH&Co KG | 40442002 | microscopic counting chamber for HUVECs |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% (PFA) | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710-S | for cross linking of samples |
| Perfusion Set | ibidi | 10964 | Perfusion Set Yellow/Green has a tubing diameter of 1.6 mm, a tube length of 50 cm, a total working volume of 13.6 mL, a dead tube volume of 2.8 mL and a reservoir size of 10 mL. combined with the µ-slide L0.4Luer, at 37°C and a viscosity of 0.0072 dyn x s/cm2 a flow rate range of 3.8mL/min up to 33.9 mL/min and shear stress between 3.5 dyn/cm2 and 31.2 dyn/cm2 can be reached. with 50 cm lenght for microfluidic |
| Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) | the solution was prepared using the following chemicals: 0.2 g/L KCl, 1.44 g/L Na2HPO4, 0.24 g/L KH2PO4 , pH 7.4 | ||
| Plastic cuvettes | Sarstedt | 67,741 | (2 x optic) for OD measurement at 600 nm |
| Pneumococcus-specific antiserum | Pineda | raised in rabbit using heat-inactivated Streptococcus pneumoniae NCTC10319 and D39, IgG-purified using proteinA-sepharose column. | |
| Polystyrene or Styrofoam plate | this is a precaution step to avoid cold stress on the cells seeded in the channel slides. Any type of styrofoam such as packaging box-material can be used. The plate might by 0.5 cm thick and should have a size of 20 cm2. | ||
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | 6781.1 | used for PBS buffer |
| Pump Control Software (PumpControl v1.5.4) | ibidi | v1.5.4 | Computer software for controlling the pressure pump, setting the flow conditions and start/end the flow |
| reaction tubes 1.5/ 2.0mL | Sarstedt | 72.706/ 72.695.500 | required for antibody dilutions |
| reaction tubes with 50 mL volume | Sarstedt | 6,25,48,004 | |
| RFP-expressing pneumococci | National Collection of Type Cultures, Public Health England | 10,319 | Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 47 expressing RFP fused to ahistone-like protein integrated into the genome |
| serological pipets 5, 10 mL | Sarstedt | 86.1253.025/ 86.1254.025 | for pipeting larger volumes |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3, water free) | Sigma Aldrich | 451614-25G | for preparation of 100 mM Sodium Carbonate buffer |
| Sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4) | Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG, Karlsruhe | P030.2 | used for PBS buffer |
| Spectral Photometer Libra S22 | Biochrom | 80-2115-20 | measurement of optical density (OD) of bacterial suspension at 600 nm |
| Sucrose | Sigma Aldrich | S0389-500G | for preparation of blocking buffer |
| Triton X-100 | Sigma Aldrich | T9284-500ML | Used in 0.1% end concentration diluted in dH20 for eukaryotic cell permeabilization after PFA fixation |
| Yeast extract | oxoid | LP0021 | bacteria are cultivated in THB supplement with 1% [w/w] yeast extract = complete bacterial cultivation medium THY |
References
- Weiser, J. N., Ferreira, D. M., Paton, J. C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 16 (6), 355-367 (2018).
- Bergmann, S., Hammerschmidt, S. Versatility of pneumococcal surface proteins. Microbiology. 152, 295-303 (2006).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Integrin-linked kinase is required for vitronectin-mediated internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae by host cells. Journal of Cell Science. 122, 256-267 (2009).
- Bergmann, S., Schoenen, H., Hammerschmidt, S. The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and endothelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 303, 452-462 (2013).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Chhatwal, G. S., Hammerschmidt, S. Alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae is a plasmin(ogen)-binding protein displayed on the bacterial cell surface. Molecular Microbiology. 40, 1273-1287 (2001).
- Bergmann, S., et al. Identification of a novel plasmin(ogen)-binding motif in surface displayed alpha-enolase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Molecular Microbiology. 49, 411-423 (2003).
- Bergmann, S., Rohde, M., Preissner, K. T., Hammerschmidt, S. The nine residue plasminogen-binding motif of the pneumococcal enolase is the major cofactor of plasmin-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix, dissolution of fibrin and transmigration. Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 94, 304-311 (2005).
