Respiratory Exam II: Percussion and Auscultation
203,551 Views
•
•
Visão Geral
Source: Suneel Dhand, MD, Attending Physician, Internal Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Learning the proper technique for percussion and auscultation of the respiratory system is vital and comes with practice on real patients. Percussion is a useful skill that is often skipped during everyday clinical practice, but if performed correctly, it can help the physician to identify underlying lung pathology. Auscultation can provide an almost immediate diagnosis for a number of acute pulmonary conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, and pneumothorax.
The areas for auscultating the lungs correspond to the lung zones. Each lung lobe can be pictured underneath the chest wall during percussion and auscultation (Figure 1). The right lung has three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. The left lung has two lobes: the superior and inferior lobes. The superior lobe of the left lung also has a separate projection known as the lingual.
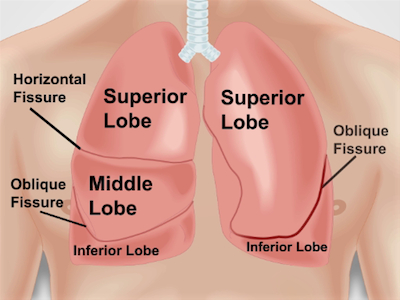
Figure 1. Anatomy of lungs with respect to the chest wall. An approximate projection of lungs and their fissures and lobes to the chest wall anteriorly. RUL – right upper lobe; RML – right middle lobe; RLL – right lower lobe; LUL – left upper lobe; LLL – left lower lobe.
Procedimento
1. Positioning
- Make sure the patient is undressed down to the waist.
- Position the patient on the examination table at a 30- to 45-degree angle and approach from the right side. Examining the posterior of the lung requires the patient to be leaning forward or sitting on the edge of the bed.
2. Percussion
- Percuss both posteriorly and anteriorly, starting on the back.
- Place non-dominant hand with middle finger (pleximeter finger) pressed and hyperextended firmly on the patient's right or left mid-back area (lower levels of lungs posteriorly). The firmer the finger is pressed to the chest wall, the louder the percussion note tends to be.
- Make sure the other fingers and palm are not pressed against the patient's chest.
- Use the tip of the middle finger (plexor finger) of the dominant hand to tap firmly on the top third (middle or distal phalanx) of the pleximeter finger of the non-dominant hand at least twice (it is advisable to keep fingernails short). The sound should be hollow, representing an air-filled lung.
- Repeat the percussion at four and five levels, comparing each lung level side by side, working up to the chest wall, starting at the inferior lung borders. On expiration, the lower border of the lungs is at the level of the sixth rib at the midclavicular line and the eighth rib at the midaxiallary line anteriorly, approximately at the level of the T10 spinous process posteriorly.
- Percuss anteriorly and posteriorly, placing the finger on the chest in the intercostal spaces.
- Appreciate the quality of percussion sounds. The normal findings on the chest percussion are:
- Resonant percussion note: heard over a normal air-filled lung.
- Dull percussion note (the sound heard over solid tissues): over the liver in the right lower anterior chest and over the heart in the left anterior chest. When percussion of the lungs elicits this sound, it is indicative of consolidation.
- Tympanic percussion note (a drum-like sound when percussing over hollow organs): over the Traube's space, an area overlying the gastric bubble and bordered by the sixth rib, anterior axillary line, and left costal margin. Left pleural effusion produces a dull percussion sound over Traube's space.
- Note the presence of pathological percussion sounds. A "stony dull" or flat percussion note sounds duller than the "standard" dull sound. It resembles the percussion note heard over the thigh and is indicative of a pleural effusion. A hyper-resonant percussion note is a pathological percussion sound indicative of hyper-inflated lungs from advanced COPD, emphysema, or a pneumothorax.
3. Auscultation
- Position the patient: ask the patient to lean forward or sit upright in order to examine posteriorly. Asking the patient to fold arms or place hands on opposing shoulders also helps to get maximal exposure to the lung fields.
