16.4:
Расчет изменений pH в буферном растворе
47,875 Views
•
•
A buffer can prevent a sudden drop or increase in the pH of a solution after the addition of a strong acid or base up to its buffering capacity; however, such addition of a strong acid or base does result in the slight pH change of the solution. The small pH change can be calculated by determining the resulting change in the concentration of buffer components, i.e., a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. The concentrations obtained using these stoichiometric calculations can be used to determine the solution’s final pH using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation or an ICE table.
For example, a buffered solution contains 0.65 mol of formic acid and sodium formate. As the concentration of the weak acid and its conjugate base is the same here, the solution’s pH is equal to the pKa of the weak acid, which is 3.74 in this case. If 0.05 mol HNО3 is added into this solution, the resultant changes in the concentration of the formic acid and sodium formate can be determined by stoichiometric calculations as shown in the table below.
| H+ (aq) | HCOO− (aq) | HCOOH (aq) | |
| Before addition (M) | ~0.00 mol | 0.65 mol | 0.65 mol |
| Addition (M) | 0.050 mol | – | – |
| После добавления (M) | ~0.00 моль | 0.60 mol | 0.70 mol |
Конечный pH раствора можно затем определить, включив в уравнение Хендерсона-Хасселбалча измененные концентрации формальной кислоты и натрия.
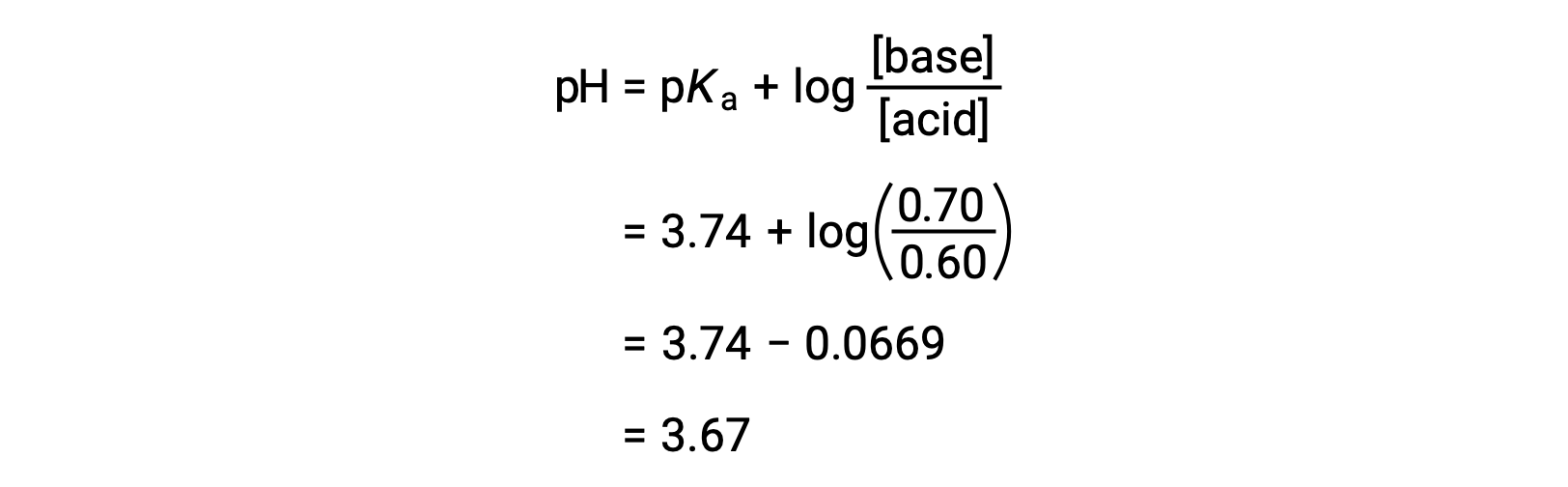
Таким образом, добавление 0.05 моль HNО3 снижает pH раствор с 3.74 до 3.67.
Аналогично, если в тот же раствор добавляется 0.10 моль NaOH, то результирующие изменения концентрации формальной кислоты и натрия формат могут быть определены стехиометрическими расчетами, как показано в таблице ниже.
| OH- (Aq) | HCOOH (Aq) | HCOO– (Aq) | H2O (л) | |
| Перед добавлением (M) | ~0.00 моль | 0.65 mol | 0.65 mol | — |
| Дополнение (M) | 0.10 mol | – | – | - |
| После добавления (M) | ~0.00 моль | 0.55 mol | 0.75 mol | - |
Конечный pH раствор можно определить путем подключения измененной концентрации формальной кислоты и натрия в уравнение Хендерсона-Хасселбаля.
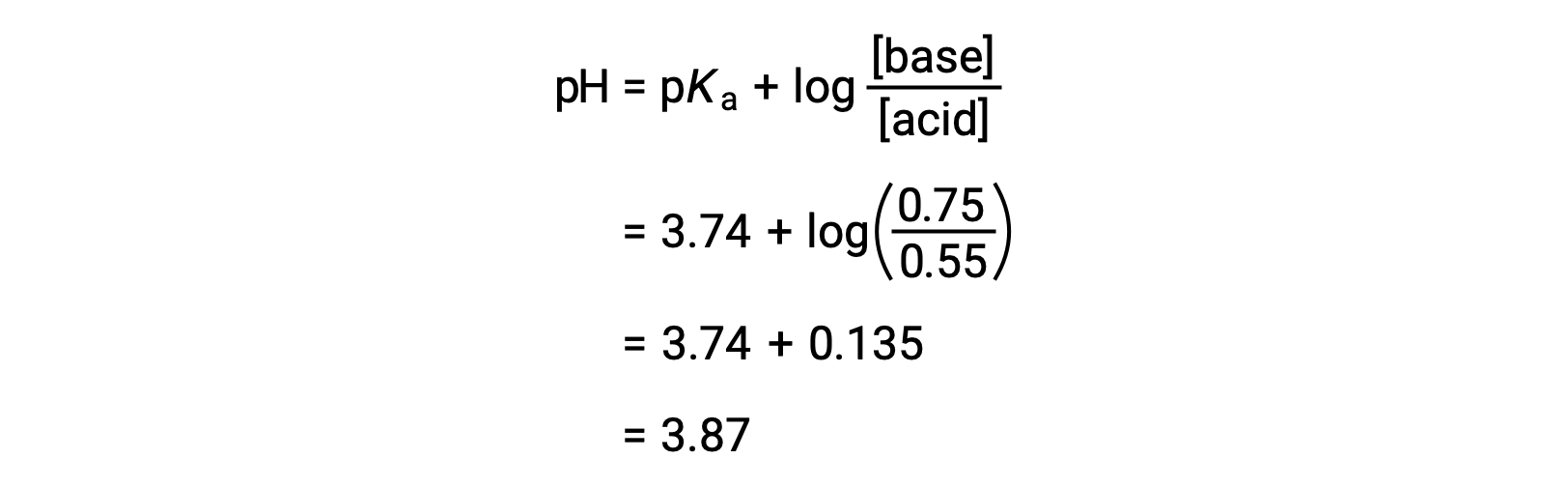
Таким образом, добавление 0.10 моль NaOH увеличивает pH раствор с 3.74 до 3.87.