- Jagau, H., et al. Von willebrand factor mediates pneumococcal aggregation and adhesion in flow. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10, 511 (2019).
- Tischer, A., et al. Enhanced local disorder in a clinically elusive von willebrand factor provokes high-affinity platelet clumping. Journal of Molecular Biology. 429, 2161-2177 (2017).
- Ruggeri, Z. M. Structure of von willebrand factor and its function in platelet adhesion and thrombus formation. Best Practice Research Clinical Haematology. 14, 257-279 (2001).
- Spiel, A. O., Gilbert, J. C., Jilma, B. Von willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117, 1449-1459 (2008).
- Springer, T. A. Von Willebrand factor, Jedi knight of the bloodstream. Blood. 124, 1412-1425 (2014).
- Luttge, M., et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae induces exocytosis of weibel-palade bodies in pulmonary endothelial cells. Cellular Microbiology. 14, 210-225 (2012).
- Cornish, R. J. Flow in a Pipe of Rectangular Cross-Section. Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 786, 691-700 (1928).
- Michels, A., Swystun, L. L., Mewburn, J., Albánez, S., Lillicrap, D. Investigating von Willebrand Factor Pathophysiology Using a Flow Chamber Model of von Willebrand Factor-platelet String Formation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 14 (126), (2017).
- Kjos, M., et al. fluorescent Streptococcus pneumoniae for live-cell imaging of host-pathogen interactions. Journal of Bacteriology. 197, 807-818 (2015).
- Bergmann, S., Steinert, M. From single cells to engineered and explanted tissues: New perspectives in bacterial infection biology. International Reviews of Cell and Molecular Biology. 319, 1-44 (2015).
- Harrison, D. J., et al. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science. 261 (5123), 895-897 (1993).
- Magnusson, M. K., Mosher, D. F. Fibronectin: Structure, assembly, and cardiovascular implications. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 18, 1363-1370 (1998).
- Zerlauth, G., Wolf, G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (4), 685-689 (1984).
- Li, X. J., Valadez, A. V., Zuo, P., Nie, Z. 2012. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 4, 1509-1525 (2019).
- Fiddes, L. K., et al. A circular cross-section PDMS microfluidics system for replication of cardiovascular flow conditions. Biomaterials. 31, 3459-3464 (2010).
- Schimek, K., et al. Integrating biological vasculature into a multi-organ-chip microsystem. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3588-3598 (2013).
- Pappelbaum, K. I., et al. Ultralarge von willebrand factor fibers mediate luminal Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to an intact endothelial cell layer under shear stress. Circulation. 128, 50-59 (2013).
- Schneider, S. W., et al. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von willebrand factor fibers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104, 7899-7903 (2007).
- Reneman, R. S., Hoek, A. P. G. Wall shear stress as measured in vivo: consequences for the design of the arterial system. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing. 46 (5), 499-507 (2008).
- Valentijn, K. M., Sadler, J. E., Valentijn, J. A., Voorberg, J., Eikenboom, J. Functional architecture of Weibel- Palade bodies. Blood. 117, 5033-5043 (2011).
- Freshney, R. I. . Culture of animal cells: A manual of basic Technique, 5th edition. , (2005).
- Shaw, J. A., Shaw, A. J. . Epithelial cell culture- a practical approach. , 218 (1996).
- Elm, C., et al. Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR) mediate invasion of Streptococcus pneumoniae into the epithelium. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (8), 6296-6304 (2004).
- Nerlich, A., et al. Invasion of endothelial cells by tissue-invasive M3 type group A streptococci requires Src kinase and activation of Rac1 by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (30), 20319-20328 (2009).
- Ho, C. T., et al. Liver-cell patterning lab chip: mimicking the morphology of liver lobule tissue. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3578-3587 (2013).
- Huh, D., et al. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 328, 1662-1668 (2010).
- Harink, B., Le Gac, S., Truckenmuller, R., van Blitterswijk, C., Habibovic, P. Regeneration-on-a-chip? The perspectives on use of microfluidics in regenerative medicine. Lab on a Chip. 13, 3512-3528 (2013).