- Place the diaphragm of the stethoscope on the patient's chest, and ask the patient to take deep breaths in and out through the mouth.
- Auscultate at five levels posteriorly and anteriorly, comparing side by side.
- Normal breath sounds are called vesicular breath sounds, which are low-pitched sounds louder on inspiration and softer on expiration. They should be symmetrical posteriorly.
- Note the presence and location of abnormal (adventitious) extra breath sounds, such as crackles, wheezing, rhonchi, stridor, or pleural friction rub (Table 1).
- Note the following characteristics of any abnormal breath sounds (if present): loudness, quality, duration, and whether they occur during inspiration or expiration (i.e., timing in the respiratory cycle). Many abnormal breath sounds are best heard after asking the patient to cough.
- Assess for bronchophony, an increased sound transmission over the consolidated lung, when asking the patient to say "99" or "1-2-1." Egophony is when an "E" sound changes to an "A" over consolidated lung.
- Assess for whispering pectoriloquy. While auscultating with the stethoscope, ask the patient to whisper "99" or "1-2-1." In the consolidated lung, the sound will actually be heard better and more clearly with the stethoscope.
| Breath sounds | Description | ||
| Bronchial | Harsh or hollow breath sounds, similar to what you would hear if you placed your stethoscope over the trachea or main bronchi. In other areas they can be a sign of underlying consolidation | ||
| Bronchovesicular | Normal over the large airways and sternum, abnormal in other areas | ||
| Crackles or Crepitations or Rales | Caused by fluid in the airways and are more commonly heard during inspiration at the bases of the lungs. They can be classified as fine; which are soft, brief high-pitched sounds or "pops", or coarse; which are louder and lower pitched than fine crackles. Fine crackles can be heard in pulmonary fibrosis and course crackles in COPD and pneumonia. Note the timing of the crackles. Congestive heart failure typically produces late crackles | ||
| Wheeze | Distinctive high-pitched continuous sound heard in asthma and COPD | ||
| Rhonchi | Low-pitched "snoring" sound that can be auscultated in any condition causing reactive airways disease, including pneumonia, COPD, and CHF | ||
| Stridor | An abnormal high-pitched sound generated from the upper airways, usually during inspiration (this is often a medical emergency) | ||
| Rub | Caused by pleural surfaces rubbing against each other (pleural friction rub), and heard more in pleurisy as well as other conditions, such as pericarditis | ||
Table 1. A table summarizing potential findings during auscultation of the lungs.
Learning the proper technique for percussion and auscultation of the respiratory system is vital for the bedside diagnosis of lung disorders. Percussion is a simple yet useful skill, which, if performed correctly, can help the physician identify the underlying lung pathology. On the other hand, auscultation can provide an almost immediate diagnosis for a number of pulmonary conditions including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pneumonia, and pneumothorax.
In another video, we covered how to perform inspection and palpation of the respiratory system. This video will focus on the percussion and auscultation steps of this exam.
Before going into the details of the clinical exam, let’s review the lung lobes and breath sounds. This will help us better understand the anatomical locations and results of percussion and auscultation.
The areas for percussion and auscultation of lungs correspond to the lung lobes and each lung lobe can be pictured underneath the chest wall. The right lung, which is the larger of the two, has three lobes-superior, middle, and inferior. The horizontal fissure separates the superior from the middle lobe, whereas the right oblique fissure separates the middle from the inferior. The left lung only has two lobes- superior and inferior-separated by the left oblique fissure. Since lungs are mostly filled with air that we breathe in, percussion performed over most of the lung area produces a resonant sound, which is a low pitched, hollow sound. Therefore, any dullness or hyper-resonance is indicative of lung pathology, such as pleural effusion or pneumothorax, respectively.
Breath sounds heard through the stethoscope during auscultation are peculiar as well. The two sounds heard during normal breathing are bronchial and vesicular. Bronchial sound, which is more tubular and hollow, is heard over the large airways in the anterior chest. Whereas, vesicular sound, which is soft, low-pitched and rustling, can be heard over most of the lung tissue area. Abnormal breath sounds include crackles also known as rales,which are indicative of fluid in small airways. On the other hand, wheezes or rhonchi suggest airway constriction or swelling, which causes partial airway obstruction. Pleural rubs occur when inflamed pleural surfaces slide against one another during respiration, and lastly stridor is caused by obstruction of the upper airway.
With this knowledge of where and what to look for during respiratory percussion and auscultation, let’s discuss the procedural steps starting with percussion. Ask the patient to sit straight or lean forward. Start with the percussion of the posterior surface. Place your non-dominant hand with middle finger pressed and hyperextended firmly over the patient’s mid-back area. Use the tip of the middle finger of the dominant hand to tap firmly on the top third phalanx of the middle finger of the pressing hand at least twice. Repeat this at four to five levels, comparing side-to-side.
Perform the same procedure on the anterior chest wall, working from the inferior lung borders. Both anteriorly and posteriorly, make sure the middle finger of the pressing hand is placed in the intercostal spaces and not on the ribs. Appreciate the percussion sound quality. Tapping over normal air-filled lung should produce a resonant percussion note. On the contrary percussion over solid tissues such as the liver or the heart should produce a dull note. And percussion over hollow spaces, like the Traube’s space should yield a Tympanic note, which is a drum-like sound.
Lastly, let’s move to auscultation, which is listening to breath sounds using a stethoscope. To start, instruct the patient to lean forward or sit upright in order to examine posteriorly. Request the patient to place their hands on opposing shoulders to get maximum exposure to the lung fields. Place the diaphragm on the patient’s mid-back area and ask them to take deep breaths in and out through their mouth. Auscultate at five levels posteriorly, and then repeat the same procedure anteriorly, comparing side-to-side. Normal breath sounds should be symmetrical both posteriorly and anteriorly; any deviation is a possible indicator of a lung disease.
The last three steps of auscultation are tests aiming to identify lung consolidation. First of these tests is to assess for bronchophony. Ask the patient to say “99”, while auscultating the chest area. An increased sound transmission indicates a consolidated lung. Second is to assess for egophony. Ask the patient to say “E”. When an “E” sound changes to an “A” through the stethoscope, it is an indication of a consolidated lung. Lastly, assess for whispering pectoriloquy. Ask the patient to whisper “99”. In case of a consolidated lung, the sound will actually be heard better and more clearly through the stethoscope. All these steps should also be performed posteriorly at different locations in order to cover the entire lung area. At the end of the examination, thank the patient and have them change back.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s video on percussion and auscultation for respiratory evaluation. Distinguishing between sounds heard during this portion of the exam can occasionally seem subjective, but the assessment becomes clearer and easier with practice, leading to a “spot diagnosis” for many pulmonary conditions. As always, thanks for watching!
Applications and Summary
Percussion and auscultation should always be done in sequence whenever performing a full respiratory examination. Learning how to percuss correctly takes time and practice (practice can be done on yourself or other surfaces, such as a table). Note how the percussion note changes naturally over air-filled lung, ribs, and solid organs, such as the heart.
Auscultation must be performed over each lung zone to give the physician the best chance of identifying the focus of any lung pathology. Abnormal breath sounds should be easily recognizable when occurring in a patient. Allow enough time to classify the breath sounds. Listen for several breathing cycles in one area, if necessary, to hear the exact nature of the crackles, wheezes, rhonchi, or other pathological findings. Distinguishing between certain breath sounds can occasionally seem subjective, but will become easier with practice, leading to a "spot diagnosis" for many pulmonary conditions.
Transcrição
Learning the proper technique for percussion and auscultation of the respiratory system is vital for the bedside diagnosis of lung disorders. Percussion is a simple yet useful skill, which, if performed correctly, can help the physician identify the underlying lung pathology. On the other hand, auscultation can provide an almost immediate diagnosis for a number of pulmonary conditions including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pneumonia, and pneumothorax.
In another video, we covered how to perform inspection and palpation of the respiratory system. This video will focus on the percussion and auscultation steps of this exam.
Before going into the details of the clinical exam, let’s review the lung lobes and breath sounds. This will help us better understand the anatomical locations and results of percussion and auscultation.
The areas for percussion and auscultation of lungs correspond to the lung lobes and each lung lobe can be pictured underneath the chest wall. The right lung, which is the larger of the two, has three lobes-superior, middle, and inferior. The horizontal fissure separates the superior from the middle lobe, whereas the right oblique fissure separates the middle from the inferior. The left lung only has two lobes- superior and inferior-separated by the left oblique fissure. Since lungs are mostly filled with air that we breathe in, percussion performed over most of the lung area produces a resonant sound, which is a low pitched, hollow sound. Therefore, any dullness or hyper-resonance is indicative of lung pathology, such as pleural effusion or pneumothorax, respectively.
Breath sounds heard through the stethoscope during auscultation are peculiar as well. The two sounds heard during normal breathing are bronchial and vesicular. Bronchial sound, which is more tubular and hollow, is heard over the large airways in the anterior chest. Whereas, vesicular sound, which is soft, low-pitched and rustling, can be heard over most of the lung tissue area. Abnormal breath sounds include crackles also known as rales,which are indicative of fluid in small airways. On the other hand, wheezes or rhonchi suggest airway constriction or swelling, which causes partial airway obstruction. Pleural rubs occur when inflamed pleural surfaces slide against one another during respiration, and lastly stridor is caused by obstruction of the upper airway.
With this knowledge of where and what to look for during respiratory percussion and auscultation, let’s discuss the procedural steps starting with percussion. Ask the patient to sit straight or lean forward. Start with the percussion of the posterior surface. Place your non-dominant hand with middle finger pressed and hyperextended firmly over the patient’s mid-back area. Use the tip of the middle finger of the dominant hand to tap firmly on the top third phalanx of the middle finger of the pressing hand at least twice. Repeat this at four to five levels, comparing side-to-side.
Perform the same procedure on the anterior chest wall, working from the inferior lung borders. Both anteriorly and posteriorly, make sure the middle finger of the pressing hand is placed in the intercostal spaces and not on the ribs. Appreciate the percussion sound quality. Tapping over normal air-filled lung should produce a resonant percussion note. On the contrary percussion over solid tissues such as the liver or the heart should produce a dull note. And percussion over hollow spaces, like the Traube’s space should yield a Tympanic note, which is a drum-like sound.
Lastly, let’s move to auscultation, which is listening to breath sounds using a stethoscope. To start, instruct the patient to lean forward or sit upright in order to examine posteriorly. Request the patient to place their hands on opposing shoulders to get maximum exposure to the lung fields. Place the diaphragm on the patient’s mid-back area and ask them to take deep breaths in and out through their mouth. Auscultate at five levels posteriorly, and then repeat the same procedure anteriorly, comparing side-to-side. Normal breath sounds should be symmetrical both posteriorly and anteriorly; any deviation is a possible indicator of a lung disease.
The last three steps of auscultation are tests aiming to identify lung consolidation. First of these tests is to assess for bronchophony. Ask the patient to say “99”, while auscultating the chest area. An increased sound transmission indicates a consolidated lung. Second is to assess for egophony. Ask the patient to say “E”. When an “E” sound changes to an “A” through the stethoscope, it is an indication of a consolidated lung. Lastly, assess for whispering pectoriloquy. Ask the patient to whisper “99”. In case of a consolidated lung, the sound will actually be heard better and more clearly through the stethoscope. All these steps should also be performed posteriorly at different locations in order to cover the entire lung area. At the end of the examination, thank the patient and have them change back.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s video on percussion and auscultation for respiratory evaluation. Distinguishing between sounds heard during this portion of the exam can occasionally seem subjective, but the assessment becomes clearer and easier with practice, leading to a “spot diagnosis” for many pulmonary conditions. As always, thanks for watching!
